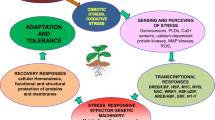
Abstract
In the past decade, the scientific community has witnessed a major leap in our understanding about how plant perceives and respond to abiotic stresses. Various candidates participating in this coordinated and orchestrated relays have been identified and their molecular mechanisms of operation have also been worked out. This analysis has clearly established a complex network of cellular machinery operative in plants under such conditions. Tools of functional genomics have been utilized to decipher the contributions of several of these individual components towards the complex stress response. Some of these studies have also been extended beyond model plants, and crop systems such as rice have been utilized to document the usefulness of some of these strategies towards genetic modifications of crop plants which are better adapted towards unfavorable environmental conditions. It is heartening to see the extension of few efforts beyond laboratory to field level testing. Indeed, a few of selected candidate genes have also passed these field level tests. However, it is also true that drought/salinity tolerant transgenic crop plants are yet away from the reach of farmers. A conscious deliberate and strategic action plan along with the right choice of battery of genes is required to achieve this important goal
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal PK, Agarwal P, Reddy MK and Sopory SK. (2006) Role of DREB transcription factors in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 25:1263–1274.
Amtmann A, Bohnert HJ and Bressan RA. (2005) Abiotic stress and plant genome evolution. Search for new models. Plant Physiol. 138:127–130.
Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA and Blumwald E. (1999) Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science 285:1256–1258.
Arabidopsis Genome Initiative. (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815.
Badawi GH, Kawano N, Yamauchi Y, Shimada E, Sasaki R, Kubo A and Tanaka K. (2004) Over-expression of ascorbate peroxidase in tobacco chloroplasts enhances the tolerance to salt stress and water deficit. Physiol. Plant. 121:231–238.
Bae H, Herman EM and Sicher Jr RC. (2005) Exogenous trehalose I induces chemical detoxification and stress response proteins and promotes nonstructural carbohydrate accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana grown in liquid Culture. Plant Sci.168:1293–1301.
Bahieldin A, Mahfouz HT, Eissa HF, Saleh OM, Ramadan AM, Ahmed IA, Dyer WE, El-Itriby HA and Madkour MA. (2005) Field evaluation of transgenic wheat plants stably expressing the HVA1 gene for drought tolerance. Physiol. Plant. 123:421–427.
Bajaj S and Mohanty A. (2005) Recent advances in rice biotechnology – towards genetically superior transgenic rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 3:275–307.
Bohnert HJ, Gong Q, Li P and Ma S. (2006) Unraveling abiotic stress tolerance mechanisms—getting genomics going. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 9:180–188.
Bressan RA, Zhang C, Zhang H, Hasegawa PM, Bohnert HJ and Zhu JK. (2001) Learning from the Arabidopsis experience. The next gene search paradigm. Plant Physiol. 127:1354–1360.
Catala R, Santos E, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Martinez-Zapater JM and Salinas J. (2003) Mutations in the Ca2+/H+ transporter CAX1 increase CBF/DREB1 expression and the cold-acclimation response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:2940–2951.
Chini A, Grant JJ, Seki M, Shinozaki K and Loake GJ. (2004) Drought tolerance established by enhanced expression of the CC-NBS-LRR gene, ADR1, requires salicylic acid, EDS1 and ABI1. Plant J. 38:810–822.
Chinnusamy V, Schumaker K and Zhu JK. (2004) Molecular genetic perspectives on cross-talk and specificity in abiotic stress signaling in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 55:225–236.
Cho EK and Hong CB. (2006) Over-expression of tobacco NtHSP70–1 contributes to drought-stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 25:349–358.
Cortina C and Culianez-Macia FAB. (2005) Tomato abiotic stress enhanced tolerance by trehalose biosíntesis. Plant Sci. 169:75–82.
Cuartero J, Bolarin MC, Asins MJ and Moreno V. (2006) Increasing salt tolerance in the tomato. J Exp. Bot. 57:1045–1058.
Das-Chatterjee A, Goswami L, Maitra S, Dastidar KG, Ray S and Majumder AL. (2006) Introgression of a novel salt-tolerant L-myo-inositol 1-phosphate synthase from Porteresia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoka (PcINO1) confers salt tolerance to evolutionary diverse organisms. FEBS Lett. 580:3980–3988.
De Las Mercedes Dana M, Pintor-Toro JA and Cubero B. (2006) Transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing chitinases of fungal origin show enhanced resistance to biotic and abiotic stress agents. Plant Physiol. Epublished ahead of print.
Dezar CA, Gago GM, Gonzalez DH and Chan RL. (2005) Hahb-4, a sunflower homeobox-leucine zipper gene, is a developmental regulator and confers drought tolerance to Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Trans. Res. 14:429–440.
