Abstract
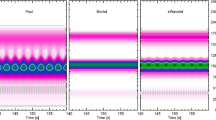
We use wavelet transform-based multi-scale analysis to identify localized structures in pseudorapidity space in high-energy nuclear collisions of \(^{16}\)O–Ag/Br and \(^{32}\)S–Ag/Br at 60A GeV and 200A GeV, respectively. Our analysis specifically focuses on ring-like and jet-like events and incorporate simulation models such as FRITIOF, UrQMD, and AMPT. Comparing experimental and simulated data, it is evidently found that the data obtained through different models reproduce the coarse features of the high-energy experiments but with minute differences. The absence of certain irregularities in the simulated data may be due to higher statistics in the simulations resulting in smoother distributions. We also observed distinct differences between experimentally observed ring-like and jet-like events, confirming their different origins. Our findings suggest that this approach is one of the most promising way to investigate the complex dynamics of high-energy nuclear collisions.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: In this paper, the simulated data have been generated using the FRITIOF model, the UrQMD model, and AMPT model simulation method. All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article. The experimental data used in the present study were published by EPL [42, 62] and is available at, https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/80/22003, and https://doi.org/10.1209/epl/i2003-10104-5.]
References
G. Roland, K. Šafařík, P. Steinberg, Heavy-ion collisions at the LHC. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 77, 70–127 (2014)
J. Adams et al., Experimental and theoretical challenges in the search for the quark-gluon plasma: the STAR Collaboration’s critical assessment of the evidence from RHIC collisions. Nucl. Phys. A 757(1–2), 102–183 (2005)
K. Adcox et al., Formation of dense partonic matter in relativistic nucleus–nucleus collisions at RHIC: experimental evaluation by the PHENIX collaboration. Nucl. Phys. A 757, 184–283 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2005.03.086. arXiv:arXiv:nucl-ex/0410003 [nucl-ex]
M. Gyulassy, L. McLerran, New forms of QCD matter discovered at RHIC. Nucl. Phys. A 750(1), 30–63 (2005)
I. Dremin, Ring-like events: Cherenkov gluons or Mach waves? Nucl. Phys. A 767, 233–247 (2006)
D. Ghosh, A. Deb, P.K. Haldar, S. Guptaroy, Azimuthal pion fluctuation and phase transition in ultra-relativistic ring-like and jet-like events. Indian J. Phys. 80, 807–813 (2006)
B. Ali, S. Singh, A. Chandra, S. Ahmad, Event-by-event multiplicity fluctuations and correlations in ring-like and jet-like events in 197Au-AgBr collisions at 11.6 A GeV/C. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 32(03n04), 2350018 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218301323500180
P.K. Haldar, S.K. Manna, P. Saha, D. Ghosh, Non-statistical fluctuations of pions for ring-and jet-like events at CERN SPS energy—an in-depth analysis with factorial correlator. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 20(09), 2027–2038 (2011)
D. Ghosh, A. Deb, P.K. Haldar, S. Guptaroy, Fluctuation and fractal characteristics of ring like and jet like events produced at SPS energies. Indian J. Phys. 82, 1339–1371 (2008)
D. Ghosh et al., Ring type events and nuclear collision at SPS energies and nuclear refractive index. Acta Phys. Pol. B 40(8), 2355–2361 (2009)
M. Ghosha, P. Haldarb, S. Mannab, A. Mukhopadhyaya, G. Singhc, Ring and jet-like structures and two-dimensional intermittency in nucleus–nucleus collisions at 200 AGeV/C. Nucl. Phys. A 858, 67–85 (2011)
J. Takahashi et al., Topology studies of hydrodynamics using two-particle correlation analysis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103(24), 242301 (2009)
J. Casalderrey-Solana et al., Angular structure of jet quenching within a hybrid strong/weak coupling model. J. High Energy Phys. 2017(3), 1–69 (2017)
H. Appelshäuser et al., Event-by-event fluctuations of average transverse momentum in central Pb+ Pb collisions at 158 GeV per nucleon. Phys. Lett. B 459(4), 679–686 (1999)
F. Sikler et al., Hadron production in nuclear collisions from the NA49 experiment at 158 GeV/C A. Nucl. Phys. A 661(1–4), 45–54 (1999)
C. Roland, N. Collaboration et al., Event-by-event fluctuations of particle ratios in central Pb+ Pb collisions at 20–158 A GeV. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 30(8), 1381 (2004)
M. Cherry et al., Event-by-event analysis of high multiplicity Pb (158 GeV/nucleon)-Ag/Br collisions. Acta Phys. Pol. Ser. B 29, 2129–2146 (1998)
W.M. Alberico, A. Lavagno, P. Quarati, Non-extensive statistics, fluctuations and correlations in high-energy nuclear collisions. Eur. Phys. J. C Part. Fields 12, 499–506 (2000)
C. Bignamini, F. Becattini, F. Piccinini, A Monte-Carlo generator for statistical hadronization in high energy e+ e− collisions. Eur. Phys. J. C 72, 1–18 (2012)
Y. Yariv, Z. Fraenkel, Intranuclear cascade calculation of high energy heavy ion collisions: effect of interactions between cascade particles. Phys. Rev. C 24(2), 488 (1981)
G. Bertsch, J. Cugnon, Entropy production in high energy collisions. Phys. Rev. C 24(6), 2514 (1981)
S.A. Voloshin, Transverse radial expansion in nuclear collisions and two particle correlations. Phys. Lett. B 632(4), 490–494 (2006)
A. Dumitru, J. Jalilian-Marian, Two-particle correlations in high-energy collisions and the gluon four-point function. Phys. Rev. D 81(9), 094015 (2010)
S. Catani et al., Longitudinally-invariant k⊥-clustering algorithms for hadron–hadron collisions. Nucl. Phys. B 406(1–2), 187–224 (1993)
I. Daubechies, J.C. Lagarias, Two-scale difference equations II. Local regularity, infinite products of matrices and fractals. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 23(4), 1031–1079 (1992)
Y. Meyer, Progress in wavelet analysis and applications, wavelets: their past and their future. Prog. Wavel. Anal. Appl. 11, 9–18 (1993)
N. Astaf’Eva, Wavelet analysis: basic theory and some applications. Phys. USPEKHI 39(11), 1085 (1996)
I.M. Dremin, O.V. Ivanov, V.A. Nechitailo, Wavelets and their uses. Phys. USPEKHI 44(5), 447 (2001)
J. van den Berg, Wavelets in physics provided by the SAO/NASA astrophysics data system (2004)
A. Kumar, M.H. Kolekar, Machine learning approach for epileptic seizure detection using wavelet analysis of EEG signals, in 2014 International Conference on Medical Imaging, m-Health and Emerging Communication Systems (MedCom) (IEEE, 2014), pp. 412–416
P. Kumar, E. Foufoula-Georgiou, Wavelet analysis for geophysical applications. Rev. Geophys. 35(4), 385–412 (1997)
W. Greiner, H. Stöcker, A. Gallmann, Hot and Dense Nuclear Matter 335 (2012)
P. Lipa, M. Greiner, P. Carruthers, Wavelet analysis of multiparticle correlations, in Soft Physics and Fluctuations-Proceedings of the Cracow Workshop on Multiparticle Production (World Scientific, 1994), p. 105
M. Greiner et al., Wavelet correlations in hierarchical branching processes. Z. Phys. C Part. Fields 69, 305–321 (1995)
N. Suzuki, M. Biyajima, A. Ohsawa, Wavelet spectra of JACEE events. Prog. Theor. Phys. 94(1), 91–103 (1995)
D.-W. Huang, Wavelet analysis in multiplicity fluctuations. Phys. Rev. D 56(7), 3961 (1997)
Z. Huang et al., Domain structure of a disoriented chiral condensate from a wavelet perspective. Phys. Rev. D 54(1), 750 (1996)
I.M. Dremin, Long-range particle correlations and wavelets. Phys. USPEKHI 43(11), 1137 (2000)
I. Dremin et al., Wavelet patterns in nucleus–nucleus collisions at 158A GeV. Phys. Lett. B 499(1–2), 97–103 (2001)
V. Uzhinsky et al., Wavelet analysis of angular distributions of secondary particles in high-energy nucleus–nucleus interactions: irregularity of particle pseudorapidity distributions. Phys. At. Nuclei 67, 156–162 (2004)
J. Fedorišin, S. Vokál, Wavelet analysis of multiparticle correlations. FIZIKA B 17(2), 273–278 (2008)
D. Ghosh, A. Deb, P. Haldar, S. Sahoo, D. Maity, Validity of the negative binomial multiplicity distribution in case of ultra-relativistic nucleus–nucleus interaction in different azimuthal bins. Europhys. Lett. 65(3), 311 (2004)
M. Adamovich et al., On the jet-like and ring-like substructure in distributions of produced particles in central heavy-ion collisions at ultra-relativistic energies. J. Phys. G 19(LUNFD–6–NFFK–713), 2035–2044 (1993)
D. Ghosh, A. Deb, A. Dhar, R. Saha, D. Bhattacharya, P.K. Haldar, Levy index analysis for a multifractality and phase transition study of target fragments in ring-like and jet-like events. Phys. Scr. 82(4), 045201 (2010)
M. Ghosh, P. Haldar, S. Manna, A. Mukhopadhyay, G. Singh, Ring and jet-like structures and two-dimensional intermittency in nucleus–nucleus collisions at 200 AGeV/C. Nucl. Phys. A 858(1), 67–85 (2011)
I. Dremin, Coherent hadron radiation at extremely high energies. ZhETF Pisma Redaktsiiu 30, 152–156 (1979)
I. Dremin, L. Sarycheva, K.Y. Teplov, High energy Cherenkov gluons at RHIC and LHC. Eur. Phys. J. C Part. Fields 46, 429–432 (2006)
I. Dremin, L. Sarycheva, K.Y. Teplov, The background for Cherenkov gluons at RHIC and LHC energies (2005). arXiv preprint arXiv:hep-ph/0510248
J. Adams et al., Distributions of charged hadrons associated with high transverse momentum particles in pp and Au + Au collisions at S(NN)**(1/2) = 200-GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 152301 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.152301. arXiv:arXiv:nucl-ex/0501016
S.S. Adler et al., Dense-medium modifications to jet-induced hadron pair distributions in Au + Au collisions at S(NN)**(1/2) = 200-GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 052301 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.052301. arXiv:arXiv:nucl-ex/0507004
B.I. Abelev et al., Indications of conical emission of charged hadrons at RHIC. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 052302 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.052302. arXiv:arXiv:0805.0622 [nucl-ex]
J. Adams et al., Azimuthal anisotropy in Au+ Au collisions at S(NN) = 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. C 72(1), 014904 (2005)
S.S. Adler et al., Systematic studies of the centrality and s NN dependence of the dET/dη and dNch/dη in heavy ion collisions at midrapidity. Phys. Rev. C 71(3), 034908 (2005)
S. Adler et al., J/ψ production from proton–proton collisions at s= 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(5), 051802 (2004)
B. Abelev et al., Centrality dependence of charged hadron and strange hadron elliptic flow from s NN = 200 GeV Au+ Au collisions. Phys. Rev. C 77(5), 054901 (2008)
J. Adams et al., Event-wise< p t> fluctuations in Au–Au collisions at s NN = 130 GeV. Phys. Rev. C 71(6), 064906 (2005)
S. Adler et al., Centrality dependence of charm production from a measurement of single electrons in Au+ Au collisions at s NN = 200 GeV. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(8), 082301 (2005)
B.I. Abelev, Charge independent (CI) and charge dependent (CD) correlations vs. centrality from ΔΔϕη charged pairs in minimum bias Au + Au collisions at 200 GeV (2008)
J. Fedorisin, S. Vokál, Search for the ring-like structures in the emission of secondary particles in central 197 Au collisions with emulsion nuclei at 11.6 A GeV/c. Technical report, Veksler and Baldin Laboratory of High Energies (2008)
J. Fedorisin, S. Vokal, Wavelet analysis of angular spectra of relativistic particles in 208 Pb induced collisions with emulsion nuclei at 158A GeV/c. Technical report, Veksler and Baldin Laboratory of High Energies (2008)
I. Dremin, From e+e to Heavy Ion Collisions-Proceedings of the Xxx International Symposium on Multiparticle Dynamics, Status of Ring-like Correlations and Wavelets (World Scientific, 2001)
D. Ghosh, A. Deb, P.K. Haldar, A. Dhar, Pronounced pionic self-similarity in ring-like events in 16O–AgBr interactions. Europhys. Lett. 80(2), 22003 (2007)
P.K. Haldar, S.K. Manna, Factorial correlators and oscillatory multiplicity moments at the CERN SPS energy for ring-like and jet-like events. Chin. Phys. Lett. 28(1), 012502 (2011)
N. Subba, A. Ahmed, P.K. Haldar, A.N. Tawfik, Pronounced fluctuations of pions in ring-like events in 16O–Ag/Br interactions at 60 A GeV/C in the framework of complex network analysis. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 30(01), 2150002 (2021)
M. Gyulassy, L. McLerran, New forms of QCD matter discovered at RHIC. Nucl. Phys. A 750, 30–63 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2004.10.034. arXiv:arXiv:nucl-th/0405013 [nucl-th]
P. Jacobs, X.-N. Wang, Matter in extremis: ultrarelativistic nuclear collisions at RHIC. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 54, 443–534 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppnp.2004.09.001. arXiv:arXiv:hep-ph/0405125 [hep-ph]
F. Wang, Novel phenomena in particle correlations in relativistic heavy-ion collisions. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 74, 35–54 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppnp.2013.10.002. arXiv:arXiv:1311.4444 [nucl-ex]
U. Heinz, R. Snellings, Collective flow and viscosity in relativistic heavy-ion collisions. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 63, 123–151 (2013)
J.-Y. Ollitrault, Anisotropy as a signature of transverse collective flow. Phys. Rev. D 46(1), 229 (1992)
M. Connors, C. Nattrass, R. Reed, S. Salur, Jet measurements in heavy ion physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 90(2), 025005 (2018)
T. Sjostrand, The FRITIOF model for very high-energy hadronic collisions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 43(3), 367–389 (1987)
S.A. Bass et al., Microscopic models for ultrarelativistic heavy ion collisions. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 41, 255–369 (1998)
M. Bleicher et al., Relativistic hadron-hadron collisions in the ultra-relativistic quantum molecular dynamics model. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 25(9), 1859 (1999)
Z.-W. Lin, C.M. Ko, B.-A. Li, B. Zhang, S. Pal, Multiphase transport model for relativistic heavy ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 72(6), 064901 (2005)
P.D. Lett, R.N. Watts, C.I. Westbrook, W.D. Phillips, P.L. Gould, H.J. Metcalf, Observation of atoms laser cooled below the doppler limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61(2), 169 (1988)
K. Sengupta, P. Jain, G. Singh, S. Kim, Intermittency in multiparticle production at ultra-relativistic heavy ion collisions. Phys. Lett. B 236(2), 219–223 (1990)
D. Ghosh et al., Signature of void probability scaling in jet-like events in 16o-AgBr interactions at 60 GeV/N. Astropart. Phys. 27(2–3), 127–133 (2007)
P.K. Haldar, S.K. Manna, P. Saha, D. Ghosh, Multidimensional intermittency study of target fragments at CERN SPS energies. Astropart. Phys. 42, 76–85 (2013)
S. Bhattacharyya, M. Haiduc, A.T. Neagu, E. Firu, Different aspects of multiplicity distribution of shower particles in central collisions with AgBr target. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 26(04), 1750016 (2017)
S. Bhattacharyya, M. Haiduc, A.T. Neagu, E. Firu, Target dependence of clan model parameters at Dubna energy-chaotic pion production. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 40(2), 025105 (2013)
C.F. Powell, P.H. Fowler, D.H. Perkins, The study of elementary particles by the photographic method: an account of the principal techniques and discoveries illustrated by an atlas of photomicrographs (1959)
B. Andersson, G. Gustafson, G. Ingelman, T. Sjöstrand, Parton fragmentation and string dynamics. Phys. Rep. 97(2–3), 31–145 (1983)
