Abstract
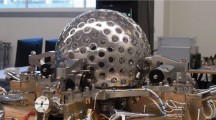
LARES and LARES 2 are two laser-ranged satellites of the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to test general relativity and gravitational physics. LARES was successfully launched on 13 February 2012 and provided a number of tests of an intriguing phenomenon predicted by General Relativity called “dragging of inertial frames”, or “frame-dragging”, with an accuracy of almost one per cent. LARES provided other tests of gravitational physics, among which a test of the equivalence principle with an accuracy of about one part in a billion, using materials never tested before and at unprecedented new ranges. LARES 2, of ASI, is ready for launch in 2022, to provide tests of dragging of inertial frames with an accuracy of almost one part in a thousand and other accurate tests of gravitational physics. In this paper, the latest results obtained with the LARES satellite are reported and a design comparison of LARES 2 with respect to the LARES satellite is described.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: All data included in this manuscript are available upon request by contacting with the corresponding author.]
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
C.W. Misner, K.S. Thorne, J.A. Wheeler, Gravitation (Freeman, San Francisco, 1973)
S.W. Hawking, G.F.R. Ellis, The Large Scale Structure of Space-Time (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1975)
I. Ciufolini, J.A. Wheeler, Gravitation and Inertia (Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, 1995)
Y.B. Zeldovich, I.D. Novikov, Relativistic Astrophysics Stars and Relativity, vol. I (University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1971)
S. Weinberg, Gravitation and Crif Okosmology: Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity (Wiley, New York, 1972)
S.G. Turyshev, Experimental tests of general relativity: recent progress and future directions. Phys. Usp. 52, 1 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3367/UFNe.0179.200901a.0003
C.M. Will (2014) The confrontation between general relativity and experiment. Living Rev. Relativ. 17:4. https://doi.org/10.12942/lrr-2014-4
B.P. Abbott et al., Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 061102 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.061102
I.H. Stairs, Testing general relativity with pulsar timing. Living Rev. Relativ. (2003). https://doi.org/10.12942/Irr-2003-5
R. Penrose, Gravitational collapse and space-time singularities. Phys. Rev. Lett. 14, 57–59 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.14.57
A. Riess et al., Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron. J. 116, 1009–1038 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1086/300499
S. Perlmutter et al., Measurements of Omega and Lambda from 42 high redshift supernovae. Astrophys. J. 517, 565–586 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1086/307221
S. Perlmutter, Supernovae, dark energy, and the accelerating universe. Phys. Today 56, 53–60 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1580050
R.R. Caldwell, Dark energy. (Physics World, 2004), https://physicsworld.com/a/dark-energy/. Accessed 20 August 2021
I. Ciufolini, A. Paolozzi, E.C. Pavlis, J. Ries, V. Gurzadyan, R. Koenig, R. Matzner, R. Penrose, G. Sindoni, Testing general relativity and gravitational physics using the LARES satellite. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 127, 133 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2012-12133-8
I. Ciufolini, E.C. Pavlis, F. Chieppa, E. Fernandes-Vieira, J. Pérez-Mercader, Test of general relativity and measurement of the Lense-Thirring effect with two Earth satellites. Science 279, 2100–2103 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.279.5359.2100
I. Ciufolini, E.C. Pavlis, A confirmation of the general relativistic prediction of the Lense-Thirring effect. Nature 431, 958–960 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03007
I. Ciufolini, E.C. Pavlis, R. Peron, Determination of frame-dragging using Earth gravity models from CHAMP and GRACE. New Astron. 11, 527–550 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.newast.2006.02.001
I. Ciufolini, E.C. Pavlis, J. Ries, R. Koenig, G. Sindoni, A. Paolozzi, H. Newmayer, in General Relativity and John Archibald Wheeler, ed. by I. Ciufolini and R. Matzner. Astrophysics and Space Science Library, vol 367, pp. 371–434. Springer, Dordrecht, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3735-0_17
C. Reigber, F. Flechtner, R. Koenig, U. Meyer, K. Neumayer, R. Schmidt, P. Schwintzer, S. Zhu, GRACE orbit and gravity field recovery at GFZ Potsdam—first experiences and perspectives. Eos. Trans. AGU 83(47), Fall Meet. Suppl. Abstract G12B–03 (2002).
