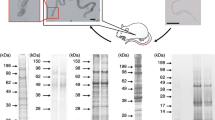
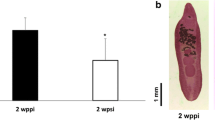
Abstract
Echinostomes are excellent models to study host-parasite interactions in intestinal helminthiases. In this chapter, data available from genomic and proteomic studies are analyzed in detail to indicate advantages and pitfalls in the research using these organisms. The lack of a genome sequence project and the low number of sequences deposited in the databases not only affect the genomic studies but also debilitate proteomic findings since in most cases, although good spectrometric data can be obtained, the available database often fail to identify the protein from the peptides obtained.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton, P.D., Curwen, R.S., and Wilson, R.A. 2001. Linking proteome and genome: how to identify parasite proteins. Trends in Parasitology 17: 198–202.
Bernal, D., De la Rubia, J.E., Carrasco-Abad, A.M., Toledo, R., Mas-Coma, S., and Marcilla, A. 2004. Identification of enolase as a plasminogen-binding protein in excretory–secretory products of Fasciola hepatica. FEBS Letters 563: 203–206.
Bernal D., Carpena I., Espert A.M., De la Rubia, J.E., Esteban, J.G., Toledo, R., and Marcilla, A. 2006. Identification of proteins in excretory/secretory extracts of Echinostoma friedi. (Trematoda) from chronic and acute infections Proteomics 6: 2835–2843.
Biron, D.G., Brun, C., Lefevre, T., Lebarbenchon, C., Loxdale, H.D., Chevenet, F., Brizard, J.P., and Thomas, F. 2006. The pitfalls of proteomics experiments without the correct use of bioinformatics tools. Proteomics 6: 5577–5596.
Bouchut, A., Coustau, C., Gourbal, B., and Mitta, G. 2007. Compatibility in the Biomphalaria glabrata./Echinostoma caproni model: new candidate genes evidenced by a suppressive subtractive hybridization approach Parasitology 134: 575–88.
Braschi, S., Borges, W.C., and Wilson, R.A. 2006a. Proteomic analysis of the schistosome tegument and its surface membranes. Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 101: S205–S212.
Braschi, S., Curwen, R.S., Ashton, P.D., Verjovski-Almeida, S., and Wilson, R.A. 2006b. The tegument surface membranes of the human blood parasite Schistosoma mansoni.: a proteomic analysis after differential extraction Proteomics 6: 1471–1482.
Carpena, I., Espert A., Muñoz-Antoli, C., Marcilla, A., Esteban, J.G., and Toledo, R. 2007. Antigenic characterization of Echinostoma friedi. (Trematoda) in hamsters and rats experimentally infected Revista Ibérica de Parasitología 67: 127–134.
Chang, Y.-W.E., Jakobi, R., McGinty, A., Foschi, M., Dunn, M.J., and Sorokin, A. 2000. Cyclooxygenase 2 promotes cell survival by stimulation of dynein light chain expression and inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase activity. Molecular and Cell Biology 20: 8571–8579.
Coustau, C., Mitta, G., Dissous, C., Guillou, F., Galinier, R., Allienne, J.F., and Modat, S. 2003. Schistosoma mansoni and Echinostoma caproni excretory–secretory products differentially affect gene expression in Biomphalaria glabrata embryonic cells Parasitology 127: 533–542.
Damian, R.T. 1997. Parasite immune evasion and exploitation: reflections and projections. Parasitology 115: S169–S175.
Davies, R.E. 1997. Surprising diversity and distribution of spliced leader RNAs in flatworms. Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology 87: 29–48.
Fujino, T., Fried, B., and Takamiya, S. 1995. Cytochemical localization of cytochrome c oxidase activity in mitochondria in the tegument and tegumental and parenchymal cells of the trematodes Echinostoma trivolvis., Zygocotyle lunata, Schistosoma mansoni, Fasciola gigantica and Paragonimus ohirai Journal of Helminthology 69: 195–201.
