Abstract
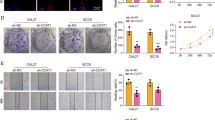
MUC4 is a predominant membrane-tethered mucin lubricating and protecting the epithelial surface and playing various biological roles in the renewal and differentiation of epithelial cells, cell signaling, cell adhesion, and carcinogenesis. Interestingly, recent studies have demonstrated that MUC4 expression regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cancer cells in ovarian, pancreatic, and lung cancer. However, the effects of MUC4 expression on EMT in human airway epithelial cells are not yet well known. Here, we describe the effects of transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1)-induced MUC4 expression on EMT and evaluate its downstream signaling pathway in human airway epithelial cells. In human airway epithelial NCI-H292 cells, exposure to TGF-β1 induced expression of MUC4, CDH2, VIM and SNAI1 genes and encoded by them proteins, MUC4, N-cadherin, vimentin and Snail, and reduced the level of CDH1 and its product, E-cadherin. In MUC4-knockdown cells, TGF-β1-induced expression levels of MUC4, CDH2, VIM and SNAI1 and corresponding proteins were suppressed, but CDH1 and E-cadherin levels were not. In addition, TGF-β1-induced phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) was suppressed, but that of Smad2/3, Akt, and p38 was not. The results of this study suggest that MUC4 silencing inhibits TGF-β1-induced EMT via the ERK1/2 pathway, and a possible role of MUC4 in the induction of EMT in human airway epithelial cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ma J., Rubin B.K., Voynow J.A. 2018. Mucins, mucus, and goblet cells. Chest. 154, 169‒176.
Rowson-Hodel A.R., Wald J.H., Hatakeyama J., O’Neal W.K., Stonebraker J.R., VanderVorst K., Saldana M.J., Borowsky A.D., Sweeney C., Carraway K.L. 3rd. 2018. Membrane mucin Muc4 promotes blood cell association with tumor cells and mediates efficient metastasis in a mouse model of breast cancer. Oncogene. 37, 197‒207.
Govindarajan B., Gipson I.K. 2010. Membrane-tethered mucins have multiple functions on the ocular surface. Exp. Eye Res. 90, 655‒663.
van Putten J.P.M., Strijbis K. 2017. Transmembrane mucins: Signaling receptors at the intersection of inflammation and cancer. J. Innate Immun. 9, 281‒299.
Xia P., Choi A.H., Deng Z., Yang Y., Zhao J., Wang Y., Hardwidge P.R., Zhu G. 2017. Cell membrane-anchored MUC4 promotes tumorigenicity in epithelial carcinomas. Oncotarget. 8, 14147‒14157.
Kim Y.D., Bae C.H., Song S.Y., Choi Y.S. 2015. Effect of β-glucan on MUC4 and MUC5B expression in human airway epithelial cells. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 5, 708‒715.
Ponnusamy M.P., Lakshmanan I., Jain M., Das S., Chakraborty S., Dey P., Batra S.K. 2010. MUC4 mucin-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition: a novel mechanism for metastasis of human ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. 29, 5741‒5754.
Komai T., Okamura T., Yamamoto K., Fujio K. 2016. The effects of TGF-βs on immune responses. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi (Jpn.). 39, 51‒58.
Hao Y., Baker D., Ten Dijke P. 2019. TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 2767.
Nakao A., Afrakhte M., Morén A., Nakayama T., Christian J.L., Heuchel R., Itoh S., Kawabata M., Heldin N.E., Heldin C.H., ten Dijke P. 1997. Identification of Smad7, a TGFβ-inducible antagonist of TGF-β signalling. Nature. 389, 631‒635.
Kolosova I., Nethery D., Kern J.A. 2011. Role of Smad2/3 and p38 MAP kinase in TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pulmonary epithelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 226, 1248‒1254.
Ponnusamy M.P., Seshacharyulu P., Lakshmanan I., Vaz A.P., Chugh S., Batra S.K. 2013. Emerging role of mucins in epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 13, 945‒956.
Xu D., Liu S., Zhang L., Song L. 2017. MiR-211 inhibits invasion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cervical cancer cells via targeting MUC4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 485, 556‒562.
Matull W.R., Andreola F., Loh A., Adiguzel Z., Deheragoda M., Qureshi U., Batra S. K., Swallow D.M., Pereira S.P. 2008. MUC4 and MUC5AC are highly specific tumour-associated mucins in biliary tract cancer. Br. J. Cancer. 98, 1675‒1681.
Hu J., Zhou Z., Shi S., Zhu X., Wang X., Zhang W., Hu S., Qian H., Xu W. 2013. Mesenchymal stem-like cells isolated from human esophageal carcinoma and adjacent non-cancerous tissues. Oncol. Lett. 5, 179‒184.
Chaturvedi P., Singh A.P., Batra S.K. 2008. Structure, evolution, and biology of the MUC4 mucin. FASEB. J. 22, 966‒981.
Rachagani S., Macha M.A., Ponnusamy M.P., Haridas D., Kaur S., Jain M., Batra S.K. 2012. MUC4 potentiates invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells through stabilization of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1. Carcinogenesis. 33, 1953‒1964.
Majhi P.D., Lakshmanan I., Ponnusamy M.P., Jain M., Das S., Kaur S., Shimizu S.T., West W.W., Johansson S.L., Smith L.M., Yu F., Rolle C.E., Sharma P., Carey G.B., Batra S.K., Ganti A.K. 2013. Pathobiological implications of MUC4 in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 8, 398‒407.
Gao L., Liu J., Zhang B., Zhang H., Wang D., Zhang T., Liu Y., Wang C. 2014. Functional MUC4 suppress epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma metastasis. Tumor Biol. 35, 1335‒1341.
Jonckheere N., Van Seuningen I. 2018. Integrative analysis of the cancer genome atlas and cancer cell lines encyclopedia large-scale genomic databases: MUC4/MUC16/MUC20 signature is associated with poor survival in human carcinomas. J. Transl. Med. 16, 259.
Reynolds I.S., Fichtner M., McNamara D.A., Kay E.W., Prehn J.H.M., Burke J.P. 2019. Mucin glycoproteins block apoptosis; promote invasion, proliferation, and migration; and cause chemoresistance through diverse pathways in epithelial cancers. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 38, 237‒257.
Funding
This study was supported by the 2017 Yeungnam University Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
COMPLIANCE WITH ETHICAL STANDARDS
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors. All experimental protocols were approved by the Yeungnam University Hospital-Institutional Review Board (file no. 2018-08-011).
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
The text was submitted by the author(s) in English.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YD., Choi, Y.S., Na, H.G. et al. MUC4 Silencing Inhibits TGF-β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via the ERK1/2 Pathway in Human Airway Epithelial NCI-H292 Cells. Mol Biol 55, 565–572 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321030079
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893321030079