Abstract
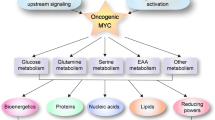
The MYC gene regulates normal cell growth and is deregulated in many human cancers, contributing to tumor growth and progression. The MYC transcription factor activates RNA polymerases I, II, and III target genes that are considered housekeeping genes. These target genes are largely involved in ribosome biogenesis, fatty acid, protein and nucleotide synthesis, nutrient influx or metabolic waste efflux, glycolysis, and glutamine metabolism. MYC’s function as a driver of cell growth has been revealed through RNA sequencing, genome-wide chromatin immunoprecipitation, proteomics, and importantly metabolomics, which is highlighted in this chapter.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dang CV (2012) MYC on the path to cancer. Cell 149:22–35
Eilers M, Eisenman RN (2008) Myc’s broad reach. Genes Dev 22:2755–2766
Johnston LA et al (1999) Drosophila myc regulates cellular growth during development. Cell 98:779–790
van Riggelen J, Yetil A, Felsher DW (2010) MYC as a regulator of ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. Nat Rev Cancer 10:301–309
Dang CV (2016) A time for MYC: metabolism and therapy. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 81:79–83
Wang R et al (2011) The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity 35:871–882
Kress TR, Sabò A, Amati B (2015) MYC: connecting selective transcriptional control to global RNA production. Nat Rev Cancer 15:593–607
Bass J, Takahashi JS (2010) Circadian integration of metabolism and energetics. Science 330:1349–1354
Altman BJ et al (2015) MYC disrupts the circadian clock and metabolism in cancer cells. Cell Metab 22:1009–1019
Le A et al (2012) Glucose-independent glutamine metabolism via TCA cycling for proliferation and survival in B cells. Cell Metab 15:110–121
Murphy TA, Dang CV, Young JD (2013) Isotopically nonstationary 13C flux analysis of Myc-induced metabolic reprogramming in B-cells. Metab Eng 15:206–217
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Schug ZT et al (2015) Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2 promotes acetate utilization and maintains cancer cell growth under metabolic stress. Cancer Cell 27:57–71
Jang C, Chen L, Rabinowitz JD (2018) Metabolomics and isotope tracing. Cell 173:822–837
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Tang, HY., Goldman, A.R., Zhang, X., Speicher, D.W., Dang, C.V. (2021). Measuring MYC-Mediated Metabolism in Tumorigenesis. In: Soucek, L., Whitfield, J. (eds) The Myc Gene. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2318. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1476-1_11
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1476-1_11
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1475-4
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1476-1
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols