Abstract
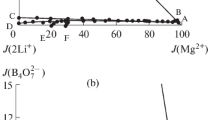
The isothermal equilibrium method was used to study the stable phase equilibria of the quinary system Li+, K+, Mg2+//Cl‒, \({{{\text{B}}}_{{\text{4}}}}{\text{O}}_{7}^{{2 - }}\)–H2O at 273 K. The solubility data of each component in this system were measured through experiments, and the isothermal phase diagram of this system was also drawn. For the identification of the equilibrium solid phases of the invariant points, X-ray diffraction characterization was used. The projection surface of the stable phase diagram of the quinary system Li+, K+, Mg2+//Cl‒, \({{{\text{B}}}_{{\text{4}}}}{\text{O}}_{7}^{{2 - }}\)‒H2O at 273 K was drawn under the saturation condition of MgB4O7. The simplified dry-salt diagram has carnallite (KCl·MgCl2·6H2O) and lithium carnallite (LiCl·MgCl2·7H2O), and it contains eleven univariate solubility curves, five invariant points and seven crystallization regions corresponding to K2B4O7·4H2O, Li2B4O7·3H2O, KCl, MgCl2·6H2O, and LiCl·2H2O and double salts carnallite (KCl·MgCl2·6H2O) and lithium carnallite (LiCl·MgCl2·7H2O). In the quinary system, by comparing the area of each crystalline phase zone, lithium chloride is a highly soluble salt, therefore, in the solubility diagram, in comparison with magnesium tetraborate, it corresponds to the smallest crystallization area.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Q. Wu, X. F. Liu, et al., J. Mod. Chem. Ind. 37, 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.16606/j.cnki.issn.0253-4320.2017.05.001
W. C. Du and N. Song, J. China Chem. Trade 004, 22 (2012). http://www.cqvip.com/qk/71210x/201203/ 41862784.html.
K. S. Kwok, K. M. Ng, M. E. Taboada, et al., AIChEJ 54, 706 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.11421
H. M. Yang and X. B. Li, J. Haihu Salt Chem. Ind. 5, 15 (2002). http://www.cqvip.com/qk/92939x/200205/ 6936120.html.
P. S. Song, B. Sun, and D. W. Zeng, J. Pure Appl. Chem. 85, 2097 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1351/pac-con-13-04-05
C. H. Fang, P. S. Song, and J. Q. Chen, J. Salt Lake Sci. 02, 21 (1993). https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:YHYJ.0.1993-02-004
S. S. Guo, X. D. Yu, and Y. Zeng, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 61, 1566 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.5b00938
P. S. Song, Y. P. Dong, and W. Li, J. Salt Lake Res. 25, 9 (2017). http://www.cqvip.com/qk/93634x/201703/ 673535664.html.
B. Sun and P. S. Song, J. Salt Lake Res. 23, 50 (2015). https://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/YHYJ2015040-13.htm.
S. H. Sang, H. A. Yin, S. J. Ni, et al., JCHUS 4, 414 (2006). http://www.docin.com/p-1559520170.html.
S. H. Sang, T. Li, and R. Z. Cui, J. Salt Lake Res. 21, 29 (2013). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YHYJ201302008.htm.
X. Y. Zhao, S. H. Sang, and M. L. Sun, J. Salt Lake Res. 19, 35 (2011). https://www.doc88.com/p-5931644917485.html.
S. Q. Wang, D. Zhao, Y. Song, et al., Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 64, 661 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602361905019X
D. Wang, S. H. Sang, X. Zeng, et al., J. Petrochem. Technol. 40, 285 (2011). http://www.docin.com/p-1212879704.html.
K. J. Zhang, S. H. Sang, T. Li, et al., J. Chem. Eng. Data 58, 115 (2013). https://doi.org/org/10.1021/je3009717
Y. X. Hu, S. H. Sang, R. Z. Cui, et al., J. Chem. Eng. Data 59, 1886 (2014). https://doi.org/org/10.1021/je500051e
X. D. Yu, Y. L. Luo, L. T. Wu, et al., J. Chem. Eng. Data 61, 3311 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.6b00359
S. H. Sang, H. A. Yin, M. L. Tang, et al., J. Chem. Eng. Data 49, 1586 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/je034280k
S. Q. Wang, D. Zhao, Y. Song, et al., Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 63, 116 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023618010175
S. H. Sang and J. Peng, J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 25, 381 (2011). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-GXHX201103005.htm.
T. Li, S. H. Sang, and R. Z. Cui, J. Chem Eng. 40, 35 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2012.11.009
S. Tursunbadalov, Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 65, 412 (2020). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1134%2-FS0036023620030195.
S. Tursunbadalov and L. Soliev, Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 37, 577 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43153-020-00054-6
S. H. Sang, L. F. Lei, R. Z. Cui, et al., J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 28, 21 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2013.12.31.02
Y. Zeng, X. T. He, and H. A. Yin, J. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 20, 946 (2004). http://www.cqvip.com/read/ read.aspx?id=10016140.
R. Z. Cui, S. H. Sang and T. Li, et al., J. CIESC 64, 804 (2013). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2013.03.007
T. L. Deng, J. Chem. Eng. Data 49, 1295 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1021/je049975f
Y. Jing, J. Sea-Lake Salt Chem. Ind. 29, 24 (2000). https://wenku.baidu.com/view/69f69f5d804d2b160b4-ec0e5.html.
S. Q. Wang, J. Gao, X. Yu, et al., J. Salt Lake Res. 15, 44 (2007). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?filename=YHYJ200701008&dbcode=CJFQ&dbname=cjfd2007.
Funding
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41873071, U1407108) and scientific research and innovation team in Universities of Sichuan Provincial Department of Education (15TD0009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chun-Xia He, Xu, JS., Sang, SH. et al. Studies on the Stable Phase Equilibria of Quinary System Li+, K+, Mg2+//Cl–, \({{{\text{B}}}_{{\text{4}}}}{\text{O}}_{7}^{{2 - }}\)–H2O at 273 K. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 66, 714–723 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023621050065
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036023621050065