Abstract
The separation of oil-water mixtures is a widely utilized unit operation, used for handling a wide variety of mixtures from industry including: petroleum drilling and refining, fracking, waste-water treatment, mining, metal fabrication and machining, textile and leather processing, and rendering. Membrane-based methods have become increasingly attractive for the separation of oil-water mixtures because they are relatively energy-efficient, can be readily used to separate a variety of industrial feed streams, and provide consistent permeate quality. In this perspective, we discuss the design strategies for membranes with selective wettability i.e., membranes that are either selectively wet by, or prevent wetting by, the oil or water phase. The design strategies include the parameterization of two important physical characteristics: the surface porosity and the breakthrough pressure. We also discuss how they are related for membranes with a periodic geometry. On the basis of this understanding, we explore principles that allow for the systematic design of membranes with selective wettability. A review of the current literature on the separation of oil-water mixtures using membranes with differing wettabilities is also presented. Finally, we conclude by discussing the current challenges and outlook for the future of the field.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.-T.H.P. Kajitvichyanukul and L.K. Wang: Handbook of Environmental Engineering, Vol 13: Membrane and Desalination Technologies (The Humana Press Inc., New York, 2011).
Office of the Federal Register: Code of Federal Regulations, Title 40-Protection of the Environment, Vol. 30, Part 435.13 (Washington, DC, 2014), pp. 299.
J.W. Patterson: Industrial Wastewater Treatment Technology, 2nd ed. (Buttersworth, Stoneham, MA, 1985).
T.G. Mason, J.N. Wilking, K. Meleson, C.B. Chang, and S.M. Graves: Nanoemulsions: formation, structure, and physical properties. J. Phys.—Condens. Matter. 18, R635 (2006).
M.O. Adebajo, R.L. Frost, J.T. Kloprogge, O. Carmody, and S. Kokot: Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: a review of synthesis and absorbing properties. J. Porous Mater. 10, 159 (2003).
M. Cheryan and N. Rajagopalan: Membrane processing of oily streams. Wastewater treatment and waste reduction. J. Membr. Sci. 151, 13 (1998).
A.A. Al-Shamrani, A. James, and H. Xiao: Destabilisation of oil-water emulsions and separation by dissolved air flotation. Water Res. 36, 1503 (2002).
J. Rubio, M.L. Souza, and R.W. Smith: Overview of flotation as a wastewater treatment technique. Miner. Eng. 15, 139 (2002).
T. Ichikawa: Electrical demulsification of oil-in-water emulsion. Colloid Surface A 302, 581 (2007).
A.A. Al-Shamrani, A. James, and H. Xiao: Separation of oil from water by dissolved air flotation. Colloid Surface A 209, 15 (2002).
M. Toyoda and M. Inagaki: Heavy oil sorption using exfoliated graphite—new application of exfoliated graphite to protect heavy oil pollution. Carbon 38, 199 (2000).
V.K. Gupta, P.J.M. Carrott, and M.M.L.R. Carrott and Suhas: Low-cost adsorbents: growing approach to wastewater treatmenta review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Tecnol. 39, 783 (2009).
G. Rios, C. Pazos, and J. Coca: Destabilization of cutting oil emulsions using inorganic salts as coagulants. Colloid Surface A 138, 383 (1998).
L.F. Song: Flux decline in crossflow microfiltration and ultrafiltration: mechanisms and modeling of membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 139, 183 (1998).
J. Kong and K. Li: Oil removal from oil-in-water emulsions using PVDF membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 16, 83 (1999).
M. Kai, K. Ishii, H. Tsugaya, and T. Miyano: Development of polyether sulfone ultrafiltration membranes. In Reverse Osmosis and Ultrafiltration, edited by S. Sourirajan and T. Matsuura; ACS Symposium Series (ACS Publications, Washington, DC, 1985), pp. 21–33.
