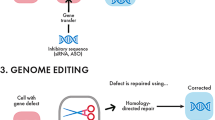
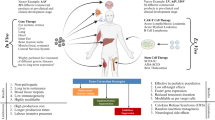
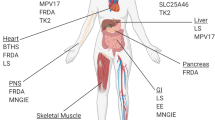
Abstract
Throughout the years, several hundred million people with rare genetic disorders have been receiving only symptom management therapy. However, research and development efforts worldwide have led to the development of long-lasting, highly efficient, and safe gene therapy for a wide range of hereditary diseases. Improved viral vectors are now able to evade the preexisting immunity and more efficiently target and transduce therapeutically relevant cells, ensuring genome maintenance and expression of transgenes at the relevant levels. Hematological, ophthalmological, neurodegenerative, and metabolic therapeutic areas have witnessed successful treatment of hemophilia and muscular dystrophy, restoration of immune system in children with immunodeficiencies, and restoration of vision. This review focuses on three leading vector platforms of the past two decades: adeno-associated viruses (AAVs), adenoviruses (AdVs), and lentiviruses (LVs). Special attention is given to successful preclinical and clinical studies that have led to the approval of gene therapies: six AAV-based (Glybera® for lipoprotein lipase deficiency, Luxturna® for retinal dystrophy, Zolgensma® for spinal muscular atrophy, Upstaza® for AADC, Roctavian® for hemophilia A, and Hemgenix® for hemophilia B) and three LV-based (Libmeldy® for infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy, Zynteglo® for β-thalassemia, and Skysona® for ALD). The review also discusses the problems that arise in the development of gene therapy treatments, which, nevertheless, do not overshadow the successes of already developed gene therapies and the hope these treatments give to long-suffering patients and their families.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 April 2024
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297924030167
References
Mahoney, A. L. G., Nassif, N. T., O’Brien, B. A., and Simpson, A. M. (2022) Viral Vectors in Gene Therapy and Clinical Applications in Molecular Cloning, IntechOpen.
Flotte, T., Carter, B., Conrad, C., Guggino, W., Reynolds, T., Rosenstein, B., Taylor, G., Walden, S., and Wetzel, R. (1996) A phase I study of an adeno-associated Virus-CFTR gene vector in adult CF patients with mild lung disease, Hum. Gene Ther., 7, 1145-1159, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.1996.7.9-1145.
Manno, C. S., Arruda, V. R., Pierce, G. F., Glader, B., Ragni, M., Rasko, J., Ozelo, M. C., Hoots, K., Blatt, P., Konkle, B., et al. (2006) Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response, Nat. Med., 12, 342-347, https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1358.
Mease, P. J., Hobbs, K., Chalmers, A., El-Gabalawy, H., Bookman, A., Keystone, E., Furst, D. E., Anklesaria, P., and Heald, A. E. (2009) Local delivery of a recombinant adenoassociated vector containing a tumour necrosis factor α antagonist gene in inflammatory arthritis: A phase 1 dose-escalation safety and tolerability study, Ann. Rheum. Dis., 68, 1247-1254, https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.089375.
Russell, S., Bennett, J., Wellman, J. A., Chung, D. C., Yu, Z. F., Tillman, A., Wittes, J., Pappas, J., Elci, O., McCague, S., et al. (2017) Efficacy and safety of voretigene neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in patients with RPE65-mediated inherited retinal dystrophy: a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial, Lancet, 390, 849-860, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31868-8.
Trapani, I. (2019) Adeno-associated viral vectors as a tool for large gene delivery to the retina, Genes (Basel), 10, 287, https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10040287.
Chang, Y. X., Zhao, Y., Pan, S., Qi, Z. P., Kong, W. J., Pan, Y. R., Li, H. R., and Yang, X. Y. (2019) Intramuscular injection of adenoassociated virus encoding human neurotrophic factor 3 and exercise intervention contribute to reduce spasms after spinal cord injury, Neural Plast., 2019, 3017678, https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3017678.
Giannakopoulos, A., Quiviger, M., Stavrou, E., Verras, M., Marie, C., Scherman, D., and Athanassiadou, A. (2019) Efficient episomal gene transfer to human hepatic cells using the pFAR4-S/MAR vector, Mol. Biol. Rep., 46, 3203-3211, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-04777-9.
Gaspar, H. B., Cooray, S., Gilmour, K. C., Parsley, K. L., Zhang, F., Adams, S., Bjorkegren, E., Bayford, J., Brown, L., Davies, E. G., et al. (2011) Immunodeficiency: Hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy for adenosine deaminase-deficient severe combined immunodeficiency leads to long-term immunological recovery and metabolic correction, Sci. Transl. Med., 3, 97ra80, https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3002716.
Kotin, R. M. (2011) Large-scale recombinant adeno-associated virus production, Hum. Mol. Genet., 20, R2-R6, https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr141.
Wu, Z., Asokan, A., and Samulski, R. J. (2006) Adeno-associated virus serotypes: vector toolkit for human gene therapy, Mol. Ther., 14, 316-327, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2006.05.009.
Schaffer, D. V., Koerber, J. T., and Lim, K.-Il (2008) Molecular engineering of viral gene delivery vehicles, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 10, 169-194, https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bioeng.10.061807.160514.
Colella, P., Ronzitti, G., and Mingozzi, F. (2018) Emerging issues in AAV-mediated in vivo gene therapy, Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev., 8, 87-104, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2017.11.007.
Mingozzi, F., Meulenberg, J. J., Hui, D. J., Basner-Tschakarjan, E., Hasbrouck, N. C., Edmonson, S. A., Hutnick, N. A., Betts, M. R., Kastelein, J. J., Stroes, E. S., et al. (2009) AAV-1-mediated gene transfer to skeletal muscle in humans results in dose-dependent activation of capsid-specific T cells, Blood, 114, 2077-2086, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-07-167510.
Lebherz, C., Maguire, A., Tang, W., Bennett, J., and Wilson, J. M. (2008) Novel AAV serotypes for improved ocular gene transfer, J. Gene Med., 10, 375-382, https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.1126.
Ojala, D. S., Amara, D. P., and Schaffer, D. V. (2015) Adeno-associated virus vectors and neurological gene therapy, Neuroscientist, 21, 84-98, https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858414521870.
Sen, D., Balakrishnan, B., Gabriel, N., Agrawal, P., Roshini, V., Samuel, R., Srivastava, A., and Jayandharan, G. R. (2013) Improved adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype 1 and 5 vectors for gene therapy, Sci. Rep., 6, 1832, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01832.
Kattenhorn, L. M., Tipper, C. H., Stoica, L., Geraghty, D. S., Wright, T. L., Clark, K. R., and Wadsworth, S. C. (2016) Adeno-associated virus gene therapy for liver disease, Hum. Gene Ther., 27, 947-961, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2016.160.
McCarty, D. M. (2008) Self-complementary AAV vectors; advances and applications, Mol. Ther., 16, 1648-1656, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2008.171.
Nathwani, A. C., Gray, J. T., Ng, C. Y. C., Zhou, J., Spence, Y., Waddington, S. N., Tuddenham, E. G. D., Kemball-Cook, G., McIntosh, J., Boon-Spijker, M., et al. (2006) Self-complementary adeno-associated virus vectors containing a novel liver-specific human factor IX expression cassette enable highly efficient transduction of murine and nonhuman primate liver, Blood, 107, 2653-2661, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-10-4035.
Nathwani, A. C., Tuddenham, E. G. D., Rangarajan, S., Rosales, C., McIntosh, J., Linch, D. C., Chowdary, P., Riddell, A., Pie, A. J., Harrington, C., et al. (2011) Adenovirus-associated virus vector-mediated gene transfer in hemophilia B, N. Engl. J. Med., 365, 2357-2365, https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1108046.
