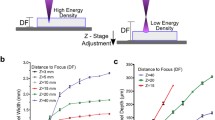
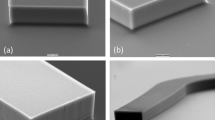
Abstract
Thermoplastic polymers are besides glass the material of choice for the industrialization of microfluidic and organ-on-chip applications. In most cases, however, such devices are developed on the basis standard lithographic clean room technologies and subsequent casting into PDMS. This results in comparably fast progress in the development of functional designs but important aspects with respect to later industrialization are thereby largely neglected. For that reason, it is advisable to switch at a rather early stage of development from PDMS to a thermoplastic polymer such as, for instance, cyclo-olefin (co)polymer (COC, COP). By making this step, additional challenges related to the anticipated manufacturing process can be identified, which is particularly important when aiming at industrialization. We present herein a standard process sequence for mastering of microfluidic devices by two-photon polymerization and final transfer into COC films by hot embossing. In addition, we describe the laser micromanufacturing of polymeric mold inserts and subsequent prototype injection molding of small series of COP samples.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker H, Gärtner C (2012) Microfluidics and the life sciences. Sci Prog 95(2):175–198
Becker H (2009) It’s the economy. Lab Chip 9:2759–2762
Schift H, Urwyler P, Kristiansen PM, Gobrecht J (2014) Nanoimprint lithography process chains for the fabrication of micro- and nanodevices. J Micro/Nanolith. MEMS MOEMS 13(3):031303
Imhof I, Müller E, Kristiansen PM, Kresak S, Tiefenauer L (2013) Polymer-based microfluidic device for measuring membrane protein activities. Microfluid Nanofluid 14(3):412–429
Karpik A, Martiel I, Kristiansen PM, Padeste C (2020) Fabrication of ultrathin suspended polymer membranes as supports for serial protein crystallography. Micro Nano Eng 7:100053
Rytka C, Lungershausen J, Kristiansen PM, Neyer A (2016) Multiscale 3D filling simulation of micro- and nanostructures in comparison to iso- and variothermal injection molding trials. J Micromech Microeng 26(6):065018
Rytka C, Opara N, Andersen NK, Kristiansen PM, Neyer A (2016) On the role of wetting and flow characteristics in polymer replication on the micro- and nanoscale. Macromol Mater Eng 301(5):597–609
Rytka C, Kristiansen PM, Neyer A (2015) Iso- and variothermal injection compression molding of polymer micro- and nanostructures for optical and medical applications. J Micromech Microeng 25(6):065008
See https://www.nilt.com/solutions/tools/cni/ for more information
Stutzmann N (2001) Microstructuring of polymers and polymer-supported matter: process and application. Dissertation, ETH Zürich
Park S, Schift H, Padeste C, Scheybal A, Jung T, Schnyder B, Kötz R, Gobrecht J (2004) Improved anti-adhesive coating for nanoimprint lithography by co-evaporation of tri- and monochlorosilanes. Mat Res Soc Proc EXS-2:37–39
Schift H, Saxer S, Park S, Padeste C, Pieles U, Gobrecht J (2005) Controlled co-evaporation of silanes for nanoimprint stamps. Nanotechnology 16:S171–S175
Goodship V (ed) (2004) Practical guide to injection molding. Rapra Technology Limited and ARBURG Limited. ISBN 1-85957-444-0
https://www.ensingerplastics.com/en/shapes/high-performance-plastics/pi-polyimide. Accessed 20 Dec 2020
Du Q, Chen T, Liu J, Zeng X (2018) Surface microstructure and chemistry of polyimide by single pulse ablation of picosecond laser. Appl Surf Sci 434:588–595
Acknowledgments
Parts of this work were supported by Innosuisse under grant no. KTI 18487.1 (project FaCoProTeMo) as well as by the Swiss Nanoscience Institute under grant no. A14-08 (project LASTRUPOL). Samuele Tosatti from SuSoS A.G. is acknowledged for supplying the proprietary hydrophilic coating for demonstration of the capillary pumps (see Fig. 5d).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Kristiansen, P.M., Karpik, A., Werder, J., Guilherme, M., Grob, M. (2022). Thermoplastic Microfluidics. In: Rasponi, M. (eds) Organ-on-a-Chip. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2373. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1693-2_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1693-2_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1692-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1693-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols