Abstract
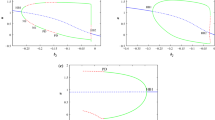
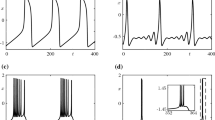
This contribution considers the isolated and collective dynamics of a FitzHugh–Rinzel (FHR) neuron obtained by adding a third variable to the generic FitzHugh–Nagumo neural circuit. From the Kirchhoff electrical circuit laws, the state equations of the model are derived; afterward, the stability around a zero time constant is investigated, and the hidden dynamics of the model is revealed. Analytical and theoretical investigation of the energy is done to support the various firing activities, such as bursting and spiking, captured in the model. Using the well-known modulation instability theory, the collective behavior of a network made of 50 neurons is analyzed in a chain configuration. As a result, regular patterns consisting of alternate bright and dark bands that are almost periodic and localized in space and time are found. Also, the brighter regions correspond to the regions where the neurons fire, while in the dark regions, the neurons are quiescent. Finally, the brighter regions could be pictured as individual spikes within a burst.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.]
References
D. Purves, D. et al., Neuroscience; Sinauer: Sunderland, MA, USA (2019).
E.R. Kandel, E.R., et al., Principles of neural science, Vol. 4. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2000).
G.M. Shepherd, The synaptic organization of the brain. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2003).
W. Gerstner, et al., Neuronal dynamics: From single neurons to networks and models of cognition. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2014).
E.M. Izhikevich, Dynamical systems in neuroscience. (MIT Press, Cambridge, 2007).
A.L. Hodgkin, A.F. Huxley, A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117(4), 500 (1952)
J. Cronin, Mathematical aspects of Hodgkin-Huxley neural theory. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987).
X. Hu, C. Liu, Dynamic property analysis and circuit implementation of simplified memristive Hodgkin-Huxley neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 97, 1721–1733 (2019)
A. Moujahid et al., Energy and information in Hodgkin-Huxley neurons. Phys. Rev. E 83(3), 031912 (2011)
Q. Xu et al., Dynamical analysis of an improved FitzHugh-Nagumo neuron model with multiplier-free implementation. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(9), 8737–8749 (2023)
X. Zhang et al., Bifurcation analysis of a modified FitzHugh-Nagumo neuron with electric field. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 170, 113415 (2023)
X. Chen et al., Memristor initial-offset boosting and its bifurcation mechanism in a memristive FitzHugh-Nagumo neuron model with hidden dynamics. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 174, 113836 (2023)
Z.T. Njitacke et al., An enhanced FitzHugh–Nagumo neuron circuit, microcontroller-based hardware implementation: light illumination and magnetic field effects on information patterns. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 167, 113014 (2023)
B. Ambrosio et al., Non-trivial dynamics in the Fizhugh–Rinzel model and non-homogeneous oscillatory-excitable reaction-diffusions systems. Biology 12(7), 918 (2023)
Z.T. Njitacke et al., Dynamics of a memristive FitzHugh–Rinzel neuron model: application to information patterns. Euro Phys J Plus 138(5), 473 (2023)
Z.N. Tabekoueng, et al., Investigation of an improved FitzHugh–Rinzel neuron and its multiplier-less circuit implementation. Chaos Interdisciplinary J Nonlinear Sci 33(6) (2023).
F.K. Nando Tezoh, A. Dang Koko, and H. Ekobena Fouda, Modes of electrical activities and energy of Hindmarsh–Rose model coupled by memristive synapses. Euro Phys J 138(3), 267 (2023).
Y. Xie et al., Estimate physical reliability in Hindmarsh-Rose neuron. Phys. Lett. A 464, 128693 (2023)
E. Slepukhina, et al., Noise-driven bursting birhythmicity in the Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary J Nonlinear Sci 33(3) (2023).
S.D. Vijay, K. Thamilmaran, A.I. Ahamed, Superextreme spiking oscillations and multistability in a memristor-based Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 111(1), 789–799 (2023)
Q. Xu et al., Electromagnetic induction effects on electrical activity within a memristive Wilson neuron model. Cogn. Neurodyn. 16(5), 1221–1231 (2022)
Z. Ju et al., Electromagnetic radiation induced non-chaotic behaviors in a Wilson neuron model. Chin. J. Phys. 77, 214–222 (2022)
W. Fan et al., Firing patterns and synchronization of Morris-Lecar neuron model with memristive autapse. AEU-Int J Electron Commun 158, 154454 (2023)
X. Yu et al., Energy balance via memristor synapse in Morris-Lecar two-neuron network with FPGA implementation. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 171, 113442 (2023)
M. Xing et al., Bifurcations and excitability in the temperature-sensitive Morris-Lecar neuron. Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 2687–2698 (2020)
K. Rajagopal et al., Wave propagation in a network of extended Morris-Lecar neurons with electromagnetic induction and its local kinetics. Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 3625–3644 (2020)
M. Ma et al., Dynamic behavior analysis and synchronization of memristor-coupled heterogeneous discrete neural networks. Mathematics 11(2), 375 (2023)
M. Ma et al., Multistability and phase synchronization of Rulkov neurons coupled with a locally active discrete memristor. Fractal and Fractional 7(1), 82 (2023)
R. FitzHugh, Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J . 1(6), 445–466 (1961)
E.M. Izhikevich, Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks 14(6), 1569–1572 (2003)
E.L. Schwartz, Computational neuroscience. (MIT Press, New York, 1993).
H. Bao et al., Hidden bursting firings and bifurcation mechanisms in memristive neuron model with threshold electromagnetic induction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(2), 502–511 (2019)
H. Lin, C. Wang, Y. Tan, Hidden extreme multistability with hyperchaos and transient chaos in a Hopfield neural network affected by electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(3), 2369–2386 (2020)
Z.T. Njitacke et al., Extremely rich dynamics of coupled heterogeneous neurons through a Josephson junction synapse. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 164, 112717 (2022)
Z. Wang et al., Complex dynamics in a discrete adaptive synapse-based neuron model. Euro Phys J Plus 138(6), 545 (2023)
S. Majhi et al., Chimera states in neuronal networks: a review. Phys. Life Rev. 28, 100–121 (2019)
A. Andreev et al., Chimera state in complex networks of bistable Hodgkin-Huxley neurons. Phys. Rev. E 100(2), 022224 (2019)
C.N. Takembo et al., Modulated wave formation in myocardial cells under electromagnetic radiation. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32(14), 1850165 (2018)
C. Chen et al., Memristive electromagnetic induction effects on Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 106, 2559–2576 (2021)
C. Chen et al., ReLU-type Hopfield neural network with analog hardware implementation. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 167, 113068 (2023)
C. Chen et al., Analog/digital circuit simplification for Hopfield neural network. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 173, 113727 (2023)
Y. Yao, J. Ma, Logical stochastic and vibrational resonances induced by periodic force in the FitzHugh–Nagumo neuron. Euro Phys J Plus 137(11), 1–10 (2022)
G. Bary, Analysis of chaos-coherence peculiarities within the chaotic phenomena of fluid at finite temperature. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 164, 112572 (2022)
G. Bary et al., A new analytical approach to study chaos fraction characterization by using intensity interferometry. Chaos, Solitons Fractals 152, 111414 (2021)
Z. T. Njitacke, et al., Novel extreme multistable tabu learning neuron: circuit implementation and application to cryptography. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 19(8), 8943–8952 (2023).
C.N. Takembo, Information pattern stability in memristive Izhikevich neural networks. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 36(12), 2250021 (2022)
C.N. Takembo et al., Effect of electromagnetic radiation on the dynamics of spatiotemporal patterns in memristor-based neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 1067–1078 (2019)
A. Mvogo et al., Pattern formation in diffusive excitable systems under magnetic flow effects. Phys. Lett. A 381(28), 2264–2271 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work is partially funded by Centre for Nonlinear Systems, Chennai Institute of Technology, India, vide Funding Number CIT/CNS/2023/RP/005. Jan Awrejcewicz has been supported by the Polish National Science Centre under the Grant OPUS 18No.2019/35/B/ST8/00980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have contributed equally to this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramadoss, J., Takembo, C.N., Karthikeyan, A. et al. Effect of external excitation on the isolated and collective dynamics of a generic FitzHugh–Rinzel neuron. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 138, 962 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04620-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-023-04620-y