Dhlamini Z, Spillane C, Moss JP, Ruane J, Urquia N and Sonnino A. (2005) FAO research and technology development service status of research and application of crop biotechnologies in developing countries. Preliminary assessment: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Ellul P, Rios G, Atares A, Roig LA, Serrano R and Moreno V. (2003) The expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae HAL1 gene increases salt tolerance in transgenic watermelon [Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsun. & Nakai.]. Theor. Appl. Genet. 107:462–469.
Foyer CH and Noctor G. (2005) Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling:a metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell 17:1866–1875.
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Maruyama K, Seki M, Hiratsu K, Ohme-Takagi M, Tran LP, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K and Shinozaki K. (2004) A dehydration-induced NAC protein, RD26, is involved in a novel ABA-dependent stress-signaling pathway. Plant J. 39:863–873.
Fujita M, Fujita Y, Noutoshi Y, Takahashi F, Narusaka Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K and Shinozaki K. (2006) Crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses:a current view from the points of convergence in the stress signaling networks. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 9:436–442.
Fukushima E, Arata Y, Endo T, Sonnewald U and Sato F. (2001) Improved salt tolerance of transgenic tobacco expressing apoplastic yeast-derived invertase. Plant Cell Physiol. 42:245–249.
Galinski EA, Pfeiffer HP and Truper HG. (1985) 1,4,5,6-Tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. A novel cyclic amino acid from halophilic phototrophic bacteria of the genus Ectothiorhodospira. Eur. J Biochem. 149:135–139.
Galston AW and Kaur-Sawhney R. (1990) Polyamines in plant physiology. Plant Physiol.94:406–410.
Gapper C and Dolan L. (2006) Control of plant development by reactive oxygen species. Plant Physiol. 141:341–345.
Garg AK, Kim JK, Owens TG, Ranwala AP, Choi YD, Kochian LV and Wu RJ. (2002) Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abiotic stresses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:15898–15903.
Gaxiola RA, Li J, Undurraga S, Dang LM, Allen GJ, Alper SL and Fink GR. (2001) Drought- and salt-tolerant plants result from overexpression of the AVP1 H+-pump. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 98:11444–11449.
Ghosh-Dastidar, Maitra S, Goswami L, Roy D, Das KP and Majumder AL. (2006) An insight into the molecular basis of salt tolerance of L-myo-inositol 1-P synthase (PcINO1) from Porteresia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoka, a halophytic wild rice. Plant Physiol. 40:1279–1296.
Gisbert C, Rus AM, Bolarin MC, Lopez-Coronado JM, Arrillaga I, Montesinos C, Caro M, Serrano R and Moreno V. (2000) The yeast HAL1 gene improves salt tolerance of transgenic tomato. Plant Physiol. 123:393–402
Goddijn OJM and VanDun K. (1999) Trehalose metabolism in plants. Trends Pl. Sci. 4:315–319.
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchison D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange BM, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong J, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang S, Colbert M, Sun WL, Chen L, Cooper B, Park S, Wood TC, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller RM, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A and Briggs S. (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. sp. japonica). Science 296:92–100.
Goyal K, Walton LJ and Tunnacliffe A. (2005) LEA proteins prevent protein aggregation due to water stress. Biochem. J. 388:151–157.
Grennan AK. (2006) Abiotic stress in rice. An “omic” approach. Plant Physiol. 140:1139–1141.
Grover A, Agarwal PK, Kapoor A, Katiyar-Agarwal S and Agarwal M. (2003) Production of abiotic stress tolerant transgenic crops:present accomplishments and future needs. Curr. Sci. 84:355–367.
Guo Y, Qiu QS, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM, Ohta M, Zhang C, Schumaker KS and Zhu JK. (2004) Transgenic evaluation of activated mutant alleles of SOS2 reveals a critical requirement for its kinase activity and C-terminal regulatory domain for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 16:435–449.
Guo S, Yin H, Zhang X, Zhao F, Li P, Chen S, Zhao Y and Zhang H. (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of a vacuolar H+ -pyrophosphatase gene, SsVP, from the halophyte Suaeda salsa and its overexpression increases salt and drought tolerance of Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol.60:41–50.
Hayashi H, Alia, Mustardy L, Deshnium P, Ida M and Murata N. (1997) Transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana with the cod A gene for choline oxidase: accumulation of glycine betaine and enhanced tolerance to salt and cold stress. Plant J.12:133–142.