B.D. Tapley, The GRACE mission: status and performance assessment. Eos. Trans. AGU 83(47), Fall Meet. Suppl. Abstract G12B–01 (2002)
I. Ciufolini, On a new method to measure the gravitomagnetic field using two orbiting satellites. Nuovo Cimento A 109, 1709–1720 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02773551
C.W. Everitt et al., Gravity Probe B: final results of a space experiment to test general relativity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 22110 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.221101
I. Ciufolini, A. Paolozzi, E.C. Pavlis, J. Ries, R. Koenig, R. Matzner, G. Sindoni, The LARES space experiment: LARES orbit, error analysis and satellite structure, in General relativity and John Archibald Wheeler, ed. by I. Ciufolini, R. Matzner, Astrophysics and Space Science Library, vol 367, (Springer, Dordrecht, 2010), pp. 467–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-3735-0_19
I. Ciufolini, A. Paolozzi, E.C. Pavlis, R. Koenig, J. Ries, V. Gurzadyan, R. Matzner, R. Penrose, G. Sindoni, C. Paris, H. Khachatryan, S. Mirzoyan, A test of general relativity using the LARES and LAGEOS satellites and a GRACE Earth gravity model. Eur. Phys. J. C 76, 120 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-016-3961-8
I. Ciufolini, A. Paolozzi, E.C. Pavlis, G. Sindoni, J. Ries, R. Matzner, R. Koenig, C. Paris, V. Gurzadyan, R. Penrose, An improved test of the general relativistic effect of frame-dragging using the LARES and LAGEOS satellites. Eur. Phys. J. C 79, 872 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-019-7386-z
D. Lucchesi et al., A 1% measurement of the gravitomagnetic field of the earth with laser-tracked satellites. Universe 6(9), 139 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/universe6090139
I. Ciufolini, A. Paolozzi, E.C. Pavlis, G. Sindoni, J. Ries, V. Gurzadyan, R. Koenig, Satellite laser-ranging as a probe of fundamental physics. Sci. Rep. 9, 15881 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52183-9
M.R. Pearlman, C.E. Noll, E.C. Pavlis, F.G. Lemoine, L. Combrink, J.J. Degnan, G. Kirchner, Ulrich Schreiber, The ILRS: approaching 20 years and planning for the future. J. Geodesy 93, 2161–2180 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01241-1
W.J. Bencze, D.B. DeBra, L. Herman, T. Holmes, M. Adams, G.M. Keiser, C.W.F. Everitt, On-orbit performance of the Gravity Probe B drag-free translation control system. in Advances In The Astronautical Sciences, vol. 125, Guidance & Control 2006, ed. By S.D. Jolly and R.D. Culp, pp. 425–440 (Univelt, Inc. 2006)
J.G. Marsh, F.J. Lerch, R.G. Williamson, Precision geodesy and geodynamics using Starlette laser ranging. J. Geophys. Res. 90(B11), 9335–9345 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1029/JB090iB11p09335
E.C. Pavlis, S.G. Poulose, S.C. Rowton, J.J. McCarthy, S.B. Luthcke, GEODYN operations manuals (Contractor Report, Raytheon, ITSS, Landover MD, 1998).
C.F. Martin, D.P. Rubincam, Effects of earth albedo on the LAGEOS I satellite. J. Geophys. Res. 101(B2), 3215–3226 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1029/95JB02810
D.P. Rubincam, On the secular decrease in the semimajor axis of LAGEOS’s orbit. Celest. Mech. 26, 361–382 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01230417
A. Paolozzi, I. Ciufolini, C. Vendittozzi, Engineering and scientific aspects of LARES satellite. Acta Astronaut. 69, 127–134 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2011.03.005
T.L. Smith, A.L. Erickcek, R.R. Caldwell, M. Kamionkowski, Effects of Chern-Simons gravity on bodies orbiting the Earth. Phys. Rev. D 77, 024015 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.77.024015
I. Ciufolini, A. Paolozzi, E.C. Pavlis, G. Sindoni, R. Koenig, J.C. Ries, R. Matzner, V. Gurzadyan, R. Penrose, D. Rubincam, C. Paris, A new laser-ranged satellite for General Relativity and space geodesy: I. An introduction to the LARES2 space experiment. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 336 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11635-1
I. Ciufolini, E.C. Pavlis, G. Sindoni, J. Ries, A. Paolozzi, R. Matzner, R. Koenig, C. Paris, A new laser-ranged satellite for General Relativity and space geodesy: II. Monte Carlo simulations and covariance analyses of the LARES 2 experiment. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132, 337 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2017-11636-0
I. Ciufolini, R. Matzner, V. Gurzadyan, R. Penrose, A new laser-ranged satellite for General Relativity and space geodesy: III. De Sitter effect and the LARES 2 space experiment. Eur. Phys. J. C 77, 819 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-017-5339-y
I. Ciufolini, R. Matzner, J. Feng, D.P. Rubincam, E.C. Pavlis, J.C. Ries, G. Sindoni, A. Paolozzi, C. Paris, A new laser-ranged satellite for General Relativity and space geodesy: IV. Thermal drag and the LARES 2 space experiment. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 133, 333 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2018-12174-y
I. Ciufolini, Theory and Experiments in General Relativity and other Metric Theories, PhD Dissertation, Univ. of Texas, Austin (Pub. Ann Arbor, Michigan, 1984).
I. Ciufolini, Measurement of the Lense-Thirring drag on high-altitude, laser-ranged artificial satellites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 278 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.278
B. Tapley, J.C. Ries, R.J. Eanes, M.M. Watkins, NASA-ASI Study on LAGEOS III, CSR-UT publication n. CSR-89–3, Austin, Texas (1989).
I. Ciufolini, P. Farinella, A.M. Nobili, D. Lucchesi, L. Anselmo, ASI-NASA Study on LAGEOS III, CNR, Rome, Italy (1989).
I. Ciufolini, A comprehensive introduction to the LAGEOS gravitomagnetic experiment: from the importance of the gravitomagnetic field in physics to preliminary error analysis and error budget. Int. J. of Mod. Phys. A 04, 13 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0217751X89001266
J.C. Ries, Simulation of an experiment to measure the Lense-Thirring precession using a second LAGEOS satellite, PhD Dissertation, Univ. of Texas, Austin (1989).
R. Matzner et al., LARES satellite thermal forces and a test of general relativity. Proc. MetroAeroSpace (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/MetroAeroSpace.2016.7573269
A. Brotzu, F. Felli, D. Pilone, A. Paolozzi, I. Ciufolini, Toughness evaluation of LARES satellite tungsten alloy. Procedia Eng. 109, 517–524 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2015.06.259
A. Paolozzi, I. Ciufolini, G. Sindoni, C. Paris, The LARES 2 satellite: new challenges for design and ground test. Aerotec. Missili Spaz. 97, 135–144 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03404767
A. Paolozzi, G. Sindoni, F. Felli, D. Pilone, A. Brotzu, I. Ciufolini, E.C. Pavlis, C. Paris, Studies on the materials of LARES 2 satellite. J. Geod. 93, 2437–2446 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-019-01316-z
A. Paolozzi, F. Felli, D. Pilone, A. Brotzu, I. Ciufolini, Development and analysis of a new alloy candidate for LARES 2 satellite. in Proceedings of 69th International Astronautical Congress (IAC), 1–5 October 2018 (Bremen, Germany)
A. Brotzu, F. Felli, D. Pilone, A. Paolozzi, C. Paris, F. Iacoviello, C. Bellini, V. Di Cocco, Study of the fracture behavior of a CuCrZr alloy. Mat. Design Process. Comm. 2, e113 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/mdp2.113
J.J. Degnan, Millimeter accuracy satellite laser ranging: a review. in Contributions of Space Geodesy to Geodynamics: Technology, ed. by D.E. Smith and D.L. Turcotte (1993) https://doi.org/10.1029/GD025p0133
T. Otsubo, R.A. Sherwood, G.M. Appleby, R. Neubert, Center-of-mass corrections for sub-cm-precision laser-ranging targets: Starlette. Stella and LARES. J. Geod. 89, 303–312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-014-0776-y
B.W. Clare, D.L. Kepert, The closest packing of equal circles on a sphere. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 405, 329–344 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1986.0056
G. Sindoni, C. Paris, I. Ciufolini, Vibration tests of a cube corner reflector assembly of LARES2 satellite, in Proceedings of the AIDAA 2019 International Conference, pp 1627–1633 (2019).
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Italian Space Agency (ASI) for supporting LARES mission under Agreement No. 2020-7-H.H.0 and LARES 2 mission under Agreement No. 2017-23-H.0. The authors acknowledge the International Laser Ranging Service (ILRS) for tracking the two LAGEOS and the LARES satellite, for agreeing to track LARES 2 after its launch and for providing the Normal Points of their orbits.
Funding
The authors did not receive any additional founding for writing this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ciufolini, I., Paris, C. Status of the LARES and LARES 2 space experiments. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 1030 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01980-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01980-1