Mendell, J. R., Al-Zaidy, S., Shell, R., Arnold, W. D., Rodino-Klapac, L. R., Prior, T. W., Lowes, L., Alfano, L., Berry, K., Church, K., et al. (2017) Single-dose gene-replacement therapy for spinal muscular atrophy, N. Engl. J. Med., 377, 1713-1722, https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1706198.
Calcedo, R., Morizono, H., Wang, L., McCarter, R., He, J., Jones, D., Batshaw, M. L., and Wilson, J. M. (2011) Adeno-associated virus antibody profiles in newborns, children, and adolescents, Clin. Vaccine Immunol., 18, 1586-1588, https://doi.org/10.1128/CVI.05107-11.
Erles, K., Sebökovà, P., and Schlehofer, J. R. (1999) Update on the prevalence of serum antibodies (IgG and IgM) to adeno-associated virus (AAV), J. Med. Virol., 59, 406-411, https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-9071(199911)59:3<406::aid-jmv22>3.0.co;2-n.
Li, C., Narkbunnam, N., Samulski, R. J., Asokan, A., Hu, G., Jacobson, L. J., Manco-Johnson, M. L., Monahan, P. E., Riske, B., Kilcoyne, R., et al. (2012) Neutralizing antibodies against adeno-associated virus examined prospectively in pediatric patients with hemophilia, Gene Ther., 19, 288-294, https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.90.
Wright, J. F. (2008) Manufacturing and characterizing AAV-based vectors for use in clinical studies, Gene Ther. 2008 1511, 15, 840-848, https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.65.
Grieger, J. C., and Samulski, R. J. (2012) Adeno-Associated virus Vectorology, Manufacturing, and Clinical Applications, in Methods in Enzymology, Academic Press, https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-386509-0.00012-0.
Schultz, B. R., and Chamberlain, J. S. (2008) Recombinant adeno-associated virus transduction and integration, Mol. Ther., 16, 1189-1199, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2008.103.
Valdmanis, P. N., Lisowski, L., and Kay, M. A. (2012) RAAV-Mediated tumorigenesis: still unresolved after an AAV assault, Mol. Ther., 20, 2014-2017, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2012.220.
El Andari, J., and Grimm, D. (2021) Production, processing, and characterization of synthetic AAV gene therapy vectors, Biotechnol. J., 16, 2000025, https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.202000025.
Bertin, B., Veron, P., Leborgne, C., Deschamps, J. Y., Moullec, S., Fromes, Y., Collaud, F., Boutin, S., Latournerie, V., van Wittenberghe, L., et al. (2020) Capsid-specific removal of circulating antibodies to adeno-associated virus vectors, Sci. Rep., 10, 864, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-57893-z.
Leborgne, C., Barbon, E., Alexander, J. M., Hanby, H., Delignat, S., Cohen, D. M., Collaud, F., Muraleetharan, S., Lupo, D., Silverberg, J., et al. (2020) IgG-cleaving endopeptidase enables in vivo gene therapy in the presence of anti-AAV neutralizing antibodies, Nat. Med., 26, 1096-1101, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-020-0911-7.
Elmore, Z. C., Oh, D. K., Simon, K. E., Fanous, M. M., and Asokan, A. (2020) Rescuing AAV gene transfer from neutralizing antibodies with an IgG-degrading enzyme, JCI Insight, 5, e139881, https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.139881.
Ghosh, A., Yue, Y., Lai, Y., and Duan, D. (2008) A hybrid vector system expands adeno-associated viral vector packaging capacity in a transgene-independent manner, Mol. Ther., 16, 124-130, https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mt.6300322.
Lai, Y., Yue, Y., Liu, M., Ghosh, A., Engelhardt, J. F., Chamberlain, J. S., and Duan, D. (2005) Efficient in vivo gene expression by trans-splicing adeno-associated viral vectors, Nat. Biotechnol., 23, 1435-1439, https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1153.
Chew, W. L., Tabebordbar, M., Cheng, J. K. W., Mali, P., Wu, E. Y., Ng, A. H. M., Zhu, K., Wagers, A. J., and Church, G. M. (2016) A multifunctional AAV-CRISPR-Cas9 and its host response, Nat. Methods, 13, 868-874, https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3993.
Li, J., Sun, W., Wang, B., Xiao, X., and Liu, X. Q. (2008) Protein trans-splicing as a means for viral vector-mediated in vivo gene therapy, Hum. Gene Ther., 19, 958-964, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2008.009.
Stroes, E. S., Nierman, M. C., Meulenberg, J. J., Franssen, R., Twisk, J., Henny, C. P., Maas, M. M., Zwinderman, A. H., Ross, C., Aronica, E., et al. (2008) Intramuscular administration of AAV1-lipoprotein lipaseS447X lowers triglycerides in lipoprotein lipase-deficient patients, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 28, 2303-2304, https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.175620.
Gaudet, D., de Wal, J., Tremblay, K., Déry, S., van Deventer, S., Freidig, A., Brisson, D., and Méthot, J. (2010) Review of the clinical development of alipogene tiparvovec gene therapy for lipoprotein lipase deficiency, Atheroscler. Suppl., 11, 55-60, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosissup.2010.03.004.
Carpentier, A. C., Frisch, F., Labbe, S. M., Gagnon, R., De Wal, J., Greentree, S., Petry, H., Twisk, J., Brisson, D., and Gaudet, D. (2012) Effect of alipogene tiparvovec (aav1-lpls447x) on postprandial chylomicron metabolism in lipoprotein lipase-deficient patients, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 97, 1635-1644, https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2011-3002.
Bennett, J., Ashtari, M., Wellman, J., Marshall, K. A., Cyckowski, L. L., Chung, D. C., McCague, S., Pierce, E. A., Chen, Y., Bennicelli, J. L., et al. (2012) Gene therapy: AAV2 gene therapy readministration in three adults with congenital blindness, Sci. Transl. Med., 4, 120ra15, https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3002865.
Bainbridge, J. W. B., Smith, A. J., Barker, S. S., Robbie, S., Henderson, R., Balaggan, K., Viswanathan, A., Holder, G. E., Stockman, A., Tyler, N., et al. (2008) Effect of gene therapy on visual function in Leber’s congenital amaurosis, N. Engl. J. Med., 358, 2231-2239, https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMOA0802268.
Cideciyan, A. V., Hauswirth, W. W., Aleman, T. S., Kaushal, S., Schwartz, S. B., Boye, S. L., Windsor, E. A. M., Conlon, T. J., Sumaroka, A., Pang, J. J., et al. (2009) Human RPE65 gene therapy for leber congenital amaurosis: persistence of early visual improvements and safety at 1 year, Hum. Gene Ther., 20, 999-1004, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2009.086.
Maguire, A. M., Simonelli, F., Pierce, E. A., Pugh, E. N., Mingozzi, F., Bennicelli, J., Banfi, S., Marshall, K. A., Testa, F., Surace, E. M., et al. (2008) Safety and efficacy of gene transfer for Leber’s congenital amaurosis, N. Engl. J. Med., 358, 2240-2248, https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa0802315.
Cideciyan, A. V., Aleman, T. S., Boye, S. L., Schwartz, S. B., Kaushal, S., Roman, A. J., Pang, J. J., Sumaroka, A., Windsor, E. A. M., Wilson, J. M., et al. (2008) Human gene therapy for RPE65 isomerase deficiency activates the retinoid cycle of vision but with slow rod kinetics, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 105, 15112-15117, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0807027105.
Hauswirth, W. W., Aleman, T. S., Kaushal, S., Cideciyan, A. V., Schwartz, S. B., Wang, L., Conlon, T. J., Boye, S. L., Flotte, T. R., Byrne, B. J., et al. (2008) Treatment of Leber congenital amaurosis due to RPE65 mutations by ocular subretinal injection of adeno-associated virus gene vector: short-term results of a phase I trial, Hum Gene Ther., 19, 979-990, https://doi.org/10.1089/HUM.2008.107.