He XJ, Mu RL, Cao WH, Zhang ZG, Zhang JS and Chen SY. (2005) AtNAC2, a transcription factor downstream of ethylene and auxin signaling pathways, is involved in salt stress response and lateral root development. Plant J. 44:903–916.
Hong Z, Lakkineni K, Zhang Z and Verma DP. (2000) Removal of feedback inhibition of delta(1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase results in increased proline accumulation and protection of plants from osmotic stress. Plant Physiol. 122:1129–1136.
Hu L, Lu H, Liu Q, Chen X and Jiang X. (2005) Overexpression of mtID gene in transgenic Populus tomentosa improves salt tolerance through accumulation of mannitol. Tree Physiol. 25:1273–1281.
Inan G, Zhang Q, Li P, Wang Z, Cao Z, Zhang H, Zhang C, Quist TM, Goodwin SM, Zhu J, Shi H, Damsz B, Charbaji T, Gong Q, Ma S, Fredricksen M, Galbraith DW, Jenks MA, Rhodes D, Hasegawa PM, Bohnert HJ, Joly RJ, Bressan RA and Zhu JK. (2004) Salt stress. A halophyte and cryophyte Arabidopsis relative model system and its applicability to molecular genetic analyses of growth and development of extremophiles. Plant Physiol. 135:1718–1737.
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800.
Jang IC, Oh SJ, Seo JS, Choi WB, Song SI, Kim CH, Kim YS, Seo HS, Choi YD, Nahm BH and Kim JK. (2003) Expression of a bifunctional fusion of the Escherichia coli genes for trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in transgenic rice plants increases trehalose accumulation and abiotic stress tolerance without stunting growth. Plant Physiol. 131:516–524.
Jeong MJ, Park SC and Byun MO. (2001) Improvement of salt tolerance in transgenic potato plants by glyceraldehyde-3 phosphate dehydrogenase gene transfer. Mol. Cell 12:185–189.
Jin Y, Weining S and Nevo E. (2005) A MAPK gene from Dead Sea fungus confers stress tolerance to lithium salt and freezing-thawing:Prospects for saline agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:18992–18997.
Johansson I, Karlsson M, Johanson U, Larsson C and Kjellbom P. (2000) The role of aquaporins in cellular and whole plant water balance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1465:324–342.
Kasuga M, Liu Q, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K and Shinozaki K. (1999) Improving plant drought, salt, and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nat. Biotechnol. 17:287–291.
Kasuga M, Miura S, Shinozaki K and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. (2004) A combination of the Arabidopsis DREB1A gene and stress-inducible rd29A promoter improved drought and low-temperature stress tolerance in tobacco by gene transfer. Plant Cell Physiol. 45:346–350.
Kasukabe Y, He L, Nada K, Misawa S, Ihara I and Tachibana S. (2004) Overexpression of spermidine synthase enhances tolerance to multiple environmental stresses and up-regulates the expression of various stress-regulated genes in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 45:712–722.
Kavi Kishore PB, Hong Z, Miao GH, Hu CA and Verma DPS. (1995) Overexpression of pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase increases proline production and confers osmotolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol. 108:1387–1394
Kim S, Kang JY, Cho DI, Park JH and Kim SY. (2004) ABF2, an ABRE-binding bZIP factor, is an essential component of glucose signaling and its overexpression affects multiple stress tolerance. Plant J. 40:75–87.
Ko JH, Yang SH and Han KH. (2006) Upregulation of an Arabidopsis RING-H2 gene, XERICO, confers drought tolerance through increased abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant J. 47:343–355.
Koh Eun-Ji, Won-Yong Song, Youngsook Lee, Kyoung Heon Kim, Kideok Kim, Namhyun Chung, Kwang-Won Lee, Suk-Whan Hong and Hojoung Lee. (2006) Expression of yeast cadmium factor 1 (YCF1) confers salt tolerance to Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci. 170:534–541.
Kwak KJ, Kim YO and Kang H. (2005) Characterization of transgenic Arabidopsis plants overexpressing GR-RBP4 under high salinity, dehydration, or cold stress. J Exp. Bot. 56:3007–3016.
Kwon SY, Choi SM, Ahn YO, Lee HS, Lee HB, Park YM and Kwak SS. (2003) Enhanced stress-tolerance of transgenic tobacco plants expressing a human dehydroascorbate reductase gene. J Plant Physiol. 160:347–353.
Li J, Yang H, Peer WA, Richter G, Blakeslee J, Bandyopadhyay A, Titapiwantakun B, Undurraga S, Khodakovskaya M, Richards EL, Krizek B, Murphy AS, Gilroy S and Gaxiola R. (2005) Arabidopsis H+-PPase AVP1 regulates auxin- mediated organ development. Science 310:121–125.
Light GG, Mahan JR, Roxas VP and Allen RD. (2005) Transgenic cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) seedlings expressing a tobacco glutathione S-transferase fail to provide improved stress tolerance. Planta 222:346–354.
Lilius G, Holmberg N and Bulow L. (1996) Enhanced NaCl stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco expressing bacterial choline dehydrogenase. BioTechnol. 14:177–180
Lippert K and Galinski EA. (1992) Enzyme stabilisation by ectoine-type compatible solutes:protection against heating, freezing and drying. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 37:61–65.
Liu Q, Kasuga M, Sakuma Y, Abe H, Miura S, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K and Shinozaki K. (1998) Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought- and low-temperature-responsive gene expression, respectively, in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1391–1406.
Luo GZ, Wang HW, Huang J, Tian AG, Wang YJ, Zhang JS and Chen SY. (2005) A putative plasma membrane cation/proton antiporter from soybean confers salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 59:809–820.
Luo M, Gu SH, Zhao SH, Zhang F and Wu NH. (2006) Rice GTPase OsRacB:potential accessory factor in plant salt-stress signaling. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai). 38:393–402.
Ma X, Qian Q and Zhu D (2005). Expression of a calcineurin gene improves salt stress tolerance in transgenic rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 58:483–495.
Mahalakshmi S, Christopher GS, Reddy TP, Rao KV and Reddy VD (2006) Isolation of a cDNA clone (PcSrp) encoding serine-rich-protein from Porteresia coarctata T. and its expression in yeast and finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) affording salt tolerance. Planta 224:347–359.
Majee M, Maitra S, Dastidar KG, Pattnaik S, Chatterjee A, Hait NC, Das KP and Majumder AL. (2004) A novel salt-tolerant L-myo-inositol-1-phosphate synthase from Porteresia coarctata (Roxb.) Tateoka, a halophytic wild rice: molecular cloning, bacterial overexpression, characterization, and functional introgression into tobacco-conferring salt tolerance phenotype. J Biol. Chem. 279:28539–28552.
Malik V and Wu R. (2005) Transcription factor AtMyb2 increased salt-stress tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Rice Genet. Newslett. 22:63.
Marin-Manzano MC, Rodriguez-Rosales MP, Belver A, Donaire JP and Venema K. (2004) Heterologously expressed protein phosphatase calcineurin downregulates plant plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity at the post-translational level. FEBS Lett. 576:266–270.
Matityahu I, Kachan L, Bar Ilan I and Amir R. (2006) Transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing the Met25 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae exhibit enhanced levels of cysteine and glutathione and increased tolerance to oxidative stress. Amino Acids 30:185–194.
Mittler R. (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 7:405–410.
Mittler R. (2006). Abiotic stress, the field environment and stress combination. Trends in Plant Sci. 11:15–19.
Moghaieb REA, Tanaka N, Saneoka H and Kounosuke F. (2004) Expression of ectoine biosynthetic genes in tobacco plants (Nicotiana tabaccum) leads to the maintenance of osmotic potential under salt stress. 4th International Crop Science Congress.
Mohanty A, Kathuria H, Ferjani A, Sakamoto A, Mohanty P, Murata N and Tyagi AK. (2002) Transgenics of an elite indica rice variety Pusa Basmati 1 harbouring the codA gene are highly tolerant to salt stress. Theor. Appl. Genet. 106:51–57.
Mukhopadhyay A, Vij S and Tyagi AK. (2004) Overexpression of a zinc-finger protein gene from rice confers tolerance to cold, dehydration, and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:6309–6314.
Nakayama H, Yoshida K, Ono H, Murooka y and Shinmyo A. (2000) Ectoine, the compatible solute of Halomonas elongata, confers hyperosmotic tolerance in cultured tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 122:1239–1247.
Nanjo T, Kobayashi M, Yoshiba Y, Kakubari Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K and Shinozaki K. (1999) Antisense suppression of proline degradation improves tolerance to freezing and salinity in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS Lett.461:205–210.
Ogawa K. (2005) Glutathione-associated regulation of plant growth and stress responses. Antioxid. Redox Signal 7:973–981.
Oh SJ, Song SI, Kim YS, Jang HJ, Kim SY, Kim M, Kim YK, Nahm BH and Kim JK. (2005) Arabidopsis CBF3/DREB1A and ABF3 in transgenic rice increased tolerance to abiotic stress without stunting growth. Plant Physiol. 138:341–351.
Ohara K, Kokado Y, Yamamoto H, Sato F and Yazaki K. (2004) Engineering of ubiquinone biosynthesis using the yeast coq2 gene confers oxidative stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. 40:734–743.
