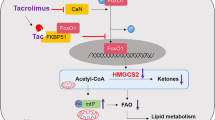
Abstract
Tacrolimus (TAC), also called FK506, is one of the classical immunosuppressants to prevent allograft rejection after liver transplantation. However, it has been proved to be associated with post-transplant hyperlipemia. The mechanism behind this is unknown, and it is urgent to explore preventive strategies for hyperlipemia after transplantation. Therefore, we established a hyperlipemia mouse model to investigate the mechanism, by injecting TAC intraperitoneally for eight weeks. After TAC treatment, the mice developed hyperlipemia (manifested as elevated triglyceride (TG) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c), as well as decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c)). Accumulation of lipid droplets was observed in the liver. In addition to lipid accumulation, TAC induced inhibition of the autophagy-lysosome pathway (microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3β (LC3B) II/I and LC3B II/actin ratios, transcription factor EB (TFEB), protein 62 (P62), and lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1)) and downregulation of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) in vivo. Overexpression of FGF21 may reverse TAC-induced TG accumulation. In this mouse model, the recombinant FGF21 protein ameliorated hepatic lipid accumulation and hyperlipemia through repair of the autophagy-lysosome pathway. We conclude that TAC downregulates FGF21 and thus exacerbates lipid accumulation by impairing the autophagy-lysosome pathway. Recombinant FGF21 protein treatment could therefore reverse TAC-caused lipid accumulation and hypertriglyceridemia by enhancing autophagy.
摘要
他克莫司(TAC), 也称为FK506, 是预防肝移植后同种异体移植排斥反应的经典免疫抑制剂之一. 然而, 它已被证明与移植后高脂血症有关. 但其背后的机制尚不清楚, 因此迫切需要探索移植后高脂血症的预防策略. 我们通过腹腔注射8周TAC建立了一个高脂血症小鼠模型来研究其机制. TAC处理后, 小鼠发生高脂血症(表现为甘油三酯(TG)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-c)升高, 以及高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-c)降低)以及肝脏脂质的累积. 除脂质积累外, TAC还抑制了自噬-溶酶体途径(LC3B II/I和LC3BII/actin比值、 转录因子EB(TFEB)、 P62和LAMP1), 并下调成纤维细胞生长因子21(FGF21)的表达. 而FGF21的过表达可逆转TAC诱导的TG积累. 在该小鼠模型中, 重组FGF21蛋白通过修复自噬-溶酶体途径改善肝脏脂质积累和高脂血症. 综上所述, TAC下调FGF21, 从而通过抑制自噬-溶酶体途径来加剧脂质积累. 此外, 重组FGF21蛋白处理可以通过增强自噬来逆转TAC引起的脂质积累和高甘油三酯血症.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achila OO, Fessahye N, Mengistu ST, et al., 2022. A community based cross sectional study on the prevalence of dyslipidemias and 10 years cardiovascular risk scores in adults in Asmara, Eritrea. Sci Rep, 12:5567. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-09446-9
Ballabio A, Bonifacino JS, 2020. Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 21(2):101–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0185-4
Byun S, Seok S, Kim YC, et al., 2020. Fasting-induced FGF21 signaling activates hepatic autophagy and lipid degradation via JMJD3 histone demethylase. Nat Commun, 11:807. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14384-z
Chen LQ, Wang K, Long AJ, et al., 2017. Fasting-induced hormonal regulation of lysosomal function. Cell Res, 27(6):748–763. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.45
Choi SW, Reddy P, 2014. Current and emerging strategies for the prevention of graft-versus-host disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 11(9):536–547. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2014.102
Dehghani SM, Taghavi SAR, Eshraghian A, et al., 2007. Hyperlipidemia in Iranian liver transplant recipients: prevalence and risk factors. J Gastroenterol, 42(9):769–774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-007-2092-2
Fisher FM, Maratos-Flier E, 2016. Understanding the physiology of FGF21. Annu Rev Physiol, 78:223–241. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105339
Geng LL, Lam KSL, Xu AM, 2020. The therapeutic potential of FGF21 in metabolic diseases: from bench to clinic. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 16(11):654–667. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-020-0386-0
Hondares E, Iglesias R, Giralt A, et al., 2011. Thermogenic activation induces FGF21 expression and release in brown adipose tissue. J Biol Chem, 286(15):12983–12990. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.215889
Inagaki T, Dutchak P, Zhao GX, et al., 2007. Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARα-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab, 5(6):415–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2007.05.003
Klionsky DJ, Abdel-Aziz AK, Abdelfatah S, et al., 2021. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition). Autophagy, 17(1):1–382. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1797280
Kurosu H, Choi M, Ogawa Y, et al., 2007. Tissue-specific expression of βKlotho and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor isoforms determines metabolic activity of FGF19 and FGF21. J Biol Chem, 282(37):26687–26695. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M704165200
Li Z, Miao ZY, Ding LL, et al., 2021. Energy metabolism disorder mediated ammonia gas-induced autophagy via AMPK/mTOR/ULK1-Beclin1 pathway in chicken livers. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 217:112219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112219
Ling Q, Huang HT, Han YQ, et al., 2020. The tacrolimus-induced glucose homeostasis imbalance in terms of the liver: from bench to bedside. Am J Transplant, 20(3):701–713. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.15665
Liu KP, Qiu DB, Liang X, et al., 2022. Lipotoxicity-induced STING1 activation stimulates MTORC1 and restricts hepatic lipophagy. Autophagy, 18(4):860–876. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1961072
Liu LH, Tao ZP, Zheng LD, et al., 2016. FoxO1 interacts with transcription factor EB and differentially regulates mitochondrial uncoupling proteins via autophagy in adipocytes. Cell Death Discov, 2:16066. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddiscovery.2016.66
Markan KR, Naber MC, Ameka MK, et al., 2014. Circulating FGF21 is liver derived and enhances glucose uptake during refeeding and overfeeding. Diabetes, 63(12):4057–4063. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-0595
