Abstract
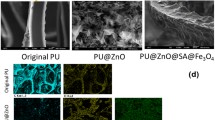
Three-dimensional porous materials with the hydrophobic/oleophilic surface have attracted significant interest in the fields of oil/water separation. In this paper, superhydrophobic magnetic polyurethane sponge was fabricated by the self-polymerization of dopamine to bind the Fe3O4 nanoparticles tightly on the sponge and then soaking in cheap stearic acid aqueous solution. The obtained sponge has the superhydrophobic property and good magnetic property. The surface structure, composition, and properties of the modified sponges were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectrometer, Fourier-transform infrared spectrum, and water contact angle (WCA) measurements. The as-prepared superhydrophobic magnetic sponge was able to collect a wide range of oils and organic solvents from oil–water mixture with an absorption capacity up to 16–60 times of its own weight. Under an external magnetic field, it can be guided to a designated area. In addition, combined with the vacuum system, continuous oil separation can be carried out, which is of great significance for removing a good deal of dirty oil on the water surface. Furthermore, the WCA of sponge remains above 141°, and the oil absorption is basically unchanged through repeated cyclic experiments.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Liu, F. Sun, and Q. Pan: Highly compressible and stretchable superhydrophobic coating inspired by bio-adhesion of marine mussels. J. Mater. Chem. 6, 11365–11371 (2014).
J. Wang, H. Wang, and G. Geng: Highly efficient oil-in-water emulsion and oil layer/water mixture separation based on durably superhydrophobic sponge prepared via a facile route. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 127, 108 (2018).
H. Gao, P. Sun, Y. Zhang, X. Zeng, D. Wang, Y. Zhang, W. Wang, and J. Wu: A two-step hydrophobic fabrication of melamine sponge for oil absorption and oil/water separation. Surf. Coat. Tech. 339, 147–154 (2018).
X. Chen, A. Justin, and V.S. Garimella: Continuous oil−water separation using polydimethylsiloxane-functionalized melamine sponge. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 3596–3602 (2016).
T. Yan, X. Chen, T. Zhang, J. Yu, X. Jiang, W. Hu, and F. Jiao: A magnetic pH-induced textile fabric with switchable wettability for intelligent oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 347, 52–63 (2018).
J.D. Wu, C. Zhang, and D.J. Jiang: Self-cleaning pH/thermo-responsive cotton fabric with smart-control and reusable functions for oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 6, 24076–24082 (2016).
F. Qiang, L. Hu, L. Gong, L. Zhao, S. Li, and L. Tang: Facile synthesis of super-hydrophobic, electrically conductive and mechanically flexible functionalized graphene nanoribbon/polyurethane sponge for efficient oil/water separation at static and dynamic states. Chem. Eng. J. 334, 2154–2166 (2018).
C. Xia, Y. Li, T. Fei, and W. Gong: Facile one-pot synthesis of superhydrophobic reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge at the presence of ethanol for oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 345, 314–321 (2018).
J. Li, Y. Chen, J. Gao, Z. Zuo, Y. Li, and Y. Li: Graphdiyne sponge for direct collection of oils from water. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 201–204 (2018).
C. Su, H. Yang, S. Song, B. Lu, and R. Chen: A magnetic superhydrophilic/oleophobic sponge for continuous oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 309, 413–426 (2017).
L. Wu, L. Li, and B. Li: Magnetic, durable, and superhydrophobic polyurethane@Fe3O4@SiO2@fluoropolymer sponges for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 4936–4946 (2015).
F. Beshkar, H. Khojasteh, and M. Salavati-Niasari: Recyclable magnetic superhydrophobic straw soot sponge for highly efficient oil/water separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 497, 57–65 (2017).
L. Liu, J. Lei, L. Li, R. Zhang, N. Mi, H. Chen, D. Huang, and N. Li: A facile method to fabricate the superhydrophobic magnetic sponge for oil-water separation. Mater. Lett. 195, 66–70 (2017).
