Abstract
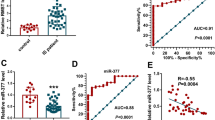
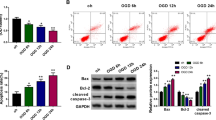
This study aimed to explore the efficacy of Xingnaojing combined with brain glycoside peptide (XCGP) in the treatment and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke (AIS). The expression levels of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)-H19 and mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 (MAPK6) in 37 AIS patients were measured using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The correlation between lncRNA-H19, microRNA (miR)-138-5p and MAPK6 was predicted using StarBase online software. In vitro and in vivo experiments were carried out using the ReNcell CX neural stem cell (NSC) line and an AIS rat model constructed by middle cerebral artery occlusion surgery, respectively. Following human ReNcell CX cell culture in a hypoxic environment, RT-qPCR was conducted to measure the expression levels of the related genes, MTT and WST-1 assays were performed to assess the proliferation and viability of ReNcell CX NSCs, and flow cytometry was utilized to assess ReNcell CX NSC apoptosis. In addition, the rotarod, beam walk, and adhesion removal tests were conducted to evaluate changes in the motility of rats with AIS, and the infarction volume was calculated. The results of RT-qPCR showed that lncRNA-H19 and MAPK6 were upregulated in AIS patients. The StarBase online software for the prediction of miRNA-target interactions showed that lncRNA-H19 targets miR-138-5p, which targets MAPK6 (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively). Further, human ReNcell CX cells that were administered XCGP displayed marked downregulation of MAPK6, and the AIS rat model with XCGP injection showed effective reduction in infarction volume, and notable recovery of motility (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001). XCGP may serve as a candidate for the treatment of AIS, thereby improving the ischemic status of ReNcell CX NSCs and the condition of rats with AIS.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Arnold, M., Halpern, M., Meier, N., Fischer, U., Haefeli, T., Kappeler, L., Brekenfeld, C., Mattle, H.P., and Nedeltchev, K., J. Neurol., 2008, vol. 255, no. 10, pp. 1503–1507.
Yang, X., Wang, L., Zheng, L., Wu, J., Liu, J., Hao, Z., Zhang, S., Wu, B., Liu, M., and Wang, D., Curr. Neurovasc. Res., 2020, vol. 17, no. pp. 385–393.
Ye, C., Wang, Y., Song, Q., Liu, J., Wei, C., and Liu, M., Curr. Neurovasc. Res., 2020, vol. 17, no. pp. 344–353.
Waqas, M., Rai, A.T., Vakharia, K., Chin, F., and Siddiqui, A.H., J. Neurointerv. Surg., 2020, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 260–265.
Lakomkin, N., Dhamoon, M., Carroll, K., Singh, I.P., Tuhrim, S., Lee, J., Fifi, J.T., and Mocco, J., J. Neurointerv. Surg., 2019, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 241–245.
Hu, S., Zheng, J., Du, Z., and Wu, G., Brain Res., 2020, vol. 1732, no. pp. 146681.
Li, P., Hu, F., Cao, X., Luo, L., and Tu, Q., J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res., 2020, vol. 40, no. 2, pp. 117–125.
Taha, S.H.N., Zaghloul, H.S., Ali, A., Gaballah, I.F., Rashed, L.A., and Aboulhoda, B.E., Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol., 2020, vol. 393, no. pp. 1635–1648.
Qin, C., Xia, T., Li, G., Zou, Y., Cheng, Z., and Wang, Q., Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol., 2019, vol. 12, no. 9, pp. 3440–3446.
Guo, W., Ma, J., Yang, Y., Guo, S., Zhang, W., Zhao, T., Yi, X., Wang, H., Wang, S., Liu, Y., Dai, W., Chen, X., Shi, Q., Wang, G., Gao, T., and Li, C., Clin. Cancer Res., 2020, vol. 26, no. pp. 2725–2739.
Yang, C., Luo, J., Luo, X., Jia, W., Fang, Z., Yi, S., and Li, L., Ann. Transl. Med., 2020, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 327.
Liu, Z., Zhang, J., Zhang, F., and Chang, Y., Gene, 2020, vol. 741, no. pp. 144562.
Yang, F., Qin, Y., Wang, Y., Li, A., Lv, J., Sun, X., Che, H., Han, T., Meng, S., Bai, Y., and Wang, L., Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 2018, vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 1230–1244.
Liu, C., Li, X., Hao, Y., Wang, F., Cheng, Z., Geng, H., and Geng, D., Aging, 2020, vol. 12, no. pp. 8680–8701.
Yuan, B., Guan, Q., Yan, T., Zhang, X., Xu, W., and Li, J., Cancer Biother. Radiopharm., 2020, vol. 35, no. pp. 711–719.
Deng, Q.W., Li, S., Wang, H., Sun, H.L., Zuo, L., Gu, Z.T., Lu, G., Sun, C.Z., Zhang, H.Q., and Yan, F.L., Clin. Sci., 2018, vol. 132, no. 14, pp. 1597–1614.