Olsen AN, Ernst HA, Leggio LL and Skriver K. (2005) NAC transcription factors:structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci. 10:79–87.
Olsson P, Yilmaz JL, Sommarin M, Persson, S and Bulow L. (2004) Expression of bovine calmodulin in tobacco plants confers faster germination on saline media. Plant Sci. 166:1595–1604.
Oraby HF, Ransom CB, Kravchenko AN and Sticklen MB.(2005) Barley HVA1 gene confers salt tolerance in R3 transgenic oat. Crop Sci. 45:2218–2227.
Owttrim GW. (2006) RNA helicases and abiotic stress. Nuc. Acids Res. 34:3220–3230.
Palmgren MG. (2001) Plant plasma membrane H+-ATPases: Powerhouses for nutrient uptake. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 52:817–845.
Pandey GK, Reddy VS, Reddy MK, Deswal R, Bhattacharya A and Sopory SK. (2002) Transgenic tobacco expressing Entamoeba histolytica calcium binding protein exhibits enhanced growth and tolerance to salt stress. Plant Sci. 162:41–47.
Pardo JM, Reddy MP, Yang S, Maggio A, Huh GH, Matsumoto T, Coca MA, Paino-D’Urzo M, Koiwa H, Yun DJ, Watad AA, Bressan RA and Hasegawa PM. (1998) Stress signaling through Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase calcineurin mediates salt adaptation in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95:9681–9686.
Park S, Li J, Pittman JK, Berkowitz GA, Yang H, Undurraga S, Morris J, Hirschi KD and Gaxiola RA. (2005a) Up-regulation of a H+-pyrophosphatase (H+-PPase) as a strategy to engineer drought-resistant crop plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 102:18830–18835.
Park BJ, Liu Z, Kanno A and Kameya T. (2005b) Transformation of radish (Raphanus sativus L.) via sonication and vacuum infiltration of germinated seeds with Agrobacterium harboring a group 3 LEA gene from B. napus. Plant Cell Rep. 24:494–500.
Perruc E, Charpenteau M, Ramirez BC, Jauneau A, Galaud JP, Ranjeva R and Ranty B. (2004) A novel calmodulin-binding protein functions as a negative regulator of osmotic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Plant J. 38:410–420.
Pilon-Smits EAH, Terry N, Sears T, Kim H, Zayed A, Hwang S, Van Dun K, Voogd E, Verwoerd TC, Krutwagen RWHH and Goddijn OJM. (1998) Trehalose-producing transgenic tobacco plants show improved growth performance under drought stress. J Plant Physiol. 152:525–532.
Pitzschke A and Hirt H. (2006) Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species signaling in plants. Plant Physiol. 141:351–356.
Prasad KVSK, Sharmila P, Kumar PA and Pardha Saradhi P. (2000) Transformation of Brassica juncea L. Czern with bacterial codA gene enhances its tolerance to salt stress. Mol. Breed. 6:489–499.
Rai M, Pal M, Sumesh KV, Jain V and Sankaranarayanan A. (2006) Engineering for biosynthesis of ectoine (2-methyl 4-carboxy tetrahydro pyrimidine) in tobacco chloroplasts leads to accumulation of ectoine and enhanced salinity tolerance. Plant Sci.170:291–306.
Rajam MV. (1997) Polyamines in Plant Ecophysiology pp. 343–374 ed MNV Prasad (New York:John Wiley).
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li LG, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY, Zhu MZ, Wang ZY, Luan S and Lin HX. (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat. Genet.37:1141–1146.
Rodrigues SM, Andrade MO, Gomes AP, Damatta FM, Baracat-Pereira MC and Fontes EP. (2006) Arabidopsis and tobacco plants ectopically expressing the soybean antiquitin-like ALDH7 gene display enhanced tolerance to drought, salinity, and oxidative stress. J Exp. Bot. 57:1909–1918.
Romero C, Belles JM, Vaya JL, Serrano R and Culianez-Macia FA. (1997) Expression of the yeast trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene in transgenic tobacco plants: pleiotropic phenotypes include drought tolerance. Planta 201:293–297.
Roxas VP, Smith RK, Allen ER and Allen RD. (1997) Overexpression of glutathione S-transferase/glutathione peroxidase enhances the growth of transgenic tobacco seedlings during stress. Nat. Biotechnol. 15:988–991.
Sahi C, Agarwal M, Reddy MK, Sopory SK and Grover A. (2003) Isolation and expression analysis of salt stress-associated ESTs from contrasting rice cultivars using a PCR-based subtraction method. Theor. Appl. Genet. 106:620–628.