Jacobson, S. G., Cideciyan, A. V., Ratnakaram, R., Heon, E., Schwartz, S. B., Roman, A. J., Peden, M. C., Aleman, T. S., Boye, S. L., Sumaroka, A., et al. (2012) Gene therapy for leber congenital amaurosis caused by RPE65 mutations: safety and efficacy in 15 children and adults followed up to 3 years, Arch. Ophthalmol., 130, 9-24, https://doi.org/10.1001/archophthalmol.2011.298.
Simonelli, F., Maguire, A. M., Testa, F., Pierce, E. A., Mingozzi, F., Bennicelli, J. L., Rossi, S., Marshall, K., Banfi, S., Surace, E. M., et al. (2010) Gene therapy for Leber’s congenital amaurosis is safe and effective through 1.5 years after vector administration, Mol. Ther., 18, 643-650, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2009.277.
Testa, F., Maguire, A. M., Rossi, S., Pierce, E. A., Melillo, P., Marshall, K., Banfi, S., Surace, E. M., Sun, J., Acerra, C., et al. (2013) Three-year follow-up after unilateral subretinal delivery of adeno-associated virus in patients with leber congenital amaurosis type 2, Ophthalmology, 120, 1283-1291, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.11.048.
Maguire, A. M., High, K. A., Auricchio, A., Wright, J. F., Pierce, E. A., Testa, F., Mingozzi, F., Bennicelli, J. L., Ying, G. shuang, Rossi, S., et al. (2009) Age-dependent effects of RPE65 gene therapy for Leber’s congenital amaurosis: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial, Lancet, 374, 1597-1605, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61836-5.
Boye, S. E., Boye, S. L., Lewin, A. S., and Hauswirth, W. W. (2013) A comprehensive review of retinal gene therapy, Mol. Ther., 21, 509-519, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2012.280.
MacLaren, R. E., Groppe, M., Barnard, A. R., Cottriall, C. L., Tolmachova, T., Seymour, L., Reed Clark, K., During, M. J., Cremers, F. P. M., Black, G. C. M., et al. (2014) Retinal gene therapy in patients with choroideremia: initial findings from a phase 1/2 clinical trial, Lancet, 383, 1129-1137, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62117-0.
Kiss, S., Osborne, A., Hoang, C., and Turpcu, A. (2020) ADVM-022 intravitreal gene therapy for neovascular AMD – results from the phase 1 OPTIC Study, Mol. Ther., 28, 220-221.
Harper, S. Q., Hauser, M. A., DelloRusso, C., Duan, D., Crawford, R. W., Phelps, S. F., Harper, H. A., Robinson, A. S., Engelhardt, J. F., Brooks, S. V., et al. (2002) Modular flexibility of dystrophin: implications for gene therapy of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Nat. Med., 8, 253-261, https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0302-253.
Salva, M. Z., Himeda, C. L., Tai, P. W. L., Nishiuchi, E., Gregorevic, P., Allen, J. M., Finn, E. E., Nguyen, Q. G., Blankinship, M. J., Meuse, L., et al. (2007) Design of tissue-specific regulatory cassettes for high-level rAAV-mediated expression in skeletal and cardiac muscle, Mol. Ther., 15, 320-329, https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mt.6300027.
BRIEF-Solid Biosciences Announces Clinical Hold On SGT-001 Phase I/Ii Clinical Trial | Reuters. URL: https://www.reuters.com/article/brief-solid-biosciences-announces-clinic/brief-solid-biosciences-announces-clinical-hold-on-sgt-001-phase-i-ii-clinical-trial-idINASC09SB8/.
Kay, M. A., Manno, C. S., Ragni, M. V., Larson, P. J., Couto, L. B., McClelland, A., Glader, B., Chew, A. J., Tai, S. J., Herzog, R. W., et al. (2000) Evidence for gene transfer and expression of factor IX in haemophilia B patients treated with an AAV vector, Nat. Genet., 24, 257-261, https://doi.org/10.1038/73464.
Manno, C. S., Chew, A. J., Hutchison, S., Larson, P. J., Herzog, R. W., Arruda, V. R., Tai, S. J., Ragni, M. V., Thompson, A., Ozelo, M., et al. (2003) AAV-mediated factor IX gene transfer to skeletal muscle in patients with severe hemophilia B, Blood, 101, 2963-2972, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-10-3296.
Mingozzi, F., Maus, M. V., Hui, D. J., Sabatino, D. E., Murphy, S. L., Rasko, J. E. J., Ragni, M. V., Manno, C. S., Sommer, J., Jiang, H., et al. (2007) CD18+ T-cell responses to adeno-associated virus capsid in humans, Nat. Med., 13, 419-422, https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1549.
Nathwani, A. C., Gray, J. T., McIntosh, J., Ng, C. Y. C., Zhou, J., Spence, Y., Cochrane, M., Gray, E., Tuddenham, E. G. D., and Davidoff, A. M. (2007) Safe and efficient transduction of the liver after peripheral vein infusion of self-complementary AAV vector results in stable therapeutic expression of human FIX in nonhuman primates, Blood, 109, 1414-1421, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-03-010181.
Meng, Y., Sun, D., Qin, Y., Dong, X., Luo, G., and Liu, Y. (2021) Cell-penetrating peptides enhance the transduction of adeno-associated virus serotype 9 in the central nervous system, Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev., 21, 28-41, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2021.02.019.
Boutin, S., Monteilhet, V., Veron, P., Leborgne, C., Benveniste, O., Montus, M. F., and Masurier, C. (2010) Prevalence of serum IgG and neutralizing factors against adeno-associated virus (AAV) types 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, and 9 in the healthy population: Implications for gene therapy using AAV vectors, Hum. Gene Ther., 21, 704-712, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2009.182.
Kruzik, A., Fetahagic, D., Hartlieb, B., Dorn, S., Koppensteiner, H., Horling, F. M., Scheiflinger, F., Reipert, B. M., and de la Rosa, M. (2019) Prevalence of anti-adeno-associated virus immune responses in international cohorts of healthy donors, Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev., 14, 126-133, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtm.2019.05.014.
Jiang, H., Couto, L. B., Patarroyo-White, S., Liu, T., Nagy, D., Vargas, J. A., Zhou, S., Scallan, C. D., Sommer, J., Vijay, S., et al. (2006) Effects of transient immunosuppression on adenoassociated, virus-mediated, liver-directed gene transfer in rhesus macaques and implications for human gene therapy, Blood, 108, 3321-3328, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-04-017913.
Monahan, P., Walsh, C. E., Konkle, B. A., Powell, J. S., Josephson, N. C., et al. (2015) Update on a phase 1/2 open-label trial of BAX335, an adeno-associated virus 8 (AAV8) vector-based gene therapy program for hemophilia B, J. Thromb. Haemost., 13, 87, https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.12993.
Herzog, R. W. (2015) hemophilia gene therapy: caught between a cure and an immune response, Mol. Ther., 23, 1411-1412, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2015.135.
Ozelo, M. C., Mahlangu, J., Pasi, K. J., Giermasz, A., Leavitt, A. D., Laffan, M., Symington, E., Quon, D. V., Wang, J.-D., Peerlinck, K., et al. (2022) Valoctocogene roxaparvovec gene therapy for hemophilia A, N. Engl. J. Med., 386, 1013-1025, https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMOA2113708.
Jessup, M., Greenberg, B., Mancini, D., Cappola, T., Pauly, D. F., Jaski, B., Yaroshinsky, A., Zsebo, K. M., Dittrich, H., and Hajjar, R. J. (2011) Calcium upregulation by percutaneous administration of gene therapy in cardiac disease (CUPID): A phase 2 trial of intracoronary gene therapy of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase in patients with advanced heart failure, Circulation, 124, 304-313, https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.022889.
Jaski, B. E., Jessup, M. L., Mancini, D. M., Cappola, T. P., Pauly, D. F., Greenberg, B., Borow, K., Dittrich, H., Zsebo, K. M., and Hajjar, R. J. (2009) Calcium upregulation by percutaneous administration of gene therapy in cardiac disease (CUPID trial), a first-in-human phase 1/2 clinical trial, J. Card. Fail., 15, 171-181, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardfail.2009.01.013.
Kaplitt, M. G., Feigin, A., Tang, C., Fitzsimons, H. L., Mattis, P., Lawlor, P. A., Bland, R. J., Young, D., Strybing, K., Eidelberg, D., et al. (2007) Safety and tolerability of gene therapy with an adeno-associated virus (AAV) borne GAD gene for Parkinson’s disease: an open label, phase I trial, Lancet, 369, 2097-2105, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60982-9.
LeWitt, P. A., Rezai, A. R., Leehey, M. A., Ojemann, S. G., Flaherty, A. W., Eskandar, E. N., Kostyk, S. K., Thomas, K., Sarkar, A., Siddiqui, M. S., et al. (2011) AAV2-GAD gene therapy for advanced Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind, sham-surgery controlled, randomised trial, Lancet Neurol., 10, 309-319, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70039-4.
Hwu, W. L., Muramatsu, S. I., Tseng, S. H., Tzen, K. Y., Lee, N. C., Chien, Y. H., Snyder, R. O., Byrne, B. J., Tai, C. H., and Wu, R. M. (2012) Gene therapy for aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency, Sci. Transl. Med., 4, 134ra61, https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3003640.
Lee, N. C., Muramatsu, S. I., Chien, Y. H., Liu, W. S., Wang, W. H., Cheng, C. H., Hu, M. K., Chen, P. W., Tzen, K. Y., Byrne, B. J., et al. (2015) Benefits of neuronal preferential systemic gene therapy for neurotransmitter deficiency, Mol. Ther., 23, 1572-1581, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2015.122.
Tai, C. H., Lee, N. C., Chien, Y. H., Byrne, B. J., Muramatsu, S. I., Tseng, S. H., and Hwu, W. L. (2022) Long-term efficacy and safety of eladocagene exuparvovec in patients with AADC deficiency, Mol. Ther., 30, 509-518, https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YMTHE.2021.11.005.
Alexander, I. E., Cunningham, S. C., Logan, G. J., and Christodoulou, J. (2008) Potential of AAV vectors in the treatment of metabolic disease, Gene Ther., 15, 831-839, https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.64.
Blankinship, M. J., Gregorevic, P., and Chamberlain, J. S. (2006) Gene therapy strategies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy utilizing recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors, Mol. Ther., 13, 241-249, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2005.11.001.
Duan, D. (2016) Systemic delivery of adeno-associated viral vectors, Curr. Opin. Virol., 21, 16-25, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2016.07.006.
Clément, N., and Grieger, J. C. (2016) Manufacturing of recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors for clinical trials, Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev., 3, 16002, https://doi.org/10.1038/mtm.2016.2.
Zhu, J., Huang, X., and Yang, Y. (2009) The TLR9-MyD88 pathway is critical for adaptive immune responses to adenoassociated virus gene therapy vectors in mice, J. Clin. Invest., 119, 2388-2398, https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI37607.
Sands, M. S. (2011) AAV-mediated liver-directed gene therapy, Methods Mol. Biol., 807, 141-157, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-370-7_6.
Saraiva, J., Nobre, R. J., and Pereira de Almeida, L. (2016) Gene therapy for the CNS using AAVs: the impact of systemic delivery by AAV9, J. Control. Release, 241, 94-109, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.09.011.
Mendell, J. R., Sahenk, Z., Lehman, K., Nease, C., Lowes, L. P., Miller, N. F., Iammarino, M. A., Alfano, L. N., Nicholl, A., Al-Zaidy, S., et al. (2020) Assessment of systemic delivery of rAAVrh74.MHCK7.micro-dystrophin in Children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: a nonrandomized controlled trial, JAMA Neurol., 77, 1122-1131, https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1484.
Stein, S., Ott, M. G., Schultze-Strasser, S., Jauch, A., Burwinkel, B., Kinner, A., Schmidt, M., Krämer, A., Schwäble, J., Glimm, H., et al. (2010) Genomic instability and myelodysplasia with monosomy 7 consequent to EVI1 activation after gene therapy for chronic granulomatous disease, Nat. Med., 16, 198-204, https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2088.
Prösen, S., Stein, J., Staak, K., Liebenthal, C., Volk, H. D., and Krüger, D. H. (1996) Inactivation of the very strong HCMV immediate early promoter by DMA CpG methylation in vitro, Biol. Chem. Hoppe. Seyler., 377, 195-201, https://doi.org/10.1515/bchm3.1996.377.3.195.
Brooks, A. R., Harkins, R. N., Wang, P., Qian, H. S., Liu, P., and Rubanyi, G. M. (2004) Transcriptional silencing is associated with extensive methylation of the CMV promoter following adenoviral gene delivery to muscle, J. Gene Med., 6, 395-404, https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.516.
Chandler, R. J., La Fave, M. C., Varshney, G. K., Trivedi, N. S., Carrillo-Carrasco, N., Senac, J. S., Wu, W., Hoffmann, V., Elkahloun, A. G., Burgess, S. M., et al. (2015) Vector design influences hepatic genotoxicity after adeno-associated virus gene therapy, J. Clin. Invest., 125, 870-880, https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI79213.
Kornegay, J. N., Li, J., Bogan, J. R., Bogan, D. J., Chen, C., Zheng, H., Wang, B., Qiao, C., Howard, J. F., and Xiao, X. (2010) Widespread muscle expression of an AAV9 human mini-dystrophin vector after intravenous injection in neonatal dystrophin-deficient dogs, Mol. Ther., 18, 1501-1508, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2010.94.
Lange, A. M., Altynova, E. S., Nguyen, G. N., and Sabatino, D. E. (2016) Overexpression of factor VIII after AAV delivery is transiently associated with cellular stress in hemophilia A mice, Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev., 3, 16064, https://doi.org/10.1038/mtm.2016.64.
Watakabe, A., Ohtsuka, M., Kinoshita, M., Takaji, M., Isa, K., Mizukami, H., Ozawa, K., Isa, T., and Yamamori, T. (2015) Comparative analyses of adeno-associated viral vector serotypes 1, 2, 5, 8 and 9 in marmoset, mouse and macaque cerebral cortex, Neurosci. Res., 93, 144-157, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2014.09.002.
Klein, R. L., Dayton, R. D., Leidenheimer, N. J., Jansen, K., Golde, T. E., and Zweig, R. M. (2006) Efficient neuronal gene transfer with AAV8 leads to neurotoxic levels of tau or green fluorescent proteins, Mol. Ther., 13, 517-527, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2005.10.008.
Follenzi, A., Battaglia, M., Lombardo, A., Annoni, A., Roncarolo, M. G., and Naldini, L. (2004) Targeting lentiviral vector expression to hepatocytes limits transgene-specific immune response and establishes long-term expression of human antihemophilic factor IX in mice, Blood, 103, 3700-3709, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2003-09-3217.
Gernoux, G., Guilbaud, M., Dubreil, L., Larcher, T., Babarit, C., Ledevin, M., Jaulin, N., Planel, P., Moullier, P., and Adjali, O. (2015) Early interaction of adeno-associated virus serotype 8 vector with the host immune system following intramuscular delivery results in weak but detectable lymphocyte and dendritic cell transduction, Hum. Gene Ther., 26, 1-13, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2014.070.
Xiong, W., Wu, D. M., Xue, Y., Wang, S. K., Chung, M. J., Ji, X., Rana, P., Zhao, S. R., Mai, S., and Cepko, C. L. (2019) AAV cis-regulatory sequences are correlated with ocular toxicity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 116, 5785-5794, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1821000116.
Burdett, T., and Nuseibeh, S. (2022) Changing trends in the development of AAV-based gene therapies: a meta-analysis of past and present therapies, Gene Ther., 30, 323-335, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41434-022-00363-0.
Georgiadis, A., Duran, Y., Ribeiro, J., Abelleira-Hervas, L., Robbie, S. J., Sünkel-Laing, B., Fourali, S., Gonzalez-Cordero, A., Cristante, E., Michaelides, M., et al. (2016) Development of an optimized AAV2/5 gene therapy vector for Leber congenital amaurosis owing to defects in RPE65, Gene Ther., 23, 857-862, https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2016.66.
Beltran, W. A., Cideciyan, A. V., Boye, S. E., Ye, G. J., Iwabe, S., Dufour, V. L., Marinho, L. F., Swider, M., Kosyk, M. S., Sha, J., et al. (2017) Optimization of retinal gene therapy for X-linked retinitis pigmentosa due to RPGR mutations, Mol. Ther., 25, 1866-1880, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.05.004.
Crystal, R. G. (2014) Adenovirus: the first effective in vivo gene delivery vector, Hum. Gene Ther., 25, 3-11, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2013.2527.
Benihoud, K., Yeh, P., and Perricaudet, M. (1999) Adenovirus vectors for gene delivery, Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 10, 440-447, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-1669(99)00007-5.
Liu, Q., and Muruve, D. A. (2003) Molecular basis of the inflammatory response to adenovirus vectors, Gene Ther., 10, 935-940, https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302036.
Amalfitano, A., Hauser, M. A., Hu, H., Serra, D., Begy, C. R., and Chamberlain, J. S. (1998) Production and characterization of improved adenovirus vectors with the E1, E2b, and E3 genes deleted, J. Virol., 72, 926-933, https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.72.2.926-933.1998.
Wen, S., Schneider, D. B., Driscoll, R. M., Vassalli, G., Sassani, A. B., and Dichek, D. A. (2000) Second-generation adenoviral vectors do not prevent rapid loss of transgene expression and vector DNA from the arterial wall, Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 20, 1452-1458, https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.20.6.1452.
Sakhuja, K., Connelly, S., Reddy, P. S., Ganesh, S., Cantaniag, F., Pattison, S., Limbach, P., Kayda, D. B., Kadan, M. J., and Kaleko, M. (2003) Optimization of the generation and propagation of gutless adenoviral vectors, Hum. Gene Ther., 14, 243-254, https://doi.org/10.1089/10430340360535797.
Lee, C. S., Bishop, E. S., Zhang, R., Yu, X., Farina, E. M., Yan, S., Zhao, C., Zeng, Z., Shu, Y., Wu, X., et al. (2017) Adenovirus-mediated gene delivery: potential applications for gene and cell-based therapies in the new era of personalized medicine, Genes Dis., 4, 43-63, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2017.04.001.
Rosenfeld, M. A., Siegfried, W., Yoshimura, K., Yoneyama, K., Fukayama, M., Stier, L. E., Pääkkö, P. K., Gilardi, P., Stratford-Perricaudet, L. D., Perricaudet, M., et al. (1991) Adenovirus-mediated transfer of a recombinant α1-antitrypsin gene to the lung epithelium in vivo, Science, 252, 431-434, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2017680.
Jaffe, H. A., Danel, C., Longenecker, G., Metzger, M., Setoguchi, Y., Rosenfeld, M. A., Gant, T. W., Thorgeirsson, S. S., Stratford-Perricaudet, L. D., Perricaudet, M., et al. (1992) Adenovirus-mediated in vivo gene transfer and expression in normal rat liver, Nat. Genet., 1, 372-378, https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0892-372.
Zabner, J., Couture, L. A., Gregory, R. J., Graham, S. M., Smith, A. E., and Welsh, M. J. (1993) Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer transiently corrects the chloride transport defect in nasal epithelia of patients with cystic fibrosis, Cell, 75, 207-216, https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)80063-K.
Rosengart, T. K., Lee, L. Y., Patel, S. R., Sanborn, T. A., Parikh, M., Bergman, G. W., Hachamovitch, R., Szulc, M., Kligfield, P. D., Okin, P. M., et al. (1999) Angiogenesis gene therapy: Phase I assessment of direct intramyocardial administration of an adenovirus vector expressing VEGF121 cDNA to individuals with clinically significant severe coronary artery disease, Circulation, 100, 468-474, https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.100.5.468.
Wilson, J. M. (2018) Lessons Learned from the Gene Therapy Trial for Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency, in Getting to Good: Research Integrity in the Biomedical Sciences, Academic Press.
Wohlfart, C. (1988) Neutralization of adenoviruses: kinetics, stoichiometry, and mechanisms, J. Virol., 62, 2321-2328, https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.62.7.2321-2328.1988.
Hong, S. S., Habib, N. A., Franqueville, L., Jensen, S., and Boulanger, P. A. (2003) Identification of adenovirus (Ad) penton base neutralizing epitopes by use of sera from patients who had received conditionally replicative Ad (Addl1520) for treatment of liver tumors, J. Virol., 77, 10366-10375, https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.77.19.10366-10375.2003.
Muruve, D. A. (2004) The innate immune response to adenovirus vectors, Hum. Gene Ther., 15, 1157-1166, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2004.15.1157.
Doi, K., and Takeuchi, Y. (2015) Gene therapy using retrovirus vectors: vector development and biosafety at clinical trials [in Japanese], Uirusu, 65, 27-36, https://doi.org/10.2222/jsv.65.27.
Ghosh, S., Brown, A. M., Jenkins, C., and Campbell, K. (2020) Viral vector systems for gene therapy: a comprehensive literature review of progress and biosafety challenges, Appl. Biosaf., 25, 7-18, https://doi.org/10.1177/1535676019899502.
Kohn, D. B., and Candotti, F. (2009) Gene therapy fulfilling its promise, N. Engl. J. Med., 360, 518-521, https://doi.org/10.1056/nejme0809614.
Hacein-Bey-Abina, S., Von Kalle, C., Schmidt, M., McCormack, M. P., Wulffraat, N., Leboulch, P., Lim, A., Osborne, C. S., Pawliuk, R., Morillon, E., et al. (2003) LMO2-associated clonal T cell proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCID-X1, Science, 302, 415-419, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1088547.
Uren, A. G., Kool, J., Berns, A., and Van Lohuizen, M. (2005) Retroviral insertional mutagenesis: past, present and future, Oncogene, 24, 7656-7672, https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209043.
Griffith, L. M., Cowan, M. J., Notarangelo, L. D., Kohn, D. B., Puck, J. M., Pai, S. Y., Ballard, B., Bauer, S. C., Bleesing, J. J. H., Boyle, M., et al. (2014) Primary Immune Deficiency Treatment Consortium (PIDTC) report, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 133, 335-347, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.07.052.
Cavazzana-Calvo, M., Payen, E., Negre, O., Wang, G., Hehir, K., Fusil, F., Down, J., Denaro, M., Brady, T., Westerman, K., et al. (2010) Transfusion independence and HMGA2 activation after gene therapy of human β-thalassaemia, Nature, 467, 318-322, https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09328.
Aiuti, A., Biasco, L., Scaramuzza, S., Ferrua, F., Cicalese, M. P., Baricordi, C., Dionisio, F., Calabria, A., Giannelli, S., Castiello, M. C., et al. (2013) Lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy in patients with wiskott-aldrich syndrome, Science, 341, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1233151.
Smart, B. A. (2009) Gene therapy for immunodeficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency, Pediatrics, 124, 447-458, https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-1870AAAA.
Aiuti, A., Slavin, S., Aker, M., Ficara, F., Deola, S., Mortellaro, A., Morecki, S., Andolfi, G., Tabucchi, A., Carlucci, F., et al. (2002) Correction of ADA-SCID by stem cell gene therapy combined with nonmyeloablative conditioning, Science, 296, 2410-2413, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1070104.