Ghedin, E., Wang, S., Spiro, D., Caler, E., Zhao, Q., Crabtree, J., Allen, J.E., Delcher, A.L., Guiliano, D.B., Miranda-Saavedra, D., Angiuoli, S.V., Creasy, T., Amedeo, P., Hass, B., El-Sayed, N.M., Wortman, J.R., Feldblyum, T., Tallon, L., Shumnway, M., Koo, H., Salzberg, S.l., Schobel, S., Pertea, M., Pop, M., White, O., Barton, G.J., Carlow, C.K., Crawford, M.J., Daub, J., Dimmic, M.W., Estes, C.F., Foster, J.M., Ganatra, M., Gregory, W.F., Johnson, N.M., Jin, J., Komuniecki, R., Korf, I., Kumar, S., Laney, S., Li, W., Lindblom, T.H., Lustigman, S., Ma, D., Maina, C.V., Martin, D.M., McCarter, J.P., McReynolds, L., Mitreva, M., Nutman, T.B., Parkinson, J., Peregrín-Alvarez, J.M., Poole, C., Ren, Q., Saunders, L., Sluder, A.E., Smith, K., Stanke, M., Unnasch, T.R., Ware, J., Wei, A.D., Weil, G., Williams, D.J., Zhang, Y., Williams, S.A., Fraser-Liggett, C., Slatko, B., Blaxter, M.L., and Scott, A.L. 2007. Draft genome of the filarial nematode parasite Brugia malayi. Science 317: 1756–1760.
Goudot-Crozel, V., Caillol, D., Djabali, M., and Dessein, A.J. 1989. The major parasite surface antigen associated with human resistance to schistosomiasis is a 37-kDa glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Journal of Experimental Medicine 170: 2065–2080.
Graczyk, T.K., and Fried, B. 1994. ELISA method for detecting anti-Echinostoma caproni. (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) immunoglobulins in experimentally infected ICR mice Journal of Parasitology 80: 544–549.
Graczyk, T.K., and Fried, B. 1995. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting anti-Echinostoma trivolvis. (Trematoda) IgG in experimentally infected ICR mice Cross-reactivity with E. caproni . Parasitology Research81: 710–712.
Guillou, F., Roger, E., Moné, Y., Rognon, A., Grunau, C., Therón, A., Mitta, G., Coustau, C., and Gourbal, B.E. 2007. Excretory–secretory proteome of larval Schistosoma mansoni. and Echinostoma caproni, two parasites of Biomphalaria glabrata Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology 155: 45–56.
Haas, B.J., Berriman, M., Hirai, H., Cerqueira, G.G., LoVerde,P.T., and El-Sayed, N.M. 2007. Schistosoma mansoni. genome: closing in on a final gene set Experimental Parasitology 117: 225–228.
Haque, M., and Siddiqui, A.H. 1982. Histochemical and electrophoretic studies on phosphatases of some Indian trematodes. Journal of Helminthology 56: 111–116.
Heyneman, D., Faulk, W.P., and Fudenberg, H.H. 1971. Echinostoma lindoense: larval antigens from the snail intermediate host, Biomphalaria glabrata Experimental Parasitology 29: 480–492.
Higón, M. (2007). Cloning and molecular characterization of Echinostoma caproni. Hsp70Master Thesis, Universidad de Valencia, In Spanish.74
Hu, W., Brindley, P.J., McManus, D.P., Feng, Z., and Han, Z.G. 2004. Schistosome transcriptomes: new insights into the parasite and schistosomiasis. Trends in Molecular Medicine 10: 217–225.
Humbert E., and Coustau C. 2001. Refractoriness of host haemocytes to parasite immunosuppressive factors as a putative resistance mechanism in the Biomphalaria glabrata.–Echinostoma caproni system Parasitology 122: 651–660.
Iomini, C., and Justine, J.L. 1997. Spermiogenesis and spermatozoon of Echinostoma caproni. (Platyhelminthes, Digenea): transmission and scanning electron microscopy, and tubulin immunocytochemistry Tissue Cell 29: 107–118.
Iomini, C., Bré, M.H., Levilliers, N., and Justine, J.L. 1998. Tubulin polyglycylation in Platyhelminthes: diversity among stable microtubule networks and very late occurrence during spermiogenesis. Cell Motility and the Cytoskeleton 39: 318–330.
Jaffrey, S.R., and Snyder, S.H. 1996. PIN: an associated protein inhibitor of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Science 274: 774–777.
Kanev, I. 1994. Life-cycle, delimitation and redescription of Echinostoma revolutum. (Frölich, 1802) (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) Systematic Parasitology 28: 125–144.
Kanev, I., Dimitrov, V., Radev, V., and Fried, B. 1995a. Redescription of Echinostoma trivolvis. (Cort, 1914) with a discussion of its identity Systematic Parasitology 32: 61–70.