J. Dai, R. Zhang, W. Ge, A. Xie, Z. Chang, S. Tian, Z. Zhou, and Y. Yan: 3D macroscopic superhydrophobic magnetic porous carbon aerogel converted from biorenewable popcorn for selective oil-water separation. Mater. Design 139, 122–131 (2018).
J. Wang, G. Geng, X. Liu, F. Han, and J. Xu: Magnetically superhydrophobic kapok fiber for selective sorption and continuous separation of oil from water. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 137, 360–365 (2016).
H. Peng, H. Wang, and J. Wu: Preparation of superhydrophobic magnetic cellulose sponge for removing oil from water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55, 832–838 (2016).
Y. Ito, A. Miyazaki, K. Takai, V. Sivamurugan, T. Maeno, T. Kadono, M. Kitano, Y. Ogawa, N. Nakamura, M. Hara, S. Valiyaveettil, and T. Enoki: Magnetic sponge prepared with an alkanedithiol-bridged network of nanomagnets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 11470–11473 (2011).
M. Wriedt, A.A. Yakovenko, G.J. Halder, A.V. Prosvirin, K.R. Dunbar, and H.-C. Zhou: Reversible switching from antiferro- to ferromagnetic behavior by solvent-mediated, thermally-induced phase transitions in a trimorphic MOF-based magnetic sponge system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 4040–4050 (2013).
A.V. Dudchenko, J. Rolf, L. Shi, L. Olivas, W. Duan, and D. Jassby: Coupling underwater superoleophobic membranes with magnetic pickering emulsions for fouling-free separation of crude oil/water mixtures: An experimental and theoretical study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 9, 9930–9941 (2015).
H. Mi, X. Jing, H. Xie, H. Huang, and L. Turng: Magnetically driven superhydrophobic silica sponge decorated with hierarchical cobalt nanoparticles for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 337, 69–81 (2018).
H. Meng, T. Yan, J. Yu, and F. Jiao: Super-hydrophobic and super-lipophilic functionalized graphene oxide/polyurethane sponge applied for oil/water separation. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 26, 501–503 (2018).
Z. Li, B. Lin, L. Jiang, E. Lin, J. Chen, S. Zhang, Y. Tang, F. He, and D. Li: Effective preparation of magnetic superhydrophobic Fe3O4/PU sponge for oil-water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 427, 56–64 (2018).
Y. Wu, S. Xue, H. Yang, H. Zhang, T. Zhang, and S. Gou: Polymerization-induced phase separation for the fabrication of magnetic sponges for oil spill reclamation. Chem. Eng. J. 328, 23–34 (2017).
L. Zhang, L. Li, and Z. Dang: Bio-inspired durable, superhydrophobic magnetic particles for oil/water separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 463, 168–179 (2016).
Q. Zhu and Q. Pan: Mussel-inspired direct immobilization of nanoparticles and application for oil–water separation. ACS Nano. 8, 1402–1409 (2014).
M. Khosravi and S. Azizian: Synthesis of a novel highly oleophilic and highly hydrophobic sponge for rapid oil spill cleanup. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 25326–25333 (2015).
S. Kabiri, D.N.H. Tran, and Altalhi: Outstanding adsorption performance of graphene–carbon nanotube aerogels for continuous oil removal. Carbon 80, 523–533 (2014).
S. Liu, Q. Xu, S. Latthe, A. Gurav, and R. Xing: Superhydrophobic/superoleophilic magnetic polyurethane sponge for oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 5, 68293–68298 (2015).
Y. Xu, F. You, H. Sun, and L. Shao: Realizing mussel-inspired polydopamine selective layer with strong solvent resistance in nanofiltration towards sustanable reclamation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 3, 35–38 (2017).
Z. Wang, X. Jiang, X. Cheng, C. Lan, and L. Shao: Mussel-inspired hybrid coatings that transform membrane hydrophobicity into high hydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity for oil-in-water emulsion separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 9534–9545 (2015).
B. Ge, X. Zhu, Y. Li, X. Men, P. Li, and Z. Zhang: Versatile fabrication of magnetic superhydrophobic foams and application for oil–water separation. Colloids Surf. A 482, 1509–1517 (2015).
