Abstract
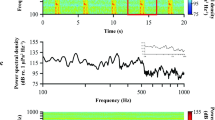
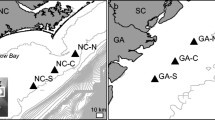
Increased sound production by fishes, which is used for communication during mating, in territorial defense, and possibly in echolocation, has been associated with decreased light and increased temperature and salinity (Luczkovich et al. 2008; Mok and Gilmore 1983). There has not been an attempt to associate changes in sound production with other environmental factors such as turbidity. Sediment deposition and resuspension commonly occur in estuaries due to changes in current velocity and direction, water runoff, and wave height. These factors can lead to shearing on the bed surface and thus an overall increase in water column turbidity (Whitehouse et al. 2000). It has been hypothesized that increased water column turbidity will lead to increased sound production in fishes because visual cues will be impaired. The goal of this research is to associate the incidence of sound production by Micropogonias undulatus (Atlantic croaker) to variations in estuarine temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, and particularly turbidity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goni M, Alleau Y, Corbett R, Walsh JP, Mallinson D, Allison MA, Gordon E, Petsch S, Dellapenna TM (2007) The effects of hurricanes Katrina and Rita on the seabed of the Louisiana shelf. Sediment Rec 5:4–9.
Locascio JV, Mann DA (2005) Effects of Hurricane Charley on fish chorusing. Biol Lett 1:362–365.
Luczkovich JJ, Pullinger RC, Johnson SE, Sprague MW (2008) Identifying the critical spawning habitats of sciaenids using passive acoustics. Trans Am Fish Soc 137:576–605.
Mok HK, Gilmore RG (1983) Analysis of sound production in estuarine aggregations of Pogonias cromis, Bairdiella chrysoura, and Cynoscion nebulosus (Sciaenidae). Bull Inst Zool Acad Sin (Taipei) 22:157–186.
Whitehouse RJS, Soulsby R, Roberts W, Mitchener HJ (2000) Dynamics of estuarine muds. Thomas Telford Publishing, London.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this paper
Cite this paper
Krahforst, C.S., Walsh, J.P., Sprague, M.W., Eulie, D.O., Corbett, D.R., Luczkovich, J.J. (2012). Influence of Turbidity on the Incidence of Sound Production in Atlantic Croaker (Micropogonias undulatus) in Pamlico Sound, North Carolina. In: Popper, A.N., Hawkins, A. (eds) The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 730. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-7311-5_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-7311-5_38
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4419-7310-8
Online ISBN: 978-1-4419-7311-5
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)