Abstract
Background and Objective: Arterial hypertension is a prime cause of morbidity and mortality in the general population. Pharmacological treatment has limitations resulting from drug side effects, costs, and patient compliance. The aim of this study was to investigate whether traditional Chinese medicine acupuncture is able to lower blood pressure.
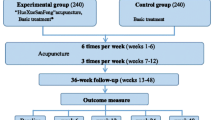
Design: A single blind randomised controlled clinical trial. Participants: 160 outpatients (age, 58 ± 8 years; 78 men) with uncomplicated arterial hypertension.
Interventions: 6-week course of active acupuncture or sham acupuncture (22 sessions of 30 minutes duration).
Main outcome measures: Primary outcome parameters were mean 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure levels after the treatment course and 3 and 6 months later.
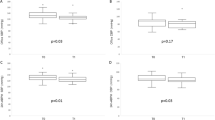
Results: One hundred forty patients finished the treatment course (72 with active treatment, 68 with sham treatment). There was a significant (P < 0.001) difference in post treatment blood pressures adjusted for baseline values between the active and sham acupuncture groups at the end of treatment. For the primary outcome, the difference between treatment groups amounted to 6.4 mm Hg (95% CI, 3.5 to 9.2) and 3.7 mm Hg (95% CI, 1.6 to 5.8) for 24-hour systolic and diastolic blood pressures, respectively. In the active acupuncture group, mean 24-hour ambulatory systolic and diastolic blood pressures decreased significantly after treatment by 5.4 mm Hg (95% CI, 3.2 to 7.6) and 3.0 mm Hg (95% CI, 1.5 to 4.6), respectively. At 3 and 6 months, mean systolic and diastolic blood pressures returned to pre-treatment levels in the active treatment group.
Conclusions: Acupuncture according to traditional Chinese medicine, but not sham acupuncture, after 6 weeks of treatment significantly lowered mean 24-hour ambulatory blood pressures; the effect disappeared after cessation of acupuncture treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Macklin EA et al. Stop Hypertension With the Acupuncture Research Program (SHARP) Hypertension. 2006;48:838
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brinkhaus, B. Akupunktur bei Patienten mit arterieller Hypertonie. Dtsch Z Akupunkt 50, 46–47 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1078/0415-6412-00288
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1078/0415-6412-00288