B. Andersson, G. Gustafson, B. Nilsson-Almqvist, A model for low-Pt hadronic reactions with generalizations to hadron–nucleus and nucleus–nucleus collisions. Nucl. Phys. B 281(1–2), 289–309 (1987)
B. Nilsson-Almqvist, E. Stenlund, Interactions between hadrons and nuclei: the Lund Monte Carlo-FRITIOF version 16. Comput. Phys. Commun. 43(3), 387–397 (1987)
H.-U. Bengtsson, T. Sjöstrand, The Lund Monte Carlo for hadronic processes-Pythia version 4.8. Technical report (Dept. of Theoretical Physics, Lund Univ.(Sweden), 1987)
F. Dominguez, J.-W. Qiu, B.-W. Xiao, F. Yuan, Linearly polarized gluon distributions in the color dipole model. Phys. Rev. D 85(4), 045003 (2012)
X.-N. Wang, M. Gyulassy, Hijing: A Monte Carlo model for multiple jet production in pp, pA, and AA collisions. Phys. Rev. D 44(11), 3501 (1991)
B. Zhang, C.M. Ko, B.-A. Li, Z. Lin, Multiphase transport model for relativistic nuclear collisions. Phys. Rev. C 61(6), 067901 (2000)
Z.-W. Lin, S. Pal, C.M. Ko, B.-A. Li, B. Zhang, Charged particle rapidity distributions at relativistic energies. Phys. Rev. C 64(1), 011902 (2001)
S. Sarkar, P. Mali, A. Mukhopadhyay, Azimuthal anisotropy in particle distribution in a multiphase transport model. Phys. Rev. C 96(2), 024913 (2017)
G. Bhoumik, A. Deb, S. Bhattacharyya, D. Ghosh, A continuous wavelet transform analysis of multiparticle emission data at SPS energies. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 28(3), 1950016 (2019)
L. Zheng, G.-H. Zhang, Y.-F. Liu, Z.-W. Lin, Q.-Y. Shou, Z.-B. Yin, Investigating high energy proton proton collisions with a multi-phase transport model approach based on pythia8 initial conditions. Eur. Phys. J. C 81(8), 755 (2021)
N. Subba et al., R/S analysis on multiparticle production process in nucleus–nucleus collisions at different SPS energies. Bulg. J. Phys. 20(2023), 1–14 (2023)
P. Mali, S. Manna, P. Haldar, A. Mukhopadhyay, G. Singh, Detrended analysis of shower track distribution in nucleus–nucleus interactions at CERN SPS energy. Chaos Solitons Fractals 94, 86–94 (2017)
D. Ghosh, A. Deb, S. Sarkar, P.K. Haldar, Strong self-similar fluctuations of target fragments in ring-like events in ultra-relativistic nuclear collision. Chin. Phys. Lett. 23(11), 2944 (2006)
I. Daubechies, Ten lectures on wavelets (1992) https://epubs.siam.org/doi/pdf/10.1137/1.9781611970104. https://doi.org/10.1137/1.9781611970104
P. Saha, N. Subba, A. Ahmed, P.K. Haldar, Wavelet analysis of produced pions in 24 mg-Ag/Br interactions at 4.5 A GeV/c. Braz. J. Phys. 50, 105–111 (2020)
X. Mi, H. Ren, Z. Ouyang, W. Wei, K. Ma, The use of the Mexican hat and the Morlet wavelets for detection of ecological patterns. Plant Ecol. 179, 1–19 (2005)
C. Torrence, G.P. Compo, A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 79(1), 61–78 (1998)
P. Mali, A. Mukhopadhyay, S. Sarkar, G. Singh, Azimuthal structure of charged particle emission in 28 Si–Ag/Br interaction at 14.5 A GeV and 32 S–Ag/Br interaction at 200A GeV. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 23(05), 1450027 (2014)
G. Kestin, U. Heinz, Hydrodynamic radial and elliptic flow in heavy-ion collisions from AGS to LHC energies. Eur. Phys. J. C 61, 545–552 (2009)
C. Shen, U. Heinz, Collision energy dependence of viscous hydrodynamic flow in relativistic heavy-ion collisions. Phys. Rev. C 85(5), 054902 (2012)
X.-Y. Wu, L.-G. Pang, G.-Y. Qin, X.-N. Wang, Longitudinal fluctuations and decorrelations of anisotropic flows at energies available at the CERN large hadron collider and at the BNL relativistic heavy ion collider. Phys. Rev. C 98(2), 024913 (2018)
B. Alver et al., Charged-particle multiplicity and pseudorapidity distributions measured with the PHOBOS detector in Au + Au, Cu+ Cu, d+ Au, and p+ p collisions at ultrarelativistic energies. Phys. Rev. C 83(2), 024913 (2011)