Saijo Y, Hata S, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K and Izui K. (2000) Over-expression of a single Ca2+-dependent protein kinase confers both cold and salt/drought tolerance on rice plants. Plant J. 23:319–327.
Sakamoto A, Alia and Murata N. (1998) Metabolic engineering of rice leading to biosynthesis of glycinebetaine and tolerance to salt and cold. Plant Mol. Biol. 38:1011–1019.
Sanan-Mishra N, Pham XH, Sopory SK and Tuteja N. (2005) Pea DNA helicase 45 overexpression in tobacco confers high salinity tolerance without affecting yield. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 102:509–514.
Schouten HJ, Krens FA and Jacobsen E. (2006) Cisgenic plants are similar to traditionally bred plants:international regulations for genetically modified organisms should be altered to exempt cisgenesis. EMBO Rep. 7:750–753.
Shen V, Jensen RG, and Bohnert HJ. (1997) Increased resistance to oxidative stress in transgenic plants by targeting mannitol biosynthesis to chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 113:1177–1183.
Shi H, Lee BH, Wu SJ and Zhu JK. (2003) Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Biotechnol. 21:81–85.
Shirasawa K, Takabe T, Takabe T and Kishitani S. (2006) Accumulation of glycinebetaine in rice plants that overexpress choline monooxygenase from spinach and evaluation of their tolerance to abiotic stress. Ann. Bot. (Lond). 98:565–571.
Shukla RK, Raha S, Tripathi V and Chattopadhyay D. (2006) Expression of CAP2, an AP2-family transcription factor from chickpea enhances growth and tolerance to dehydration and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Plant Physiol. Epublished ahead of print.
Singla-Pareek SL, Reddy MK and Sopory SK. (2001) Transgenic approach towards developing abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Proc. Indian Natn. Sci. Acad. 67:265–284.
Singla-Pareek SL, Reddy MK and Sopory SK. (2003) Genetic engineering of the glyoxalase pathway in tobacco leads to enhanced salinity tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:4672–14677.
Singla-Pareek SL, Yadav SK, Pareek A, Reddy MK and Sopory SK. (2006) Transgenic tobacco overexpressing glyoxalase pathway enzymes grow and set viable seeds in zinc-spiked soils. Plant Physiol. 140:613–623.
Sreenivasulu N, Altschmied L, Radchuk V, Gubatz S, Wobus U and Weschke W. (2004) Transcript profiles and deduced changes of metabolic pathways in maternal and filial tissues of developing barley grains. Plant J. 37:539–553.
Stockinger EJ, Gilmour SJ and Thomashow MF. (1997) Arabidopsis thaliana CBF1 encodes an AP2 domain-containing transcriptional activator that binds to the C-repeat/DRE, a cis-acting DNA regulatory element that stimulates transcription in response to low temperature and water deficit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94:1035–1040.
Sulpice R, Tsukaya H, Nonaka H, Mustardy L, Chen TH and Murata N. (2003) Enhanced formation of flowers in salt-stressed Arabidopsis after genetic engineering of the synthesis of glycine betaine. Plant J. 36:165–176.
Sun W, Bernard C, van de Cotte B, Van Montagu M and Verbruggen N. (2001) At-HSP17.6A, encoding a small heat-shock protein in Arabidopsis, can enhance osmotolerance upon overexpression. Plant J. 27:407–415
Suzuki N, Rizhsky L, Liang H, Shuman J, Shulaev V and Mittler R. (2005) Enhanced tolerance to environmental stress in transgenic plants expressing the transcriptional coactivator multiprotein bridging factor 1c. Plant Physiol. 139:1313–1322.
Taji T, Seki M, Satou M, Sakurai T, Kobayashi M, Ishiyama K, Narusaka Y, Narusaka M, Zhu JK and Shinozaki K. (2004) Comparative genomics in salt tolerance between Arabidopsis and a Arabidopsis-related halophyte salt stress using Arabidopsis microarray. Plant Physiol. 135:1697–1709.
Tang W, Charles TM and Newton RJ. (2005) Overexpression of the pepper transcription factor CaPF1 in transgenic Virginia pine (Pinus Virginiana Mill.) confers multiple stress tolerance and enhances organ growth. Plant Mol. Biol. 59:603–617.
Tang W, Newton RJ, Lin J and Charles TM. (2006a) Expression of a transcription factor from Capsicum annuum in pine calli counteracts the inhibitory effects of salt stress on adventitious shoot formation. Mol. Gen. Genomics 276:242–253.
