Abstract
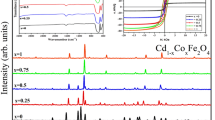
The structural, morphological, magnetic, and dielectric properties of MnxCo0.5-xNi0.5Fe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.2, and 0.4) synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion are reported in this paper. X-ray diffraction pattern of the samples confirms the formation of a single-phase spinel ferrite and the crystallite size (D) is in the range of 32.60–33.62 nm. Fourier transform infrared spectra have a vibrational band at 534.20 cm−1 and 420.13 cm−1 which corresponds to the tetrahedral and octahedral sites of the MnxCo0.5-xNi0.5Fe2O4 respectively. Field emission scanning electron microscope reveals the cubic morphology of the synthesized spinel ferrite with inhomogeneous grain size. Vibrating sample magnetometer analysis showed the ferromagnetic nature of all samples. All the samples exhibit a multi-domain because the value of Mr/Ms lies in the range of 0.153–0.336. Dielectric properties reveal the hopping of the charge carrier which has improved the conduction mechanism of the MnxCo0.5-xNi0.5Fe2O4.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data related to this research will be available on request.
References
Y. Cedeño-Mattei, O. Perales-Pérez, Synthesis of high-coercivity cobalt ferrite nanocrystals. Microelectron. J. 40(4–5), 673–676 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2008.07.040
P. Liu et al., Effect of Mn substitution on the promoted formaldehyde oxidation over spinel ferrite: catalyst characterization, performance and reaction mechanism. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 182, 476–484 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.09.055
P. Chen, B. Cui, X. Cui, W. Zhao, Y. Bu, Y. Wang, A microwave-triggered controllable drug delivery system based on hollow-mesoporous cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 699, 526–533 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.304
A. Šutka, K.A. Gross, Spinel ferrite oxide semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators, B Chem. 222, 95–105 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.08.027
W. Hu, N. Qin, G. Wu, Y. Lin, S. Li, D. Bao, Opportunity of spinel ferrite materials in nonvolatile memory device applications based on their resistive switching performances. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(36), 14658–14661 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja305681n
E.M. Masoud, Improved initial discharge capacity of nanostructured Ni-Co spinel ferrite as anode material in lithium ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 253, 247–252 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2013.10.017
Y. Chen, J.E. Snyder, K.W. Dennis, R.W. McCallum, D.C. Jiles, Temperature dependence of the magnetomechanical effect in metal-bonded cobalt ferrite composites under torsional strain. J. Appl. Phys. 87(9), 5798–5800 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.372526
H. Mahajan, S.K. Godara, A.K. Srivastava, Synthesis and investigation of structural, morphological, and magnetic properties of the manganese doped cobalt-zinc spinel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 896, 162966 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162966
M. Amiri, M. Salavati-Niasari, A. Akbari, Magnetic nanocarriers: evolution of spinel ferrites for medical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 265, 29–44 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2019.01.003
M.N. Akhtar et al., Physical, structural, conductive and magneto-optical properties of rare earths (Yb, Gd) doped Ni–Zn spinel nanoferrites for data and energy storage devices. Ceram. Int. 47(9), 11878–11886 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.01.028
M.S.I. Sarker, M. Yeasmin, M.A. Al-Mamun, S.M. Hoque, M.K.R. Khan, Influence of Gd content on the structural, Raman spectroscopic and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by sol-gel route. Ceram. Int. 48(22), 33323–33331 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.07.275
M. Abdullah-Al-Mamun et al., Effect of Er substitution on the magnetic, Mössbauer spectroscopy and dielectric properties of CoFe2−xErxO4 (x = 0.00, 0.01, 0.03, 0.05) nanoparticles. Results Phys. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104698
P. Sivakumar, R. Ramesh, A. Ramanand, S. Ponnusamy, C. Muthamizhchelvan, Preparation and properties of nickel ferrite (NiFe2O 4) nanoparticles via sol-gel auto-combustion method. Mater. Res. Bull. 46(12), 2204–2207 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2011.09.010
B.J. Rani et al., Ferrimagnetism in cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 14, 84–91 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2018.01.012
Y. Köseoǧlu, F. Alan, M. Tan, R. Yilgin, M. Öztürk, Low temperature hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Mn doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 38(5), 3625–3634 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.01.001
Hirthna, S. Sendhilnathan, Enhancement in dielectric and magnetic properties of Mg2+ substituted highly porous super paramagnetic nickel ferrite nanoparticles with Williamson-Hall plots mechanistic view. Ceram. Int. 43(17), 15447–15453 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.08.090
