Abstract
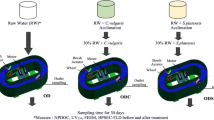
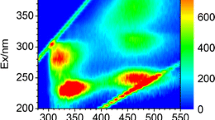
The contribution of dissolved organic matter (DOM) released from phytoplankton (Microcystis aeruginosa) during cultivation and biodegradation was examined to clarify the causes of the organic pollution of Lake Biwa. Two peaks, peak 2 (retention time (RT) = 32 min) and peak 3 (RT = 35 min), were detected in the algal DOM released from Microcystis aeruginosa during cultivation and biodegradation by gel chromatography with a fluorescence detector (Ex = 340 nm, Em = 435 nm). As these peaks correspond with the peaks detected in the surface water of Lake Biwa, one can conclude that the algal DOM released from Microcystis aeruginosa during cultivation and biodegradation makes a considerable contribution to the refractory organic matter in Lake Biwa. Three fluorescence maxima were observed in the cultivation of Microcystis aeruginosa: a fulvic-like fluorescence peak (peak A) with Ex/Em values of 320/430 nm, a protein-like fluorescence peak (peak C) with Ex/Em values of 280/360 nm, and another peak with Ex/Em values of 240/370 nm. The fluorescence material of peak C has a larger MW than that of peak A. The algal-derived DOM from Microcystis aeruginosa has similar fluorescence to fulvic acid of soil origin but exhibits mainly hydrophilic characteristics. In the biodegradation of Microcystis aeruginosa, a fulvic-like fluorescence peak (peak B) with Ex/Em values of 250/440 nm and a peak with Ex/Em values of 320/380 nm were observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shiga Prefecture, Kankyohakusyo, 2006, 42.
H. Tatsumoto, T. Hattori, T. Furukawa, I. Ikushima, M. Kurihara, and I. Abe, Nippon Kagaku Kaishi, 1991, 852.
A. Imai, T. Fukushima, K. Matsushige, T. Inoue, and T. Ishibashi, Jpn. J. Limnol, 1998, 59, 53.
T. Hori, Y. Sugiyama, and M. Sugiyama, Jpn. J. Limnol., 1998, 59, 39.
Y. Sugiyama, M. Sugiyama, and T. Hori, Limnology, 2000, 1, 171.
Y. Sugiyama and T. Kumagai, Anal. Sci., 2001, 17, 77.
E. Yamada, T. Ozaki, and M. Kimura, Anal. Sci., 1998, 14, 327.
E. Yamada, K. Doi, K. Okano, and Y. Fuse, Anal. Sci., 2000, 16, 125.
S. Aoki, Y. Fuse, and E. Yamada, Anal. Sci., 2004, 20, 159.
K. Nagai, S. Aoki, Y. Fuse, and E. Yamada, Bunseki Kagaku, 2005, 54, 923.
Shiga Pref. Inst. Pub. Hlth. & Environ. Sci., “Data Compilation of Phytoplankton in Lake Biwa,” 1984, 1985, 1986, 1991, 1995, 2000, and 2005.
F. Wu and E. Tanoue, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2001, 35, 3646.
K. M. G. Mostofa, T. Yoshioka, E. Konohira, E. Tanoue, K. Hayakawa, and M. Takahashi, Limnology, 2005, 6, 101.
N. Kishimoto, Abstracts of the 70th Conference of the Japan Society of Limnology, 2005, 178.
S. Nagao, Y. Suzuki, Y. Nakaguchi, M. Seno, and K. Hiraki, Bunseki Kagaku, 1997, 46, 335.
T. Fukushima, J. Park, A. Imai, and K. Matsushige, Aquatic Sci., 1996, 58, 139.
J. Bnffle, P. Delamdoety, J. Zunstein, W. Haerdi, and Z. Schweitz, Hydrology, 1982, 44, 325.
P. G. Coble, S. A. Green, N. V. Blough, and R. B. Gagosian, Nature, 1990, 348, 432.
P. G. Coble, Mar. Chem., 1996, 51, 325.
N. Senesi, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1990, 232, 11.
B. J. H. Matthews and A. C. Jones, Mar. Chem., 1996, 55, 317.
A. Baker, Environ. Sci. Technol, 2001, 35, 948.
J. A. Leenheer and P. Croue, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, 37, 18.
C. A. Stedmon, S. Markager, and R. Bro, Mar. Chem., 2003, 82, 239.
S. Nagao and S. Muraoka, “Understanding and Managing Organic Matter in Soils, Sediments and Waters”, ed. R. S. Swift and K. M. Spark, 2001, IHSS, 407.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aoki, S., Ohara, S., Kimura, K. et al. Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter Released from Microcystis aeruginosa. ANAL. SCI. 24, 389–394 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.24.389
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.24.389