Tang L, Kwon SY, Kim SH, Kim JS, Choi JS, Cho KY, Sung CK, Kwak SS and Lee HS. (2006b) Enhanced tolerance of transgenic potato plants expressing both superoxide dismutase and ascorbate peroxidase in chloroplasts against oxidative stress and high temperature. Plant Cell Rep. [Epublished ahead of print]
Tarczynski MC, Jensen RG and Bohnert HJ. (1993) Stress protection of the transgenic tobacco by production of the osmolyte mannitol. Science 259:508–510.
Tarczynski MC, Jensen RG, and Bohnert HJ. (1992) Expression of a bacterial mtlD gene in transgenic tobacco leads to production of accumulation of mannitol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA89:2600–2604.
Tausz M, Sircelj H and Grill D. (2004) The glutathione system as a stress marker in plant ecophysiology:is a stress-response concept valid? J Exp. Bot. 55:1955–1962.
Thomas JC, Sepahi M, Arendall B, and Bohnert HJ. (1995) Enhancement of seed germination in high salinity by engineering mannitol expression in Arabidopsis thaliana; Plant Cell Environ. 18:801–806.
Tiburcio AF, Campos JL, Figueras X, and Besford RT. (1993) Recent advances in the understanding of polyamine functions during plant development. Plant Growth Regul.12:331–340.
Umezawa T, Fujita M, Fujita Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K and Shinozaki K. (2006) Engineering drought tolerance in plants:discovering and tailoring genes to unlock the future. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 17:113–122.
Valliyodan B and Nguyen HT. (2006) Understanding regulatory networks and engineering for enhanced drought tolerance in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 9:189–195.
Van Breusegem F and Dat JF. (2006) Reactive oxygen species in plant cell death. Plant Physiol. 141:384–390.
Vashisht AA, Pradhan A, Tuteja R and Tuteja N. (2005) Cold- and salinity stress-induced bipolar pea DNA helicase 47 is involved in protein synthesis and stimulated by phosphorylation with protein kinase C. Plant J. 44:76–87.
Veena, Reddy VS and Sopory SK (1999). Glyoxalase I from Brassica juncea: molecular cloning, regulation and its over-expression confer tolerance in transgenic tobacco under stress. Plant J. 17:385–395.
Vinocur B and Altman A. (2005) Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitations. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 16:123–132.
Waie B and Rajam MV. (2003) Effect of increased polyamine biosynthesis on stress responses in transgenic tobacco by introduction of human S-adenosylmethionine gene. Plant Sci. 164:727–734.
Wang FZ, Wang QB, Kwon SY, Kwak SS and Su WA. (2005) Enhanced drought tolerance of transgenic rice plants expressing a pea manganese superoxide dismutase. J Plant Physiol. 162:465–472.
Wang H, Huang Z, Chen Q, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Wu Y, Huang D and Huang R (2004) Ectopic overexpression of tomato JERF3 in tobacco activates downstream gene expression and enhances salt tolerance. Plant Mol. Biol. 55:183–192.
Wang W, Vinocur B and Altman A. (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures:towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14.
Wong CE, Li Y, Whitty BR, Diaz-Camino C, Akhter SR, Brandle JE, Golding GB, Weretilnyk EA, Moffatt BA and Griffith M. (2005) Expressed sequence tags from the Yukon ecotype of Thellungiella reveal that gene expression in response to cold, drought and salinity shows little overlap. Plant Mol. Biol. 58:561–574.
Xiong L and Yang V. (2003) Disease resistance and abiotic stress tolerance in rice are inversely modulated by an abscisic Acid-inducible mitogen-activated protein kinase. Plant Cell15:45–59.
Xue, ZY, Zhi, DY, Xue, GP, Zhang, H, Zhao, YX, and Xia, GM (2004) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) expressing a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene with improved grain yields in saline soils in the field and a reduced level of leaf Na+. Plant Sci. 167:849–859.
Yadav SK, Singla-Pareek SL, Reddy MK and Sopory SK. (2005) Transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing glyoxalase enzymes resist an increase in methylglyoxal and maintain higher reduced glutathione levels under salinity stress. FEBS Lett. 579:6265–6271.
Yamaguchi T and Blumwald E. (2005) Developing salt-tolerant crop plants: challenges and opportunities. Trends Plant Sci. 10:615–620.
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K and Shinozaki K. (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 57:781–803.
Yamamoto A, Bhuiyan MN, Waditee R, Tanaka Y, Esaka M, Oba K, Jagendorf AT and Takabe T. (2005) Suppressed expression of the apoplastic ascorbate oxidase gene increases salt tolerance in tobacco and Arabidopsis plants. J Exp. Bot. 56:1785–1796.