Medina DL, 2021. Lysosomal calcium and autophagy. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol, 362:141–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ircmb.2021.03.002
Nezich CL, Wang CX, Fogel AI, et al., 2015. MiT/TFE transcription factors are activated during mitophagy downstream of Parkin and Atg5. J Cell Biol, 210(3):435–450. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201501002
Pereira MJ, Palming J, Rizell M, et al., 2013. The immunosuppressive agents rapamycin, cyclosporin A and tacrolimus increase lipolysis, inhibit lipid storage and alter expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism in human adipose tissue. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 365(2):260–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2012.10.030
Qiang WD, Shen TZ, Noman M, et al., 2021. Fibroblast growth factor 21 augments autophagy and reduces apoptosis in damaged liver to improve tissue regeneration in zebrafish. Front Cell Dev Biol, 9:756743. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.756743
Qin H, Song ZY, Zhao CY, et al., 2022. Liquiritigenin inhibits lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells via mTOR-mediated regulation of the autophagy mechanism. Nutrients, 14(6):1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/NU14061287
Rostaing L, Sánchez-Fructuoso A, Franco A, et al., 2012. Conversion to tacrolimus once-daily from ciclosporin in stable kidney transplant recipients: a multicenter study. Transpl Int, 25(4):391–400. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-2277.2011.01409.x
Ryan A, Heath S, Cook P, 2018. Dyslipidaemia and cardiovascular risk. BMJ, 360:k835. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k835
Settembre C, di Malta C, Polito VA, et al., 2011. TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis. Science, 332(6036):1429–1433. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1204592
She QY, Bao JF, Wang HZ, et al., 2022. Fibroblast growth factor 21: a “rheostat” for metabolic regulation? Metabolism, 130:155166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155166
Sui Y, Chen JP, 2022. Hepatic FGF21: its emerging role in interorgan crosstalk and cancers. Int J Biol Sci, 18(15):5928–5942. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.76924
Tao ZP, Aslam H, Parke J, et al., 2022. Mechanisms of autophagic responses to altered nutritional status. J Nutr Biochem, 103:108955. https://doi.org/10.1016/jonutbio.2022.108955
Veroux M, Tallarita T, Corona D, et al., 2011. Sirolimus in solid organ transplantation: current therapies and new frontiers. Immunotherapy, 3(12):1487–1497. https://doi.org/10.2217/imt.11.143
Visvikis O, Ihuegbu N, Labed S, et al., 2014. Innate host defense requires TFEB-mediated transcription of cytoprotective and antimicrobial genes. Immunity, 40(6):896–909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.05.002
Wang SY, Li HY, Yuan MH, et al., 2022. Role of AMPK in autophagy. Front Physiol, 13:1015500. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2022.1015500
Wang YH, Wang YL, Li F, et al., 2022. Psoralen suppresses lipid deposition by alleviating insulin resistance and promoting autophagy in oleate-induced L02 cells. Cells, 11(7):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/CELLS11071067
Wu AM, Feng B, Yu J, et al., 2021. Fibroblast growth factor 21 attenuates iron overload-induced liver injury and fibrosis by inhibiting ferroptosis. Redox Biol, 46:102131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.102131
Yan LS, Zhang SF, Luo G, et al., 2022. Schisandrin B mitigates hepatic steatosis and promotes fatty acid oxidation by inducing autophagy through AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Metabolism, 131:155200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155200
Zhang CZ, Chen KC, Wei RL, et al., 2020. The circFASN/miR-33a pathway participates in tacrolimus-induced dysregulation of hepatic triglyceride homeostasis. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 5:23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-0105-2
Zhang T, Liu JX, Shen SN, et al., 2020. SIRT3 promotes lipophagy and chaperon-mediated autophagy to protect hepatocytes against lipotoxicity. Cell Death Differ, 27(1):329–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-019-0356-z
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFA1100500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 92159202, 81930016, and 82102910), the Key Research & Development Plan of Zhejiang Province (No. 2019C03050), the Construction Fund of Key Medical Disciplines of Hangzhou (No. OO20200093), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020M671762), and the Medical and Health Technology Program in Zhejiang Province (No. WKJ-ZJ-2120), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zhensheng ZHANG, Li XU, Xun QIU, and Xiao XU designed the research. Zhensheng ZHANG, Li XU, Xun QIU, Xinyu YANG, and Zhengxing LIAN performed experiments. Zhensheng ZHANG, Li XU, and Xun QIU analyzed and interpreted data. Zhensheng ZHANG wrote the paper. Li XU, Xun QIU, Xuyong WEI, Di LU, and Xiao XU critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript, and therefore, have full access to all the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity and security of the data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Zhensheng ZHANG, Li XU, Xun QIU, Xinyu YANG, Zhengxing LIAN, Xuyong WEI, Di LU, and Xiao XU declare no competing interests.
All animal studies were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and the Ethics Committee of Zhejiang University (No. 1482).
Additional information
Supplementary information
Table S1; Figs. S1 and S2
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Xu, L., Qiu, X. et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) attenuates tacrolimus-induced hepatic lipid accumulation through transcription factor EB (TFEB)-regulated lipophagy. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 24, 485–495 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200562
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B2200562
Key words
- Autophagy
- Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21)
- Lipid
- Lipophagy
- Lysosome
- Tacrolimus
- Transcription factor EB (TFEB)