Abstract
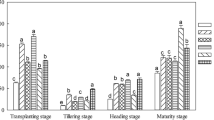
With the gradual change of climate, the organic matter and nutrients in the soil are constantly losing. It induces the creation of saltwater alkali land and quickens soil degradation, both of which further lower productivity. It will eventually lead to a serious food catastrophe. As as a consequence, the research conducted an experimental analysis on the effects of straw returning and biological carbon on saline alkali land development in northeast Jiangsu University, with the goal of addressing the issue of weak soil internal structure in some places of northeast China. The experiment analyzed the growth and photosynthesis dynamics, material accumulation and transformation, root activity, soil physical and chemical properties, and the spike characteristics of Kenjiandao 5, respectively. The experimental results showed that biochar and straw returning could effectively improve rice’s growth rate and effective tillering. Among the biochar returning treatments, 4 treatments had the highest traumatic discharge, with an increased rate of 3.13–37.65%, and 6 treatments had the highest traumatic discharge, 29.96% higher than CK. At the same time, biochar and straw returning to the soil can effectively improve the organic matter in the soil and reduce its pH value. Compared with CK, the highest increase is 27.80%. In general, the use of biological carbon and straw return can effectively optimize the soil structure, increase the yield, reduce the waste of straw resources, and have a strong practical effect on the actual saline alkali land improvement in Northeast China.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Chen, H., Zhang, D., Zhang, B., and Li, G., Environmental impacts and returning effects of garden wastes under different disposal methods, TCSAE, 2018, vol. 34, no. 21, pp. 239–244.
Huo, H.N., Li, J., Yuan, L., Xie, H.T., and Zhang, X.D., Effects of different straw returning amount on the potential gross nitrogen transformation rates of fertilized Mollisol, J. Appl. Ecol., 2020, vol. 31, no. 12, pp. 4109–4116.
Li, J.F. and Zhong, F.F., Nitrogen release and re-adsorption dynamics on crop straw residue during straw decomposition in an Alfisol, J. Integr. Agr., 2021, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 248–259.
Li, B., Bao, Z.R., Yao, M.Z., Li, C.X., and Sun, X.L., Effects of irrigation lower limit and straw returning amount on yield, quality and water use efficiency of greenhouse tomato, J. Appl. Ecol., 2020a, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 493–500.
Li, N., Han, X.Z., Sheng, M., and Long, J.H., Characteristics of soil fertility during soil fertilization from parent material of a Mollisol in Northeast China, J. Appl. Ecol., 2020b, vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 1155–1162.
Li, Y., Cao, Z., Sun, B., Ye, C., Shu, S., Huang, J., Wang, K., and Tian, Y., Model construction and application for nitrogen nutrition monitoring and diagnosis in double-cropping rice of Jiangxi Province, China, J. Appl. Ecol., 2020c, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 433–440.
Li, C., Cheng, K., Liao, Y., Guo, L., Wen, L., Tang, H., Tang, W., Wang, K., Chu, F., and Zhong, L., Effect of crushing degree and returning method on straw combustion, Chin. J. Ecol., 2021, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 922–928.
Liu, M., Zhang, A. J., Chen, X. G., Jin, R., and Tang, Z. H., Effects of straw returning and fertilization on soil fertility and yield and quality of edible sweet potato, J. Appl. Ecol., 2020, vol. 31, no. 10, pp. 3445–3452.
Ma, S., Lv, L., Meng, C., Zhang, C., and Li, Y., Integrative analysis of the metabolome and transcriptome of sorghum bicolor reveals dynamic changes in flavonoids accumulation under saline alkali stress, J. Agr. Food Chem., 2020, vol. 68, no. 50, pp. 14781–14789.
Mabagala, F.S. and Mng’Ong’O, M.E., On the tropical soils; The influence of organic matter (OM) on phosphate bioavailability, Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 2022, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 3635–3641.
Qin, W., Song, H., Fan, Y., and Cheng, F., Effects of activated coke on soil properties and growth of two plant species in saline alkali soil in northern Shanxi Province, China, J. Appl. Ecol., 2021, vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 1799–1806.