N. Zhang, W. Jiang, and T. Wang: Facile preparation of magnetic poly(styrene-divinylbenzene) foam and its application as an oil absorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54, 11033–11039 (2015).
B. Liu, L. Zhang, H. Wang, and Z. Bia: Preparation of MCC/MC silica sponge and its oil/water separation apparatus application. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 4, 5795–5801 (2017).
J. Wang and Y. Zheng: Oil/water mixtures and emulsions separation of stearic acid-functionalized sponge fabricated via a facile one-step coating method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 181, 148–157 (2017).
Q. Cheng, X. An, Y. Li, C. Huang, and J. Zeng: Sustainable and biodegradable superhydrophobic coating from epoxidized soybean oil and ZnO nanoparticles on cellulosic substrates for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 10, 11440–11450 (2017).
A. Banerjee, R. Gokhale, and S. Bhatnagar: MOF derived porous carbon-Fe3O4 nanocomposite as a high performance, recyclable environmental superadsorbent. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 19694–19699 (2017).
J. Zhang, Y. Shao, C. Hsieh, Y. Chen, T. Su, J. Hsu, and R. Juang: Synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles onto fluorinated carbon fabrics for contaminant removal and oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 147, 312–319 (2017).
S. Zhang, T. Lü, D. Qi, Z. Cao, D. Zhang, and H. Zhao: Synthesis of quaternized chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles for oil-water separation. Mater. Lett. 5, 128–131 (2016).
O. Guselnikova, A. Barras, A. Addad, E. Sviridova, S. Szunerits, P. Postnikov, and R. Boukherroub: Magnetic polyurethane sponge for efficient oil adsorption and separation of oil from oil-in-water emulsions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 240, 116627 (2020).
J.J. Li, Y.N. Zhou, and Z.H. Luo: Mussel-inspired V-shaped copolymer coating for intelligent oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 322, 693–701 (2017).
S. Rella, E. Mazzotta, A. Caroli, M. De Luca, C. Bucci, and C. Malitesta: Investigation of polydopamine coatings by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy as an effective tool for improving biomolecule conjugation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 447, 31–39 (2018).
S.W. Li, Y.J. Zheng, Z.Y. Qi, X.H. Li, and C.F. Chen: Thermal behavior of self-assembled stearic acid monolayers on sapphire surface. Phys. Procedia 85, 41–46 (2016).
R. Du, Q. Zhao, P. Li, H. Ren, X. Gao, and J. Zhang: Ultrathermostable, magnetic-driven, and superhydrophobic quartz fibers for water remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 1025–1032 (2015).
Y. Yu, H. Chen, Y. Liu, and Z. Lai: Selective separation of oil and water with mesh membranes by capillarity. Adv. Colloid Interfaces 235, 46–55 (2016).
Z. Wang, X. Yang, Z. Cheng, Y. Liu, L. Shao, and L. Jiang: Simply realizing “water diode janus” membranes for multifunctional smart applications. Chem. Eng. J. 4, 57–65 (2017).
S. Zhou, W. Jiang, T. Wang, and H. Hydrophobic: Highly hydrophobic, compressible, and magnetic polystyrene/Fe3O4/graphene aerogel composite for oil–water separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54, 5460–5467 (2015).
V. Pham and J. Dickerson: Superhydrophobic silanized melamine sponges as high efficiency oil absorbent materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 14181–14188 (2014).
X. Wang, Y. Shi, W.R. Graff, D. Lee, and H. Gao: Developing recyclable pH-responsive magnetic nanoparticles for oil–water separation. Polymer 72, 12–19 (2015).
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support from the Natural Science Fund Project of Gansu Province, China (18JR3RA109) and the Foundation of a Hundred Youth Talents Training Program of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, C., Liu, H., Su, S. et al. Preparation of superhydrophobic magnetic stearic acid polyurethane sponge for oil–water separation. Journal of Materials Research 35, 2925–2935 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.260
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2020.260