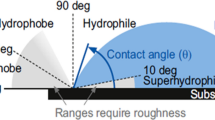
A.K. Kota, W. Choi, and A. Tuteja: Superomniphobic surfaces: design and durability. MRS Bull. 38, 383 (2013).
T. Young: An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 95, 65 (1805).
A. Tuteja, W. Choi, M.L. Ma, J.M. Mabry, S.A. Mazzella, G.C. Rutledge, G.H. McKinley, and R.E. Cohen: Designing superoleophobic surfaces. Science 318, 1618 (2007).
X.J. Feng and L. Jiang: Design and creation of superwetting/antiwetting surfaces. Adv. Mater. 18, 3063 (2006).
A.K. Kota, G. Kwon, and A. Tuteja: The design and applications of superomniphobic surfaces. NPG Asia Mater. 6, e109 (2014).
R.N. Wenzel: Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 28, 988 (1936).
A.B.D. Cassie and S. Baxter: Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 40, 0546 (1944).
W. Choi, A. Tuteja, J.M. Mabry, R.E. Cohen, and G.H. McKinley: A modified Cassie-Baxter relationship to explain contact angle hysteresis and anisotropy on non-wetting textured surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 339, 208 (2009).
R. Johnson and R. Dettre: Wettability and contact angles. Surface Colloid Sci. 2, 85 (1969).
D. Quere: Rough ideas on wetting. Physica A 313, 32 (2002).
G. McHale, N.J. Shirtcliffe, and M.I. Newton: Contact-angle hysteresis on super-hydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 20, 10146 (2004).
A. Marmur: From hygrophilic to superhygrophobic: theoretical conditions for making high-contact-angle surfaces from low-contact-angle materials. Langmuir 24, 7573 (2008).
A. Marmur: Wetting on hydrophobic rough surfaces: to be heterogeneous or not to be?Langmuir 19, 8343 (2003).
A. Tuteja, W. Choi, J.M. Mabry, G.H. McKinley, and R.E. Cohen: Robust omniphobic surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 18200 (2008).
M. Nosonovsky: Multiscale roughness and stability of superhydrophobic biomimetic interfaces. Langmuir 23, 3157 (2007).
A.K. Kota, G. Kwon, W. Choi, J.M. Mabry, and A. Tuteja: Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil-water separation. Nat Commun 3, 1025 (2012).
G.K. Batchelor: An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics (Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, 2000).
W. Choi, A. Tuteja, S. Chhatre, J.M. Mabry, R.E. Cohen, and G.H. McKinley: Fabrics with tunable oleophobicity. Adv. Mater. 21, 2190 (2009).
A. Tuteja, W.J. Choi, G.H. McKinley, R.E. Cohen, and M.F. Rubner: Design parameters for superhydrophobicity and superoleophobicity. MRS Bull. 33, 752 (2008).
S.S. Chhatre, W. Choi, A. Tuteja, K.C. Park, J.M. Mabry, G.H. McKinley, and R.E. Cohen: Scale dependence of omniphobic mesh surfaces. Langmuir 26, 4027 (2010).
K. Golovin, D.H. Lee, J.M. Mabry, and A. Tuteja: Transparent, flexible, superomniphobic surfaces with ultra-low contact angle hysteresis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 52, 13007 (2013).
R. Hensel, A. Finn, R. Helbig, H.G. Braun, C. Neinhuis, W.J. Fischer, and C. Werner: Biologically inspired omniphobic surfaces by reverse imprint lithography. Adv. Mater. 26, 2029 (2014).
L. Feng, Z.Y. Zhang, Z.H. Mai, Y.M. Ma, B.Q. Liu, L. Jiang, and D.B. Zhu: A super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic coating mesh film for the separation of oil and water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 116, 2046 (2004).
J. Wu, J. Chen, K. Qasim, J. Xia, W. Lei, and B.P. Wang: A hierarchical mesh film with superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties for oil and water separation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 87, 427 (2012).