Yan J, He C, Wang J, Mao Z, Holaday SA, Allen RD and Zhang H. (2004) Overexpression of the Arabidopsis 14-3-3 protein GF14 lambda in cotton leads to a “stay-green” phenotype and improves stress tolerance under moderate drought conditions. Plant Cell Physiol. 45:1007–1014.
Yang SX, Zhao YX, Zhang Q, He YK, Zhang H and Luo D. (2001) HAL1 mediate salt adaptation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell Res. 11:142–148.
Yeo ET , Kwon HB, Han SE, Lee JT, Ryu JC and Byu MO. (2000) Genetic engineering of drought resistant potato plants by introduction of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS1) gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell 10:263–268.
Yoo JH, Park CY, Kim JC, Heo WD, Cheong MS, Park HC, Kim MC, Moon BC, Choi MS, Kang YH, Lee JH, Kim HS, Lee SM, Yoon HW, Lim CO, Yun DJ, Lee SY, Chung WS and Cho MJ. (2005) Direct interaction of a divergent CaM isoform and the transcription factor, MYB2, enhances salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem.280:3697–3706.
Yoshimura K, Miyao K, Gaber A, Takeda T, Kanaboshi H, Miyasaka H and Shigeoka S. (2004) Enhancement of stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing Chlamydomonas glutathione peroxidase in chloroplasts or cytosol. Plant J. 37:21–33.
Yu J, Hu SN, Wang J, Wong GKS, Li SG, Liu B, Deng YJ, Dai L, Zhou Y, Zhang XQ, Cao ML, Liu J, Sun JD, Tang JB, Chen YJ, Huang XB, Lin W, Ye C, Tong W, Cong LJ, Geng JN, Han YJ, Li L, Li W, Hu GQ, Huang XG, Li WJ, Li J, Liu ZW, Li L, Liu JP, Qi QH, Liu JS, Li L, Li T, Wang XG, Lu H, Wu TT, Zhu M, Ni PX, Han H, Dong W, Ren XY, Feng XL, Cui P, Li XR, Wang H, Xu X, Zhai WX, Xu Z, Zhang JS, He SJ, Zhang JG, Xu JC, Zhang KL, Zheng XW, Dong JH, Zeng WY, Tao L, Ye J, Tan J, Ren XD, Chen XW, He J, Liu DF, Tian W, Tian CG, Xia HG, Bao QY, Li G, Gao H, Cao T, Wang J, Zhao WM, Li P, Chen W, Wang XD, Zhang Y, Hu JF, Wang J, Liu S, Yang J, Zhang GY, Xiong YQ, Li ZJ, Mao L, Zhou CS, Zhu Z, Chen RS, Hao BL, Zheng WM, Chen SY, Guo W, Li GJ, Liu SQ, Tao M, Wang J, Zhu LH, Yuan LP and Yang HM. (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. sp. indica). Science 296:79–92.
Zhang HX and Blumwald E. (2001) Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit; Nat. Biotechnol. 19:765–768.
Zhang JY, Broeckling CD, Blancaflor EB, Sledge MK, Sumner LW and Wang ZY. (2005) Overexpression of WXP1, a putative Medicago truncatula AP2 domain-containing transcription factor gene, increases cuticular wax accumulation and enhances drought tolerance in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Plant J. 42:689–707.
Zhang JZ, Creelman RA and Zhu JK. (2004) From laboratory to field. Using information from Arabidopsis to engineer salt, cold, and drought tolerance in crops. Plant Physiol. 135:615–621.
Zhao F, Wang Z, Zhang Q, Zhao Y and Zhang H. (2006a) Analysis of the physiological mechanism of salt-tolerant transgenic rice carrying a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Suaeda salsa. J. Plant Res. 119:95–104.
Zhao F, Zhang X, Li P, Zhao Y and Zhang H. (2006b) Co-expression of the Suaeda salsa SsNHX1 and Arabidopsis AVP1 confer greater salt tolerance to transgenic rice than the single SsNHX1. Mol. Breed. 17:341–354.
Zhu B, Su J, Chang MC, Verma DPS, Fan YL and Wu R. (1998) Overexpression of a pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase gene and analysis of tolerance to water and salt stress in transgenic rice. Plant Sci. 139:41–48.
Zhu JK. (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 53:247–273.
Zielinski RE. (1998) Calmodulin and calmodulin-binding proteins in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 49:697–725.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Singla-Pareek, S.L., Pareek, A., Sopory, S.K. (2007). Transgenic Plants for Dry and Saline Environments. In: Jenks, M.A., Hasegawa, P.M., Jain, S.M. (eds) Advances in Molecular Breeding Toward Drought and Salt Tolerant Crops. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5578-2_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5578-2_20
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-5577-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-5578-2
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)