Shakoor, A., Gan, Q.M., Yin, X., He, H.F.H., and Ma, Y., Influence of nitrogen fertilizer and straw returning on Ch4 emission from a paddy field in Chao Lake basin, China, Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res., 2020, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 1585–1600.
Song, D., Current situations, evolution trend, and improvement measures of soil organic matter in cultivated land of Northeast China, ASAR, 2022, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 38–41.
Song, J., Huang, J., Gao, J.S., Wang, Y.N., Zeng, X.B., Effects of green manure planted in winter and straw returning on soil aggregates and organic matter functional groups in double cropping rice area, J. Appl. Ecol., 2021, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 564–570.
Song, J.J., Xu, X.Y., Bai, J.Z., Yu, Q., Cheng, B.H., Feng, Y.Z., and Ren, G.X., Effects of straw returning and fertilizer application on soil nutrients and winter wheat yield, Huan Jing Ke Xue, 2022, vol. 43, no. 9, pp. 4839–4847.
Struijk, M., Whitmore, A.P., Mortimer, S.R., and Sizmur, T., Obtaining more benefits from crop residues as soil amendments by application as chemically heterogeneous mixtures, Soil, 2020, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 467–481.
Sun, N., Wang, X., Li, H., Wang, Q., and Liu, D., Design and experiment of rice straw spreading and plowing combined machine, Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng., 2020, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 135–143.
Tan, Z., Zou, J., Zhang, L., and Huang, Q., Morphology, pore size distribution, and nutrient characteristics in biochars under different pyrolysis temperatures and atmospheres, J. Mater. Cycles Waste, 2018, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 1036–1049.
Wang, J., Ma, L.J., Long, Z.H., Min, W., and Hou, Z.A., Effects of straw biochar on soil microbial metabolism and bacterial community composition in drip-irrigated cotton field, Huan Jing Ke Xue, 2020a, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 420–429.
Wang, Q., Li, M., Chen, X., Su, Y., Yu, M., and Shen, A., Effects of nitrogen management on soil microbial community structure at different growth stages under straw returning in paddy soils, J. Appl. Ecol., 2020, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 935–944.
Xu, H., Li, W.N., Feng, Y.Z., Ren, G.X., and Hao, J.Q., Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and straw returning methods on N2O emissions in wheat–maize rotational soils, Huan Jing Ke Xue, 2020, vol. 41, no. 12, pp. 5668–5676.
Yang, C. and Lu, S., Dynamic effects of direct returning of straw and corresponding biochar on acidity, nutrients, and exchangeable properties of red soil, Huan Jing Ke Xue, 2020, vol. 41, no. 9, pp. 4246–4252.
Yu, Y., Wang, Y., Hou, P.F., Yang, L.Z., Oduor, O.A., and Xue, L., Effects of returning nitrogen by biochar loading on paddy growth, root morphology, and nitrogen use efficiency, Huan Jing Ke Xue, 2018, vol. 39, no. 11, pp. 5170–5179.
Zhang, Y., Yang, J., Yao, R., Wang, X., and Xie, W., Short-term effects of biochar and gypsum on soil hydraulic properties and sodicity in a saline-alkali soil, Pedosphere, 2020, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 694–702.
Zhu, H., Gao, M., Long, Y., Xu, G., Wang, F., and Wang, Z., Effects of fertilizer reduction and application of organic fertilizer on soil nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients and crop yield in a purple soil sloping field, Huan Jing Ke Xue, 2020, vol. 41, no. 4, pp. 1921–1929.
Funding
The research is supported by: Science and technology research project of Jilin Provincial Department of Education: research and development of rice straw interlayer salt blocking machine in saline alkali land Contract (no. JJKH20210339KJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jingli Wang, Jing, H., Xu, T. et al. Application Effect of Straw Returning and Biochar in the Improvement of Saline-Alkali Land in Northeast China. Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 50, 825–836 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359022603226
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062359022603226