Kanev, I., Fried, B. Dimitrov, V., and Radev, V. 1995b. Redescription of Echinostoma jurini. (Skvortzov, 1924) with a discussion of its identity and characteristics Annalen des Naturhistorischen Museums in Wien Serie B Botanik und Zoologie 97B: 37–53.
Kostadinova, A., and Gibson, D.I. 2000. The systematics of the echinostomes. In: Fried and B. Graczyk, T.K. Echinostomes as experimental models for biological research, Kluwer Academic Publishers.Dordrecht: 31–57
Kostadinova, A., Herniou, E.A., Barrett, J., and Littlewood, D.T. 2003. Phylogenetic relationships of Echinostoma. Rudolphi, 1809 (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) and related genera re-assessed via DNA and morphological analyses Systematic Parasitology 54: 159–176.
Kosupko, G.A. 1971a. New data in the bioecology and morphology of Echinostoma revolutum. and E. miyagawai (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) Byulleten’ Vsesoyuznogo Instituta Gel’mintologii im. K.I. Skrjabina 5: 43–49. (In Russian).
Kosupko, G.A. 1971b. Criteria of the species Echinostoma revolutum. In, demonstrated on experimental materialSkrjabin, K.I. Sbornik rabot po gel’mintologii posvyashchen 90-letiyu so dnya rozhdeniya akademika, Moscow: ‘Kolos’ In Russian.167–175.
Kosupko, G.A. 1972. Morphology and biology of Echinostoma revolutum Frölich, 1802 and Echinostoma miyagawai Ishii, 1932 (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) studied on experimental material. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow, 258 pp. (In Russian).
Kristensen, A.R., and Fried, B. 1991. A comparison of Echinostoma caproni. and Echinostoma trivolvis (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) adults using isoelectrofocusing Journal of Parasitology 77: 496–498.
Lie K.J., and Heyneman, D. 1977. Studies on resistance in snails: interference by nonirradiated echinostome larvae with natural resistance to Schistosoma mansoni. in Biomphalaria glabrata Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 29: 118–125.
Lie K.J., and Heyneman, D. 1979. Acquired resistance to echinostomes in four Biomphalaria glabrata. strains International Journal for Parasitology 9: 533–537.
Lie K.J., Jeong K.H., and Heyneman, D. 1982. Further characterization of acquired resistance in Biomphalaria glabrata. Journal of Parasitology 68: 529–531.
Loker E.S., Bayne C.J., and Yui M.A. 1986. Echinostoma paraensei: hemocytes of Biomphalaria glabrata as targets of echinostome mediated interference with host snail resistance to Schistosoma mansoni Experimental Parasitology 62: 149–154.
Loker E.S., Cimino D.F., and Hertel L.A. 1992. Excretory–secretory products of Echinostoma paraensei. sporocysts mediate interference with Biomphalaria glabrata hemocyte functions Journal of Parasitology 78: 104–115.
Marcilla, A., De la Rubia, J.E., Espert, A., Carpena, I., Esteban, J.G., and Toledo, R. 2004. Specific tyrosine phosphorylation in response to bile in Fasciola hepatica. and Echinostoma friedi Experimental Parasitology 106: 56–58.
Marcilla, A., Pérez-García, A., Espert, A., Bernal, D., Muñoz-Antolí, C., Esteban, J.G., and Toledo, R. 2007. Echinostoma caproni: identification of enolase in excretory/secretory products, molecular cloning, and functional expression Experimental Parasitology 117: 57–64.
McKusick, V.A. (1997). Genomics: structural and functional studies of genomes. Genomics 45: 244–249.
Morgan, J.A.T., and Blair, D. 1998a. Relative merits of nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacers and mitochondrial CO1 and ND1 genes for distinguishing among Echinostoma. species (Trematoda) Parasitology 116: 289–297.
Morgan, J.A.T., and Blair, D. 1998b. Mitochondrial ND1 gene sequences used to identify echinostome isolates from Australia and New Zealand. International Journal for Parasitology 28: 493–502.
Morphew, R.M., Barrett, J., and Brophy, P.M. 2006. Flatworm parasite proteomics. In Parasitic flatworms. Maule and A.G. Marks, N.J. Molecular biology, biochemistry, immunology and physiology, Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau International Publishing.Wallingford: 327–347.