M. Gyulassy, The QGP discovered at RHIC, in Structure and Dynamics of Elementary Matter, vol. 166, ed. by W. Greiner, M.G. Itkis, J. Reinhardt, M.C. Güçlü (Springer, Dordrecht, 2004), pp.159–182
P.F. Kolb, U. Heinz, Hydrodynamic description of ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions (2004), pp. 634–714
X.-N. Wang, Why the observed jet quenching at RHIC is due to parton energy loss. Phys. Lett. B 579(3–4), 299–308 (2004)
T. Falter, U. Mosel, Hadron formation in high energy photonuclear reactions. Phys. Rev. C 66(2), 024608 (2002)
W. Cassing, K. Gallmeister, C. Greiner, Suppression of high transverse momentum hadrons at RHIC by (pre-) hadronic final state interactions. Nucl. Phys. A 735(1–2), 277–299 (2004)
X.-N. Wang, Discovery of jet quenching and beyond. Nucl. Phys. A 750(1), 98–120 (2005)
D. Enterria, B. Betz, High-pT hadron suppression and jet quenching, in The Physics of the Quark-Gluon Plasma: Introductory Lectures. ed. by S. Sarkar, H. Satz, B. Sinha (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010), pp.285–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02286-9_9
K. Gallmeister, C. Greiner, Z. Xu, Quenching of high p⊥ hadron spectra by hadronic interactions in heavy ion collisions at relativistic energies. Phys. Rev. C 67(4), 044905 (2003)
I. Dremin, G.K. Eyyubova, V. Korotkikh, L. Sarycheva, Two-dimensional discrete wavelet analysis of multiparticle event topology in heavy-ion collisions. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 35(9), 095106 (2008)
I. Dremin, G.K. Eyyubova, V. Korotkikh, L. Sarycheva, Two-dimensional discrete wavelet analysis of multiparticle event topology in heavy ion collisions. Indian J. Phys. 85, 39–44 (2011)
J. Adams et al., Minijet deformation and charge-independent angular correlations on momentum subspace (η, ϕ) in au-au collisions at s nn= 130 gev. Phys. Rev. C 73(6), 064907 (2006)
L. Adamczyk et al., Jet-like correlations with direct-photon and neutral-pion triggers at SNN= 200 GeV. Phys. Lett. B 760, 689–696 (2016)
D. Adamova et al., Modification of jet-like correlations in Pb–Au collisions at 158A GeV/C. Phys. Lett. B 678(3), 259–263 (2009)
H. Caines, for the STARA Collaboration, et al., Jet and jet-like correlations studies from star. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 38(12), 124019 (2011)
PHENIX Collaboration, A SICKLES, Jet correlations with identified particles from phenix: methods and results. Int. J. Mod. Phys. E 16(10), 3160–3167 (2007)
N. Agababyan et al., Self-affine fractality in π+ p and k+ p collisions at 250 GeV/C. Phys. Lett. B 382(3), 305–311 (1996)
I. Ajinenko et al., Intermittency patterns in π+ p and k+ p collisions at 250 GeV/C. Phys. Lett. B 222(2), 306–310 (1989)
D. Ghosh et al., Genuine pion–pion correlations in heavy-ion collisions. J. Phys. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 39(10), 105101 (2012)
N. Subba et al., Degree of multifractality and correlations in framework of multi-dimensional complex network analysis for 16O–Ag/Br interactions at 60 a GeV. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136(8), 1–13 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Prof. P. L. Jain, State University of Buffalo, Buffalo, NY, US, for providing the exposed and developed emulsion plates used for this analysis. One of the authors, P. K. Haldar, gratefully acknowledges his joint supervisor and expresses the utmost thanks to emeritus Prof. D. Ghosh and Prof. Argha Deb of Jadavpur University in Kolkata, India, for all kind of supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors affirm that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Subba, N., Haldar, P.K. Wavelet transform-based multi-scale analysis of ring-like and jet-like events in relativistic heavy-ion collisions. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 1128 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04757-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04757-w