Q.J. Wang, Z. Cui, Y. Mao, and Q.M. Chen: Stable highly hydrophobic and oleophilic meshes for oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 9054 (2007).
Y.Z. Cao, X.Y. Zhang, L. Tao, K. Li, Z.X. Xue, L. Feng, and Y. Wei: Mussel-inspired chemistry and michael addition reaction for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 5, 4438 (2013).
S.T. Wang, Y.L. Song, and L. Jiang: Microscale and nanoscale hierarchical structured mesh films with superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties induced by long-chain fatty acids. Nanotechnology 18, 015103 (2007).
B. Wang and Z.G. Guo: Superhydrophobic copper mesh films with rapid oil/water separation properties by electrochemical deposition inspired from butterfly wing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 063704 (2013).
C.X. Wang, T.J. Yao, J. Wu, C. Ma, Z.X. Fan, Z.Y. Wang, Y.R. Cheng, Q. Lin, and B. Yang: Facile approach in fabricating superhydrophobic and superoleophilic surface for water and oil mixture separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1, 2613 (2009).
N. Liu, Y.Z. Cao, X. Lin, Y.N. Chen, L. Feng, and Y. Wei: A facile solvent-manipulated mesh for reversible oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 12821 (2014).
C.R. Crick, J.A. Gibbins, and I.P. Parkin: Superhydrophobic polymer-coated copper-mesh; membranes for highly efficient oil-water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 5943 (2013).
Y.W. Shang, Y. Si, A. Raza, L.P. Yang, X. Mao, B. Ding, and J.Y. Yu: An in situ polymerization approach for the synthesis of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes for oil-water separation. Nanoscale 4, 7847 (2012).
X.M. Tang, Y. Si, J.L. Ge, B. Ding, L.F. Liu, G. Zheng, W.J. Luo, and J.Y. Yu: In situ polymerized superhydrophobic and superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes for gravity driven oil-water separation. Nanoscale 5, 11657 (2013).
M.L. Huang, Y. Si, X.M. Tang, Z.G. Zhu, B. Ding, L.F. Liu, G. Zheng, W.J. Luo, and J.Y. Yu: Gravity driven separation of emulsified oil-water mixtures utilizing in situ polymerized superhydrophobic and superoleophilic nanofibrous membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 14071 (2013).
W.B. Zhang, Z. Shi, F. Zhang, X. Liu, J. Jin, and L. Jiang: Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic PVDF membranes for effective separation of water-in-oil emulsions with high flux. Adv. Mater. 25, 2071 (2013).
S.H. Wang, M. Li, and Q.H. Lu: Filter paper with selective absorption and separation of liquids that differ in surface tension. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 677 (2010).
C. Du, J.D. Wang, Z.F. Chen, and D.R. Chen: Durable superhydrophobic and superoleophilic filter paper for oil-water separation prepared by a colloidal deposition method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 313, 304 (2014).
A. Asthana, T. Maitra, R. Buchel, M.K. Tiwari, and D. Poulikakos: Multifunctional superhydrophobic polymer/carbon nanocomposites: graphene, carbon nanotubes, or carbon black?ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 8859 (2014).
Z. Shi, W.B. Zhang, F. Zhang, X. Liu, D. Wang, J. Jin, and L. Jiang: Ultrafast separation of emulsified oil/water mixtures by ultrathin free-standing single-walled carbon nanotube network films. Adv. Mater. 25, 2422 (2013).
J.P. Zhang and S. Seeger: Polyester materials with superwetting silicone nanofilaments for oil/water separation and selective oil absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21, 4699 (2011).
J. Li, L. Shi, Y. Chen, Y.B. Zhang, Z.G. Guo, B.L. Su, and W.M. Liu: Stable superhydrophobic coatings from thiol-ligand nanocrystals and their application in oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 9774 (2012).
M.N. Kavalenka, A. Hopf, M. Schneider, M. Worgull, and H. Holscher: Wood-based microhaired superhydrophobic and underwater superoleophobic surfaces for oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 4, 31079 (2014).