T. Tchouank Tekou Carol, J. Mohammed, H.Y. Hafeez, B.H. Bhat, S.K. Godara, A.K. Srivastava, Structural, dielectric, and magneto-optical properties of Al-Cr substituted M-type barium hexaferrite. Phys. Status Solidi 216(16), 1800928 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssa.201800928
N. Murali et al., Effect of Al substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of Co-Zn ferrites. Phys. B Condens. Matter 522(July), 1–6 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2017.07.043
J. Rani, K.L. Yadav, S. Prakash, Dielectric and magnetic properties of xCoFe2O4-(1 - X)[0.5Ba(Zr0.2Ti0.8)O3–0.5(Ba0.7Ca0.3)TiO3] composites. Mater. Res. Bull. 60, 367–375 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2014.09.013
Y. Il kim, D. Kim, C.S. Lee, Synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 magnetic nanoparticles prepared by temperature-controlled coprecipitation method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 337(1–4), 42–51 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-4526(03)00322-3
M.S. Shah, K. Ali, I. Ali, A. Mahmood, S.M. Ramay, M.T. Farid, Structural and magnetic properties of praseodymium substituted barium-based spinel ferrites. Mater. Res. Bull. 98(August 2017), 77–82 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.09.063
R. Vishwarup, S.N. Mathad, Facile synthesis of nano Mg-Co ferrites (x=0.15, 0.20, 0.25, 0.30, 0.35, and 0.40) via coprecipitation route: structural characterization. Mater. Int. 2(4), 0471–0476 (2020)
S.S. Yattinahalli, S.B. Kapatkar, S.N. Mathad, Structural and mechanical properties of a nano ferrite. Adv. Sci. Focus 2(1), 42–46 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1166/asfo.2014.1079
D.V. Kurmude, R.S. Barkule, A.V. Raut, D.R. Shengule, K.M. Jadhav, X-ray diffraction and cation distribution studies in zinc-substituted nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27(2), 547–553 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-013-2305-2
R. Jabbar, S.H. Sabeeh, A.M. Hameed, Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Mn+2 doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 494, 165726 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165726
A. Amirabadizadeh, T. Amirabadi, Effect of substitution of Al for Fe on magnetic properties and particle size of Ni-Co nanoferrite. World J. Condens. Matter. Phys. 03(03), 131–135 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4236/wjcmp.2013.33021
R. Sharma, P. Thakur, P. Sharma, V. Sharma, Ferrimagnetic Ni2+doped Mg-Zn spinel ferrite nanoparticles for high density information storage. J. Alloys Compd. 704, 7–17 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.02.021
M. Bhuvaneswari, S. Sendhilnathan, M. Kumar, R. Tamilarasan, N.V. Giridharan, Synthesis, investigation on structural and electrical properties of cobalt doped Mn-Zn ferrite nanocrystalline powders. Mater. Sci. Pol. 34(2), 344–353 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/msp-2016-0046
I. Mohammed et al., Structural, morphological, optical, magnetic, and microwave properties of La3+- Mn2+ substituted Zn2-Y-type barium-strontium hexaferrite. Chinese J. Phys. 78(April), 377–390 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2022.06.025
M.A. Khan, M.U. Islam, M. Ishaque, I.Z. Rahman, Effect of Tb substitution on structural, magnetic and electrical properties of magnesium ferrites. Ceram. Int. 37(7), 2519–2526 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.03.063
S.V. Bhandare et al., Effect of Mg-substitution in Co–Ni-ferrites: cation distribution and magnetic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 251(March), 123081 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123081
M. Augustin, T. Balu, Estimation of Lattice Stress and Strain in Zinc and Manganese Ferrite Nanoparticles by Williamson-Hall and Size-Strain Plot Methods. Int. J. Nanosci. 16(3), 1–7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219581X16500356
A. Ali et al., Effect of In on superparamagnetic CoInxFe2-xO4 (x = 0–0.15) synthesized through hydrothermal method. Results Phys. 25(February), 104251 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104251
M.N. Akhtar, M.A. Khan, Effect of rare earth doping on the structural and magnetic features of nanocrystalline spinel ferrites prepared via sol gel route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 460, 268–277 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.03.069
T.M. Hammad, S. Kuhn, A.A. Amsha, N.K. Hejazy, R. Hempelmann, Comprehensive study of the impact of Mg2+ doping on optical, structural, and magnetic properties of copper nanoferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 33(10), 3065–3075 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05559-2
I. Sharifi, H. Shokrollahi, Structural, magnetic and Mössbauer evaluation of Mn substituted Co-Zn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 334, 36–40 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.01.021
A.V. Raut, R.S. Barkule, D.R. Shengule, K.M. Jadhav, Synthesis, structural investigation and magnetic properties of Zn 2+ substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by the sol-gel auto-combustion technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 358–359, 87–92 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.01.039