Biffi, A., Montini, E., Lorioli, L., Cesani, M., Fumagalli, F., Plati, T., Baldoli, C., Martino, S., Calabria, A., Canale, S., et al. (2013) Lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy benefits metachromatic leukodystrophy, Science, 341, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1233158.
Blaese, R. M., Culver, K. W., Miller, A. D., Carter, C. S., Fleisher, T., Clerici, M., Shearer, G., Chang, L., Chiang, Y., Tolstoshev, P., et al. (1995) T lymphocyte-directed gene therapy for ADA-SCID: Initial trial results after 4 years, Science, 270, 475-480, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.270.5235.475.
Bordignon, C., Notarangelo, L. D., Nobili, N., Ferrari, G., Casorati, G., Panina, P., Mazzolari, E., Maggioni, D., Rossi, C., Servida, P., et al. (1995) Gene therapy in peripheral blood lymphocytes and bone marrow for ADA- immunodeficient patients, Science, 270, 470-475, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.270.5235.470.
Kohn, D. B., Weinberg, K. I., Nolta, J. A., Heiss, L. N., Lenarsky, C., Crooks, G. M., Hanley, M. E., Annett, G., Brooks, J. S., El-Khoureiy, A., et al. (1995) Engraftment of gene-modified umbilical cord blood cells in neonates with adenosine deaminase deficiency, Nat. Med., 1, 1017-1023, https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1095-1017.
Cavazzana-Calvo, M., Hacein-Bey, S., De Saint Basile, G., Gross, F., Yvon, E., Nusbaum, P., Selz, F., Hue, C., Certain, S., Casanova, J. L., et al. (2000) Gene therapy of human severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)-X1 disease, Science, 288, 669-672, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.288.5466.669.
Candotti, F., Shaw, K. L., Muul, L., Carbonaro, D., Sokolic, R., Choi, C., Schurman, S. H., Garabedian, E., Kesserwan, C., Jagadeesh, G. J., et al. (2012) Gene therapy for adenosine deaminase-deficient severe combined immune deficiency: Clinical comparison of retroviral vectors and treatment plans, Blood, 120, 3635-3646, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-02-400937.
Aiuti, A., Cassani, B., Andolfi, G., Mirolo, M., Biasco, L., Recchia, A., Urbinati, F., Valacca, C., Scaramuzza, S., Aker, M., et al. (2007) Multilineage hematopoietic reconstitution without clonal selection in ADA-SCID patients treated with stem cell gene therapy, J. Clin. Invest., 117, 2233-2240, https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI31666.
Gaspar, H. B. (2012) Gene therapy for ADA-SCID: Defining the factors for successful outcome, Blood, 120, 3628-3629, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-08-446559.
Hacein-Bey-Abina, S., von Kalle, C., Schmidt, M., Le Deist, F., Wulffraat, N., McIntyre, E., Radford, I., Villeval, J.-L., Fraser, C. C., Cavazzana-Calvo, M., et al. (2003) A serious adverse event after successful gene therapy for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency, N. Engl. J. Med., 348, 255-256, https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm200301163480314.
Hacein-Bey-Abina, S., Garrigue, A., Wang, G. P., Soulier, J., Lim, A., Morillon, E., Clappier, E., Caccavelli, L., Delabesse, E., Beldjord, K., et al. (2008) Insertional oncogenesis in 4 patients after retrovirus-mediated gene therapy of SCID-X1, J. Clin. Invest., 118, 3132-3142, https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI35700.
Howe, S. J., Mansour, M. R., Schwarzwaelder, K., Bartholomae, C., Hubank, M., Kempski, H., Brugman, M. H., Pike-Overzet, K., Chatters, S. J., De Ridder, D., et al. (2008) Insertional mutagenesis combined with acquired somatic mutations causes leukemogenesis following gene therapy of SCID-X1 patients, J. Clin. Invest., 118, 3143-3150, https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI35798.
Rohdewohld, H., Weiher, H., Reik, W., Jaenisch, R., and Breindl, M. (1987) Retrovirus integration and chromatin structure: Moloney murine leukemia proviral integration sites map near DNase I-hypersensitive sites, J. Virol., 61, 336-343, https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.61.2.336-343.1987.
Vijaya, S., Steffen, D. L., and Robinson, H. L. (1986) Acceptor sites for retroviral integrations map near DNase I-hypersensitive sites in chromatin, J. Virol., 60, 683-692, https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.60.2.683-692.1986.
Cattoglio, C., Facchini, G., Sartori, D., Antonelli, A., Miccio, A., Cassani, B., Schmidt, M., Von Kalle, C., Howe, S., Thrasher, A. J., et al. (2007) Hot spots of retroviral integration in human CD34+ hematopoietic cells, Blood, 110, 1770-1778, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-01-068759.
Cattoglio, C., Pellin, D., Rizzi, E., Maruggi, G., Corti, G., Miselli, F., Sartori, D., Guffanti, A., Di Serio, C., Ambrosi, A., et al. (2010) High-definition mapping of retroviral integration sites identifies active regulatory elements in human multipotent hematopoietic progenitors, Blood, 116, 5507-5517, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-05-283523.
Modlich, U., Navarro, S., Zychlinski, D., Maetzig, T., Knoess, S., Brugman, M. H., Schambach, A., Charrier, S., Galy, A., Thrasher, A. J., et al. (2009) Insertional transformation of hematopoietic cells by self-inactivating lentiviral and gammaretroviral vectors, Mol. Ther., 17, 1919-1928, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2009.179.
Xu, W., Russ, J. L., and Eiden, M. V. (2012) Evaluation of residual promoter activity in γ-retroviral self-inactivating (SIN) vectors, Mol. Ther., 20, 84-90, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2011.204.
Montini, E., Cesana, D., Schmidt, M., Sanvito, F., Ponzoni, M., Bartholomae, C., Sergi, L. S., Benedicenti, F., Ambrosi, A., Di Serio, C., et al. (2006) Hematopoietic stem cell gene transfer in a tumor-prone mouse model uncovers low genotoxicity of lentiviral vector integration, Nat. Biotechnol., 24, 687-696, https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1216.
Hacein-Bey-Abina, S., Pai, S.-Y., Gaspar, H. B., Armant, M., Berry, C. C., Blanche, S., Bleesing, J., Blondeau, J., de Boer, H., Buckland, K. F., et al. (2014) A modified γ-retrovirus vector for X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency, N. Engl. J. Med., 371, 1407-1417, https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1404588.
Touzot, F., Moshous, D., Creidy, R., Neven, B., Frange, P., Cros, G., Caccavelli, L., Blondeau, J., Magnani, A., Luby, J. M., et al. (2015) Faster T-cell development following gene therapy compared with haploidentical HSCT in the treatment of SCID-X1, Blood, 125, 3563-3569, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-12-616003.
Modlich, U., Bohne, J., Schmidt, M., Von Kalle, C., Knöss, S., Schambach, A., and Baum, C. (2006) Cell-culture assays reveal the importance of retroviral vector design for insertional genotoxicity, Blood, 108, 2545-2553, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-08-024976.
Cavazza, A., Cocchiarella, F., Bartholomae, C., Schmidt, M., Pincelli, C., Larcher, F., and Mavilio, F. (2013) Self-inactivating MLV vectors have a reduced genotoxic profile in human epidermal keratinocytes, Gene Ther., 20, 949-957, https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.18.
Boztug, K., Schmidt, M., Schwarzer, A., Banerjee, P. P., Díez, I. A., Dewey, R. A., Böhm, M., Nowrouzi, A., Ball, C. R., Glimm, H., et al. (2010) Stem-cell gene therapy for the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, N. Engl. J. Med., 363, 1918-1927, https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMOA1003548.