Noda S., and Loker E.S. 1989. Effects of infection with Echinostoma paraensei. on the circulating haemocyte population of the host snail Biomphalaria glabrata Parasitology 98: 35–41.
Nowak, T.S., and Loker, E.S. 2005. Echinostoma paraensei: differential gene transcription in the sporocyst stage Experimental Parasitology 109: 94–105.
Oliveira, G. (2007). The Schistosoma mansoni. transcriptome: an update Experimental Parasitology 117: 229–235.
Oliveira, G., and Johnston, D.A. 2001. Mining the schistosome DNA sequence database. Trends in Parasitology 17:501–503.
Pinheiro, J., Maldonado, A., and Lanfredi, R.M. 2004. Light and scanning electron microscopy of the miracidium of Echinostoma paraensei. (Trematoda, Echinostomatidae) Veterinary Parasitology 121: 265–275.
Pisciotta, J.M., Ponder, E.L., Fried, B., and Sullivan, D. 2005. Hemozoin formation in Echinostoma trivolvis. rediae International Journal for Parasitology 35:1037–1042.
Ramajo-Hernández, A., Oleaga, A., Ramajo-Martín, V. and Pérez-Sánchez, R. 2007a. Carbohydrate profiling and protein identification of tegumental and excreted/secreted glycoproteins of adult Schistosoma bovis worms. Veterinary Parasitology 144: 45–60.
Ramajo-Hernández, A., Pérez-Sánchez, R., Ramajo-Martín, V., and Oleaga, A. 2007b. Schistosoma bovis: plasminogen binding in adults and the identification of plasminogen-binding proteins from the worm tegument Experimental Parasitology 115: 83–91.
Ravichandran, V., Seres, T., Moriguchi, T., Thomas, J.A., and Johnston, R.B. Jr. 1994. S-thiolation of glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase induced by the phagocytosis-related respiratory burst in blood monocytes. Journal of Biological Chemistry 269: 25010–25015.
Richard, J., Klein, M.J., and Stoeckel, M.E. 1989. Neural and glandular localisation of substance P in Echinostoma caproni. (Trematoda: Digenea) Parasitology Research 75: 641–648.
Salzet M., Capron A., and Stefano G.B. 2000. Molecular crosstalk in host–parasite relationships: schistosome– and leech–host interactions. Parasitology Today 16: 536–540.
Sapp K.K., and Loker E.S. 2000. Mechanisms underlying digenean-snail specificity: role of miracidial attachment and host plasma factors. Journal of Parasitology 86: 1012–1019.
Sebelová, S., Stewart, M.T., Mousley, A., Fried, B., Marks, N.J., and Halton, W. 2004. The musculature and associated innervation of adult and intramolluscan stages of Echinostoma caproni. (Trematoda) visualised by confocal microscopy Parasitology Research 93: 196–206.
Seres, T., Ravichandran, V., Moriguchi, T., Rokutan, K., Thomas, J.A., and Johnston, R.B. Jr. 1996. Protein S-thiolation and dethiolation during the respiratory burst in human monocytes: a reversible post-translational modification with potential for buffering the effects of oxidant stress. Journal of Immunology 156: 1973–1980.
Skelly, P.J., and Wilson, R.A. 2006. Making sense of the schistosome surface. Advances in Parasitology 63: 186–285.
Simonsen, P.E., Estambale, B.B., and Agger, M. 1991. Antibodies in the serum of golden hamsters experimentally infected with the intestinal trematode Echinostoma caproni. Journal of Helminthology 65: 239–247.
Sloss, B., Meece, J., Romano, M., and Nollen, P. 1995. The genetic relationships between Echinostoma caproni., E. paraensei, and E. trivolvis as determined by electrophoresis Journal of Helminthology 69: 243–246.
Sorensen, R.E., Curtis, J., and Minchella, D.J. 1998. Intraspecific variation in the rDNA ITS loci of 37-collar-spined echinostomes from North America: implications for sequence-based diagnoses and phylogenetics. Journal of Parasitology 85: 992–997.
Sotillo, J., Muñoz-Antoli, C., Marcilla, A., Fried, B., Esteban, J.G., and Toledo, R. 2007. Echinostoma caproni: Kinetics of IgM, IgA and IgG subclasses in the serum and intestine of experimentally infected rats and mice Experimental Parasitology 116: 390–398.