A. Maartens, E.P. Jacobs, and P. Swart: UF of pulp and paper effluent: membrane fouling-prevention and cleaning. J. Membr. Sci. 209, 81 (2002).
B. Hu and K. Scott: Influence of membrane material and corrugation and process conditions on emulsion microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 294, 30 (2007).
M.J. Liu, S.T. Wang, Z.X. Wei, Y.L. Song, and L. Jiang: Bioinspired design of a superoleophobic and low adhesive water/solid interface. Adv. Mater. 21, 665 (2009).
Z.X. Xue, M.J. Liu, and L. Jiang: Recent developments in polymeric superoleophobic surfaces. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 50, 1209 (2012).
Z.X. Xue, S.T. Wang, L. Lin, L. Chen, M.J. Liu, L. Feng, and L. Jiang: A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 23, 4270 (2011).
C. Teng, X. Lu, G. Ren, Y. Zhu, M. Wan, and L. Jiang: Underwater self-cleaning PEDOT-PSS hydrogel mesh for effective separation of corrosive and hot oil/water mixtures. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 1, 1400099 (2014).
S.Y. Zhang, F. Lu, L. Tao, N. Liu, C.R. Gao, L. Feng, and Y. Wei: Bio-inspired anti-oil-fouling chitosan-coated mesh for oil/water separation suitable for broad ph range and hyper-saline environments. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 5, 11971 (2013).
F. Lu, Y.N. Chen, N. Liu, Y.Z. Cao, L.X. Xu, Y. Wei, and L. Feng: A fast and convenient cellulose hydrogel-coated colander for high-efficiency oil-water separation. RSC Adv. 4, 32544 (2014).
B.X. Jing, H.T. Wang, K.Y. Lin, P.J. McGinn, C.Z. Na, and Y.X. Zhu: A facile method to functionalize engineering solid membrane supports for rapid and efficient oil-water separation. Polymer 54, 5771 (2013).
Y. Dong, J. Li, L. Shi, X.B. Wang, Z.G. Guo, and W.M. Liu: Underwater superoleophobic graphene oxide coated meshes for the separation of oil and water. Chem. Commun. 50, 5586 (2014).
Q. Wen, J.C. Di, L. Jiang, J.H. Yu, and R.R. Xu: Zeolite-coated mesh film for efficient oil-water separation. Chem. Sci. 4, 591 (2013).
J.W. Zeng and Z.G. Guo: Superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic MFI zeolite-coated film for oil/water separation. Colloid Surf. A 444, 283 (2014).
N. Liu, Y.N. Chen, F. Lu, Y.Z. Cao, Z.X. Xue, K. Li, L. Feng, and Y. Wei: Straightforward oxidation of a copper substrate produces an underwater superoleophobic mesh for oil/water separation. Chemphyschem 14, 3489 (2013).
Y.Z. Zhu, F. Zhang, D. Wang, X.F. Pei, W.B. Zhang, and J. Jin: A novel zwitterionic polyelectrolyte grafted PVDF membrane for thoroughly separating oil from water with ultrahigh efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 5758 (2013).
P.C. Chen and Z.K. Xu: Mineral-coated polymer membranes with superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity for effective oil/water separation. Sci. Rep. -UK 3, 2776 (2013).
H.C. Yang, K.J. Liao, H. Huang, Q.Y. Wu, L.S. Wan, and Z.K. Xu: Mussel-inspired modification of a polymer membrane for ultra-high water permeability and oil-in-water emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 10225 (2014).
H.C. Yang, J.K. Pi, K.J. Liao, H. Huang, Q.Y. Wu, X.J. Huang, and Z.K. Xu: Silica-decorated polypropylene microfiltration membranes with a mussel-inspired intermediate layer for oil-in-water emulsion separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 12566 (2014).