K.B. Modi, M.C. Chhantbar, H.H. Joshi, Study of elastic behaviour of magnesium ferri aluminates. Ceram. Int. 32(2), 111–114 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2005.01.005
G. Dhillon, N. Kumar, M. Chitkara, I.S. Sandhu, Effect of A-site substitution and calcination temperature in Fe3O4 spinel ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(21), 18903–18912 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04427-y
S. Hasan, B. Azhdar, Synthesis of Nickel-Zinc ferrite nanoparticles by the Sol-Gel auto-combustion method: study of crystal structural, cation distribution, and magnetic properties. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4603855
S. Kavitha, M. Kurian, Effect of zirconium doping in the microstructure, magnetic and dielectric properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 799, 147–159 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.183
A.A.H. El-Bassuony, H.K. Abdelsalam, Synthesis, characterization, magnetic and antimicrobial properties of silver chromite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(4), 3662–3673 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-02924-8
H. Fakhr Nabavi, M. Aliofkhazraei, M. Hasanpoor, A. Seyfoori, Combustion and coprecipitation synthesis of Co–Zn ferrite nanoparticles: comparison of structure and magnetic properties. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 13(6), 1112–1118 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.12580
S. Kumar Godara et al., Effect on Magnetic, morphological and structural properties of Zn2+-Zr4+ substituted SrM for permanent magnet based appliances. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 560(May), 169626 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169626
M. Penchal Reddy, R.A. Shakoor, A.M.A. Mohamed, M. Gupta, Q. Huang, Effect of sintering temperature on the structural and magnetic properties of MgFe2O4 ceramics prepared by spark plasma sintering. Ceram. Int. 42(3), 4221–4227 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.11.097
K. Krieble, T. Schaeffer, J.A. Paulsen, A.P. Ring, C.C.H. Lo, J.E. Snyder, Mössbauer spectroscopy investigation of Mn-substituted Co-ferrite (Co Mn x Fe2–x O4). J. Appl. Phys. 97(10), 2003–2006 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1846271
V. Verma, M. Kaur, J.M. Greneche, Tailored structural, optical and magnetic properties of ternary nanohybrid Mn 0.4 Co 0.6-x Cu x Fe2 O4 (x= 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6) spinel ferrites. Ceram. Int. 45(8), 10865–10875 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.02.164
P. Chavan, L.R. Naik, P.B. Belavi, G. Chavan, C.K. Ramesha, R.K. Kotnala, Studies on electrical and magnetic properties of Mg-substituted nickel ferrites. J. Electron. Mater. 46(1), 188–198 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4886-6
R.S. Yadav et al., Structural, magnetic, dielectric, and electrical properties of NiFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by honey-mediated sol-gel combustion. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 107, 150–161 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2017.04.004
J. Sharma, N. Sharma, J. Parashar, V.K. Saxena, D. Bhatnagar, K.B. Sharma, Dielectric properties of nanocrystalline Co-Mg ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 649(108), 362–367 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.07.103
S. Aman, M.B. Tahir, N. Ahmad, The enhanced electrical and dielectric properties of cobalt-based spinel ferrites for high-frequency applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32(17), 22440–22449 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06730-8
C.V. Ramana, Y.D. Kolekar, K. Kamala Bharathi, B. Sinha, K. Ghosh, Correlation between structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of manganese substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Appl. Phys (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4827416
A. Sharma, S.K. Godara, A.K. Srivastava, Influence of composition variation on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of Gd3Fe5O12(x)/MgFe2O4(1–x) composite. Indian J. Phys. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-022-02365-5
K.P. Padmasree, D.K. Kanchan, A.R. Kulkarni, Impedance and Modulus studies of the solid electrolyte system 20CdI 2–80[xAg2O-y(0.7V2O5-0.3B 2O3)], where 1 ≤x/y ≤ 3. Solid State Ionics 177(5–6), 475–482 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2005.12.019
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend sincere appreciation to the Central Instrumentation Facility, Lovely Professional University – Punjab, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KK: methodology, conceptualization, and writing-original draft. HM, IM, and AS: investigation of data and graphs. DB and AKS: supervision, writing-review, and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, K., Mahajan, H., Sharma, A. et al. Manganese doped cobalt–nickel spinel ferrite via. sol–gel approach: Insight into structural, morphological, magnetic, and dielectric properties. Journal of Materials Research 38, 3837–3849 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01119-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-023-01119-1