Braun, C. J., Boztug, K., Paruzynski, A., Witzel, M., Schwarzer, A., Rothe, M., Modlich, U., Beier, R., Göhring, G., Steinemann, D., et al. (2014) Gene therapy for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome-long-term efficacy and genotoxicity, Sci. Transl. Med., 6, https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3007280.
Naldini, L., Blömer, U., Gallay, P., Ory, D., Mulligan, R., Gage, F. H., Verma, I. M., and Trono, D. (1996) In vivo gene delivery and stable transduction of nondividing cells by a lentiviral vector, Science, 272, 263-267, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.272.5259.263.
Zhu, Y., Feuer, G., Day, S. L., Wrzesinski, S., and Planelles, V. (2001) Multigene lentiviral vectors based on differential splicing and translational control, Mol. Ther., 4, 375-382, https://doi.org/10.1006/mthe.2001.0469.
Yu, X., Zhan, X., D’Costa, J., Tanavde, V. M., Ye, Z., Peng, T., Malehorn, M. T., Yang, X., Civin, C. I., and Cheng, L. (2003) Lentiviral vectors with two independent internal promoters transfer high-level expression of multiple transgenes to human hematopoietic stem-progenitor cells, Mol. Ther., 7, 827-838, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1525-0016(03)00104-7.
Tian, J., and Andreadis, S. T. (2009) Independent and high-level dual-gene expression in adult stem-progenitor cells from a single lentiviral vector, Gene Ther., 16, 874-884, https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2009.46.
Abordo-Adesida, E., Follenzi, A., Barcia, C., Sciascia, S., Castro, M. G., Naldini, L., and Lowenstein, P. R. (2005) Stability of lentiviral vector-mediated transgene expression in the brain in the presence of systemic antivector immune responses, Hum. Gene Ther., 16, 741-751, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2005.16.741.
Baekelandt, V., Eggermont, K., Michiels, M., Nuttin, B., and Debyser, Z. (2003) Optimized lentiviral vector production and purification procedure prevents immune response after transduction of mouse brain, Gene Ther., 10, 1933-1940, https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302094.
Vigna, E., Cavalieri, S., Ailles, L., Geuna, M., Loew, R., Bujard, H., and Naldini, L. (2002) Robust and efficient regulation of transgene expression in vivo by improved tetracycline-dependent lentiviral vectors, Mol. Ther., 5, 252-261, https://doi.org/10.1006/mthe.2002.0542.
Brown, B. D., Venneri, M. A., Zingale, A., Sergi, L. S., and Naldini, L. (2006) Endogenous microRNA regulation suppresses transgene expression in hematopoietic lineages and enables stable gene transfer, Nat. Med., 12, 585-591, https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1398.
Duisit, G., Conrath, H., Saleun, S., Folliot, S., Provost, N., Cosset, F. L., Sandrin, V., Moullier, P., and Rolling, F. (2002) Five recombinant Simian immunodeficiency virus pseudotypes lead to exclusive transduction of retinal pigmented epithelium in rat, Mol. Ther., 6, 446-454, https://doi.org/10.1006/mthe.2002.0690.
Beard, B. C., Dickerson, D., Beebe, K., Gooch, C., Fletcher, J., Okbinoglu, T., Miller, D. G., Jacobs, M. A., Kaul, R., Kiem, H. P., et al. (2007) Comparison of HIV-derived lentiviral and MLV-based gammaretroviral vector integration sites in primate repopulating cells, Mol. Ther., 15, 1356-1365, https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mt.6300159.
Walters, M. C., Rasko, J., Hongeng, S., Kwiatkowski, J., Schiller, G. J., Kletzel, M., Ho, P. J., Vichinsky, E., von Kalle, C., Cavazzana, M., et al. (2015) Update of results from the Northstar Study (HGB-204): a phase 1/2 study of gene therapy for beta-Thalassemia major via transplantation of autologous hematopoietic stem cells transduced ex-vivo with a lentiviral beta AT87Q-globin vector (LentiGlobin BB305), Blood, 126, 201-201, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v126.23.201.201.
Cavazzana, M., Ribeil, J.-A., Payen, E., Suarez, F., Beuzard, Y., Touzot, F., Cavallesco, R., Lefrere, F., Chretien, S., Bourget, P., et al. (2015) Outcomes of gene therapy for severe sickle disease and beta-thalassemia major via transplantation of autologous hematopoietic stem cells transduced ex vivo with a lentiviral beta AT87Q-globin vector, Blood, 126, 202-202, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v126.23.202.202.
Malik, P. (2016) Gene therapy for hemoglobinopathies: tremendous successes and remaining caveats, Mol. Ther., 24, 668-670, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2016.57.
Cartier, N., and Aubourg, P. (2010) Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Gene Therapy in X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy, Brain Pathol., 20, 857-862, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2010.00394.x.
Kohn, D. B., Shaw, K. L., Garabedian, E., Carbonaro-Sarracino, D. A., Moore, T. B., De Oliveira, S. N., Crooks, G. M., Tse, J., Shupien, S., Terrazas, D., et al. (2019) Lentiviral gene therapy with autologous hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) for the treatment of severe combined immune deficiency due to adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA-SCID): results in an expanded cohort, Blood, 134, 3345-3345, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2019-123432.
Gaspar, H. B., Buckland, K. F., Rivat, C., Himoudi, N., Gilmour, K. C., and et al (2014) Immunological and metabolic correction after lentiviral vector mediated haematopoietic stem cell gene therapy for ADA deficiency, Hum. Gene Ther., Conference: Annual Conference of the British-Society-for-Gene-and-Cell-Therapy, Vol. 25.
Cicalese, M. P., and Aiuti, A. (2015) Clinical applications of gene therapy for primary immunodeficiencies, Hum. Gene Ther., 26, 210-219, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2015.047.
Qasim, W., and Gennery, A. R. (2014) Gene therapy for primary immunodeficiencies: Current status and future prospects, Drugs, 74, 963-969, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0223-7.
Ferrua, F., Cicalese, M. P., Galimberti, S., Scaramuzza, S., Giannelli, S., Pajno, R., Dionisio, F., Biasco, L., Castiello, M. C., Casiraghi, M., et al. (2015) Safety and clinical benefit of lentiviral hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, Blood, 126, 259-259, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v126.23.259.259.
Chu, J. I., Henderson, L. A., Armant, M., Male, F., Dansereau, C. H., MacKinnon, B., Burke, C. J., Cavanaugh, M. E., London, W. B., Barlan, I. B., et al. (2015) Gene therapy using a self-inactivating lentiviral vector improves clinical and laboratory manifestations of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, Blood, 126, 260-260, https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.v126.23.260.260.
Zhao, Z., Anselmo, A. C., and Mitragotri, S. (2022) Viral vector-based gene therapies in the clinic, Bioeng. Transl. Med., 7, e10258, https://doi.org/10.1002/btm2.10258.
Raman, S. S., Hecht, J. R., and Chan, E. (2019) Talimogene laherparepvec: review of its mechanism of action and clinical efficacy and safety, Immunotherapy, 11, 705-723, https://doi.org/10.2217/imt-2019-0033.
Pearson, S., Jia, H., and Kandachi, K. (2004) China approves first gene therapy., Nat. Biotechnol., 22, 3-4, https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0104-3.
Xia, Y., Li, X., and Sun, W. (2020) Applications of recombinant adenovirus-p53 gene therapy for cancers in the clinic in China, Curr. Gene Ther., 20, 127-141, https://doi.org/10.2174/1566523220999200731003206.
Liang, M. (2018) Oncorine, the world first oncolytic virus medicine and its update in China, Curr. Cancer Drug Targets, 18, 171-176, https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009618666171129221503.
Gordon, E. M., and Hall, F. L. (2010) Rexin-G, a targeted genetic medicine for cancer, Expert Opin. Biol. Ther., 10, 819-832, https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2010.481666.