Sotillo, J., Valero, L., Sánchez del Pino, M.M., Fried, B., Esteban, J.G., Marcilla, A., and Toledo, R. 2008. Identification of antigenic proteins from Echinostoma caproni. (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) recognized by mouse immunoglobulins M, A and G using an immunoproteomic approach Parasite Immunology 30: 271–279.
Taft, J.L., and Fried, B. 1968. Oxygen consumption in adult Echinostoma revolutum. Experimental Parasitology, 23: 183–186.
Thaumaturgo, N., Vilar, M.M., Edelenyi, R., and Tendler, M. 2002. Characterization of Sm14 related components in different helminths by sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and Western blotting analysis. Memorias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz 97: S115–S116.
The C. elegans Consortium 1998. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. Science 282: 2012–2018.
Thorndyke, M.C., and Whitfield, P.J. 1987. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-like immunoreactive tegumental cells in the digenean helminth Echinostoma liei.: possible role in host–parasite interactions General and Comparative Endocrinology 68: 202–207.
Toledo, R., and Fried, B. 2005. Echinostomes as experimental models for interactions between adult parasites and vertebrate hosts. Trends in Parasitology 21: 251–254.
Toledo, R., Espert, A., Muñoz-Antoli, C., Fried, B., and Esteban, J.G. 2004. Immunological characterization of somatic and excretory/secretory antigens of Echinostoma caproni. (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) in experimentally infected rats Comparative Parasitology 71: 42–48.
Trelis, M. 2004. (Echinostoma friedi Toledo et al., 2000 (Trematoda: Echnostomatidae): experimental biologic study of the binomial miracidium-gasteropoda and adult molecular characterization. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Valencia, 269 pp) (In Spanish).
Trouvé, S., and Coustau, C. 1998. Differences in adult excretory–secretory products between geographical isolates of Echinostoma caproni. Journal of Parasitology 84: 1062–1065.
Uchikawa, R., and Loker, E.S. 1991. Lectin-binding properties of the surfaces of in vitro-transformed Schistosoma mansoni. and Echinostoma paraensei sporocysts Journal of Parasitology 77: 742–748.
Van Hellemond, J.J., van Balkom, B.W.M., and Tielens, A.G.M. 2007. Schistosome biology and proteomics: progress and challenges. Experimental Parasitology 117: 267–274.
Verjovski-Almeida, S., Leite, L.C., Dias-Neto, E., Menck, C.F., and Wilson, R.A. 2004. Schistosome transcriptome: insights and perspectives for functional genomics. Trends in Parasitology 20: 304–308.
Voltz, A., Richard, J., Pesson, B., and Jourdane, J. 1986. Chemicotaxonomic study of the genus Echinostoma.: comparison of a strain isolated in the Cameroon (E. sp.) and 2 African species (E. caproni and E. togoensis) Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée 61: 617–623. (In French).
Voltz, A., Richard, J., and Pesson, B. 1987. A genetic comparison between natural and laboratory strains of Echinostoma. (Trematoda) by isoenzymatic analysis Parasitology 95: 471–477.
Voltz, A., Richard, J., Pesson, B., and Jourdane, J. 1988. Isoenzyme analysis of Echinostoma liei.: comparison and hybridization with other African species Experimental Parasitology 66: 13–17.
Walker, A.J., and Rollinson, D. 2007. Specific tyrosine phosphorylation induced in Schistosoma mansoni. miracidia by haemolymph from schistosome susceptible, but not resistant, Biomphalaria glabrata Parasitology 6: 1–9.
Wilson, R.A., Ashton, P.D., Braschi, S., Dillon, G.P., Berriman, M., and Ivens, A. 2007. “Oming” in on schistosomes: prospects and limitations for post-genomics. Trends in Parasitology, 23: 14–20.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Lynne Yenush is thanked for critically reading the manuscript. Financial support was obtained from the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (Madrid, Spain), grant CGL2005–02321/BOS; Conselleria d’Educació, Generalitat Valenciana (Valencia, Spain), grants GV07/006 and ACOMP07/071; and Universitat de València (Valencia, Spain) grant Accions Especials 20050201.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Marcilla, A. (2009). Echinostomes: genomics and proteomics. In: Toledo, R., Fried, B. (eds) The Biology of Echinostomes. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-09577-6_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-09577-6_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-0-387-09576-9
Online ISBN: 978-0-387-09577-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)