Cao, H.J., Liang, S.B., Zhou, W., Wu, J.R., and Zhang, C.L., Medicine, 2019, vol. 98, no. 15, pp. e15181.
Xu, P., Du, S.Y., Lu, Y., Bai, J., Guo, Y.W., Du, Q., and Cao, Y.F., J. Ethnopharmacol., 2014, vol. 152, no. 2, pp. 302–307.
Chen, Y., Sun, Y., Li, W., Wei, H., Long, T., Li, H., Xu, Q., and Liu, W., J. Pharmacol. Sci., 2018, vol. 136, no. 1, pp. 16–25.
Hu, Z., Shi, Y., Niu, H., Cai, Y., Jiang, G., and Wu, Y., Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2010, vol. 29, no. 9, pp. 1877–1882.
Wu, L., Zhang, H., Xing, Y., Gao, Y., Li, Y., Ren, X., Li, J., Nie, B., Zhu, L., Shang, H., and Gao, Y., Medicine, 2016, vol. 95, no. 7, pp. e2875.
Xin, H., Shi, Z., Wu, L., Zhang, M., Yuan, X., Wang, P., Xu, Y., Zeng, G., and Wang, H., Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 2019, vol. 44, no. 12, pp. 1330–1337.
Chen, X.T., Wang, X.G., Xie, L.Y., Huang, J.W., Zhao, W., Wang, Q., Yao, L.M., and Li, W.R., Biomed Res. Int., 2019, vol. 2019, no. pp. 2389485.
Gao, Y., Hu, Y.Z., Li, R.S., Han, Z.T., Geng, Y., Xia, Z., Du, W.J., Liu, L.X., Zhang, H.H., and Wang, L.N., Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat., 2015, vol. 11, no. pp. 537–548.
Livak, K.J., and Schmittgen, T.D., Methods, 2001, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 402–408.
Wang, J., Cao, B., Han, D., Sun, M., and Feng, J., Aging Dis., 2017, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 71–84.
Zhou, Y.H., Huang, Y.Y., and Ma, M., Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci., 2018, vol. 22, no. 17, pp. 5569–5575.
Yang, J.H., Li, J.H., Shao, P., Zhou, H., Chen, Y.Q., and Qu, L.H., Nucleic Acids Res., 2011, vol. 39, no. Database issue, pp. D202–D209.
Ranke, J., Molter, K., Stock, F., Bottin-Weber, U., Poczobutt, J., Hoffmann, J., Ondruschka, B., Filser, J., and Jastorff, B., Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2004, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 396–404.
Li, W., Abdul, Y., and Ergul A., Methods Mol. Biol., 2023, vol. 2616, pp. 467–479.
Hawk, T., Zhang, Y.Q., Rajakumar, G., Day, A.L., and Simpkins, J.W., Brain Res., 1998, vol. 796, no. 1–2, pp. 296–298.
Belayev, L., Alonso, O.F., Busto, R., Zhao, W., and Ginsberg, M.D., Stroke, 1996, vol. 27, no. 9, pp. 1616-1622; discussion 1623.
Liang, B., Wang, S., Zhu, X.G., Yu, Y.X., Cui, Z.R., and Yu, Y.Z., World J. Gastroenterol., 2005, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 623–628.
Al-Mahdi, R., Babteen, N., Thillai, K., Holt, M., Johansen, B., Wetting, H. L., Seternes, O.M., and Wells, C.M., Cell Adh. Migr., 2015, vol. 9, no. 6, pp. 483–494.
Zhu, R., Liu, X., and He, Z., Mol. Brain, 2018, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 58.
Shaath, H., Toor, S.M., Nada, M.A., Elkord, E., and Alajez, N.M., Sci. Rep., 2021, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 14456.
Ou, L., Wang, D., Zhang, H., Yu, Q., and Hua, F., Oncol. Res., 2018, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 401–410.
Tian, B., Zhao, J., Xie, X., Chen, T., Yin, Y., Zhai, R., Wang, X., An, W., and Li, J., Food Funct., 2021, vol. 12, no. 9, pp. 3855–3871.
Funding
No external funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval. This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethical Board of the 5th People’s Hospital of Jinan (no.: ChiCTR18000155682). All operations were approved by the Animal Use and Care Committee of the 5th People’s Hospital of Jinan.
Informed consent. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Corresponding author; address: Intensive Care Unit, The 5th People’s Hospital of Jinan, No. 24297, Jingshi Road, Jinan, Shandong, 250022 China; e-mail: liuwei065@163.com.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Zhang, M.M., Zhou, Q. et al. Xingnaojing Combined with Brain Glycoside Peptide Targets LncRNA-H19 and Regulates hsa-microRNA (miR)-138-5p/MAPK6 to Alleviate Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurochem. J. 17, 492–501 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712423030182
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712423030182