Chawla, S. P., Bruckner, H., Morse, M. A., Assudani, N., Hall, F. L., and Gordon, E. M. (2019) A phase I-II study using rexin-G tumor-targeted retrovector encoding a dominant-negative cyclin G1 inhibitor for advanced pancreatic cancer, Mol. Ther. Oncolytics, 12, 56-67, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2018.12.005.
Chawla, S. P., Chua, V. S., Fernandez, L., Quon, D., Saralou, A., Blackwelder, W. C., Hall, F. L., and Gordon, E. M. (2009) Phase I/II and phase II studies of targeted gene delivery in vivo: intravenous rexin-g for chemotherapy-resistant sarcoma and osteosarcoma, Mol. Ther., 17, 1651-1657, https://doi.org/10.1038/mt.2009.126.
Mueller, C., Gernoux, G., Gruntman, A. M., Borel, F., Reeves, E. P., Calcedo, R., Rouhani, F. N., Yachnis, A., Humphries, M., Campbell-Thompson, M., et al. (2017) 5 Year expression and neutrophil defect repair after gene therapy in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, Mol. Ther., 25, 1387-1394, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.029.
Bennett, J., Wellman, J., Marshall, K. A., McCague, S., Ashtari, M., DiStefano-Pappas, J., Elci, O. U., Chung, D. C., Sun, J., Wright, J. F., et al. (2016) Safety and durability of effect of contralateral-eye administration of AAV2 gene therapy in patients with childhood-onset blindness caused by RPE65 mutations: a follow-on phase 1 trial, Lancet, 388, 661-672, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30371-3.
George, L. A., Sullivan, S. K., Giermasz, A., Rasko, J. E. J., Samelson-Jones, B. J., Ducore, J., Cuker, A., Sullivan, L. M., Majumdar, S., Teitel, J., et al. (2017) Hemophilia B gene therapy with a high-specific-activity factor IX variant, N. Engl. J. Med., 377, 2215-2227, https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1708538.
Dicks, M. D. J., Spencer, A. J., Edwards, N. J., Wadell, G., Bojang, K., Gilbert, S. C., Hill, A. V. S., and Cottingham, M. G. (2012) A novel chimpanzee adenovirus vector with low human seroprevalence: improved systems for vector derivation and comparative immunogenicity, PLoS One, 7, e40385, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0040385.
Guo, J., Mondal, M., and Zhou, D. (2018) Development of novel vaccine vectors: chimpanzee adenoviral vectors, Hum. Vaccines Immunother., 14, 1679-1685, https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2017.1419108.
Tatsis, N., and Ertl, H. C. J. (2004) Adenoviruses as vaccine vectors, Mol. Ther., 10, 616-629, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.07.013.
Ginn, S. L., Amaya, A. K., Alexander, I. E., Edelstein, M., and Abedi, M. R. (2018) Gene therapy clinical trials worldwide to 2017: an update, J. Gene Med., 20, e3015, https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.3015.
Stirnadel-Farrant, H., Kudari, M., Garman, N., Imrie, J., Chopra, B., Giannelli, S., Gabaldo, M., Corti, A., Zancan, S., Aiuti, A., et al. (2018) Gene therapy in rare diseases: the benefits and challenges of developing a patient-centric registry for Strimvelis in ADA-SCID, Orphanet J. Rare Dis., 13, 49, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-018-0791-9.
Milone, M. C., and O’Doherty, U. (2018) Clinical use of lentiviral vectors, Leukemia, 32, 1529-1541, https://doi.org/10.1038/S41375-018-0106-0.
Zufferey, R., Dull, T., Mandel, R. J., Bukovsky, A., Quiroz, D., Naldini, L., and Trono, D. (1998) Self-inactivating lentivirus vector for safe and efficient in vivo gene delivery, J. Virol., 72, 9873-9880, https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.72.12.9873-9880.1998.
McGarrity, G. J., Hoyah, G., Winemiller, A., Andre, K., Stein, D., Blick, G., Greenberg, R. N., Kinder, C., Zolopa, A., Binder-Scholl, G., et al. (2013) Patient monitoring and follow-up in lentiviral clinical trials, J. Gene Med., 15, 78-82, https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.2691.
Baldo, A., den Akker, E., Bergmans, H., Lim, F., and Pauwels, K. (2014) General considerations on the biosafety of virus-derived vectors used in gene therapy and vaccination, Curr. Gene Ther., 13, 385-394, https://doi.org/10.2174/15665232113136660005.
Cesana, D., Sgualdino, J., Rudilosso, L., Merella, S., Naldini, L., and Montini, E. (2012) Whole transcriptome characterization of aberrant splicing events induced by lentiviral vector integrations, J. Clin. Invest., 122, 1667-1676, https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI62189.
Touw, I. P., and Erkeland, S. J. (2007) Retroviral insertion mutagenesis in mice as a comparative oncogenomics tool to identify disease genes in human leukemia, Mol. Ther., 15, 13-19, https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mt.6300040.
Suerth, J. D., Labenski, V., and Schambach, A. (2014) Alpharetroviral vectors: from a cancer-causing agent to a useful tool for human gene therapy, Viruses, 6, 4811-4838, https://doi.org/10.3390/v6124811.
Moiani, A., Paleari, Y., Sartori, D., Mezzadra, R., Miccio, A., Cattoglio, C., Cocchiarella, F., Lidonnici, M. R., Ferrari, G., and Mavilio, F. (2012) Lentiviral vector integration in the human genome induces alternative splicing and generates aberrant transcripts, J. Clin. Invest., 122, 1653-1666, https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI61852.
Emery, D. W. (2011) The use of chromatin insulators to improve the expression and safety of integrating gene transfer vectors, Hum. Gene Ther., 22, 761-774, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2010.233.
David, R. M., and Doherty, A. T. (2017) Viral vectors: the road to reducing genotoxicity, Toxicol. Sci., 155, 315-325, https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfw220.
Huang, X., and Yang, Y. (2009) Innate immune recognition of viruses and viral vectors, Hum. Gene Ther., 20, 293-301, https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2008.141.
Calcedo, R., Vandenberghe, L. H., Gao, G., Lin, J., and Wilson, J. M. (2009) Worldwide epidemiology of neutralizing antibodies to adeno-associated viruses, J. Infect. Dis., 199, 381-390, https://doi.org/10.1086/595830.
Bubela, T., Boch, R., and Viswanathan, S. (2019) Recommendations for regulating the environmental risk of shedding for gene therapy and oncolytic viruses in Canada, Front. Med., 6, 58, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2019.00058.
Schenk-Braat, E. A. M., van Mierlo, M. K. B., Wagemaker, G., Bangma, C. H., and Kaptein, L. C. M. (2007) An Inventory of Shedding Data from Clinical Gene Therapy Trials, J. Gene Med., 9, 910-921, https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.1096.
Blind, J. E., McLeod, E. N., and Campbell, K. J. (2019) Viral-mediated gene therapy and genetically modified therapeutics: A primer on biosafety handling for the health-system pharmacist, Am. J. Heal. Pharm., 76, 795-802, https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/zxz056.
The Lancet Diabets & Endocrinology (2019) Spotlight on rare diseases, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol., 7, 75, https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(19)30006-3.
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 22-14-20046). A.D.E. was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 22-14-20046). E.M., A.G., A.K., and R.A.I. were supported by the internal projects GTH-RND-2011 and GTH-RND-2112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.M. manuscript concept, writing and editing, preparation of figures; A.G. clinical data analysis and preparation of figures; A.E. manuscript writing, R.I. manuscript editing, A.K. manuscript concept and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. This article does not contain description of studies with the involvement of humans or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note. Pleiades Publishing remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minskaia, E., Galieva, A., Egorov, A.D. et al. Viral Vectors in Gene Replacement Therapy. Biochemistry Moscow 88, 2157–2178 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297923120179
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297923120179