F.E. Ahmed, B.S. Lalia, N. Hilal, and R. Hashaikeh: Underwater superoleophobic cellulose/electrospun PVDF-HFP membranes for efficient oil/water separation. Desalination 344, 48 (2014).
A. Raza, B. Ding, G. Zainab, M. El-Newehy, S.S. Al-Deyab, and J.Y. Yu: In situ cross-linked superwetting nanofibrous membranes for ultrafast oil-water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 10137 (2014).
Q.S. Liu, A.A. Patel, and L.Y. Liu: Superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate)-grafted glass fiber filters for oil-water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 8996 (2014).
Y.N. Chen, Z.X. Xue, N. Liu, F. Lu, Y.Z. Cao, Z.X. Sun, and L. Feng: Fabrication of a silica gel coated quartz fiber mesh for oil-water separation under strong acidic and concentrated salt conditions. RSC Adv. 4, 11447 (2014).
J. Yang, Z.Z. Zhang, X.H. Xu, X.T. Zhu, X.H. Men, and X.Y. Zhou: Superhydrophilic-superoleophobic coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 2834 (2012).
J.A. Howarter and J.P. Youngblood: Self-cleaning and anti-fog surfaces via stimuli-responsive polymer brushes. Adv. Mater. 19, 3838 (2007).
L.B. Zhang, Y.J. Zhong, D. Cha, and P. Wang: A self-cleaning underwater superoleophobic mesh for oil-water separation. Sci. Rep. - UK 3, 2326 (2013).
P. Gao, Z.Y. Liu, D.D. Sun, and W.J. Ng: The efficient separation of surfactant-stabilized oil-water emulsions with a flexible and superhydrophilic graphene-TiO2 composite membrane. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 14082 (2014).
Y. Sawai, S. Nishimoto, Y. Kameshima, E. Fujii, and M. Miyake: Photoinduced underwater superoleophobicity of TiO2 thin films. Langmuir 29, 6784 (2013).
J. Yang, H.J. Song, X.H. Yan, H. Tang, and C.S. Li: Superhydrophilic and superoleophobic chitosan-based nanocomposite coatings for oil/water separation. Cellulose 21, 1851 (2014).
X.Y. Zhu, H.E. Loo, and R.B. Bai: A novel membrane showing both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties and its non-fouling performances for potential water treatment applications. J. Membr. Sci. 436, 47 (2013).
X.Y. Zhu, W.T. Tu, K.H. Wee, and R.B. Bai: Effective and low fouling oil/water separation by a novel hollow fiber membrane with both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties. J. Membr. Sci. 466, 36 (2014).
J.A. Howarter and J.P. Youngblood: Amphiphile grafted membranes for the separation of oil-in-water dispersions. J. ColloidInterface Sci. 329, 127 (2009).
H. Yoon, S.H. Na, J.Y. Choi, S.S. Latthe, M.T. Swihart, S.S. Al-Deyab, and S.S. Yoon: Gravity-driven hybrid membrane for oleophobic-superhydrophilic oil-water separation and water purification by graphene. Langmuir 30, 11761 (2014).
B. Berge: Electrocapillarity and wetting of insulator films by water. C. R. Acad. Sci. II 317, 157 (1993).
G. Kwon, A.K. Kota, Y.X. Li, A. Sohani, J.M. Mabry, and A. Tuteja: On-demand separation of oil-water mixtures. Adv. Mater. 24, 3666 (2012).
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Ki-Han Kim and the Office of Naval Research (ONR) for financial support under grant N00014-12-1-0874. We also thank Dr. Charles Y. Lee and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR) for financial support under grant FA9550-10-1-0523. We also thank the National Science Foundation and the Nanomanufacturing program for supporting this work through grant no. 1351412. EP would like to acknowledge support through the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship under Grant No. DGE 1256260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, G., Post, E. & Tuteja, A. Membranes with selective wettability for the separation of oil-water mixtures. MRS Communications 5, 475–494 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2015.61
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2015.61