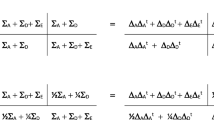Abstract
Different instruments can be used in the assessment of psychopathology in young children. In the present study the psychometric properties of a subset of items of the Devereux Child Behavior (DCB) rating scale were evaluated and the contribution of genetic and environmental influences to the variance of derived problem behavior scales was estimated. Maternal and paternal ratings were obtained in about 7600 5-year-old Dutch twin pairs. Six problem scales were derived from exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis and designated as emotional lability, aggressive behavior, attention problems, anxiety problems, physical coordination problems, and dependency. Univariate genetic analyses of the problem scales yielded large additive genetic effects. Heritability estimates ranged from 40% for aggressive behavior to 81% for attention problems. Shared environmental influences were found for aggressive behavior, anxiety problems, dependency, and emotional lability. Rater contrast and/or sibling interaction effects were found for attention problems and physical coordination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1995). Empirically based assessment and taxonomy: Applications to clinical research. Psychol. Assess. 7:261-274.
Achenbach, T. M., McConaughy, S. H., and Howell, C. T. (1987). Child/adolescent behavioral and emotional problems: Implications of cross-informant correlations for situational specificity. Psychol. Bull. 101:213-232.
American Psychiatric Association. (1996). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, DSM-IV. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association.
Bartels, M., Hudziak, J. J., Boomsma, D. I., Rietveld, M. J. H., Van Beijsterveldt, C. E. M., and Van den Oord, E. J. C. G. (2003). A study of parent ratings of internalizing and externalizing problem behavior in 12-year-old twins. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 42:1351-1359.
Bartels, M., van den Oord, E. J., Hudziak, J. J., Rietveld, M. J. H., van Beijsterveldt, C. E. M., and Boomsma, D. I. Genetic and environmental mechanisms underlying stability and change in problem behaviors at ages 3, 7, 10, and 12. (submitted).
Bentler, P. M., and Dudgeon, P. (1996). Covariance structure analysis: Statistical practice, theory, and directions. Ann. Rev. Psychol. 47:563-592.
Boomsma, D. I. (1998). Twin registers in Europe: An overview. Twin Res. 1:34-51.
Boomsma, D. I., Vink, J. M., van Beijsterveldt, C. E. M., De Geus, E. J. C., Beem, L., and Mulder, E. J. C. M. (2002). Netherlands Twin Register: A focus on longitudinal research. Twin Res. 5:1-6.
Carey, G. (1986). Sibling imitation and contrast effects. Behav. Genet. 16:319-341.
Eaves, L. J. (1976). A model of sibling effects in man. Heredity 36:206-214.
Eaves, L., Rutter, M., Silberg, J. L., Shillady, L., Maes, H., and Pickles, A. (2000). Genetic and environmental causes of covariation in interview assessments of disruptive behavior in child and adolescent twins. Behav. Genet. 30:321-334.
Eaves, L. J., Silberg, J. L., Meyer, J. M., and Maes, H. H. (1997). Genetics and developmental psychopathology. II. The main effects of genes and environment on behavioral problems in the Virginia Twin Study of adolescent behavioral development. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 38:965-980.
Edelbrock, C., Rende, R., Plomin, R., and Thompson, L. A. (1995). A twin study of competence and problem behavior in childhood and early adolescence. J. Child Psychol. Psychiat. Allied Discipl. 36:775-785.
Eley, T. C. (1999). Behavioral genetics as a tool for developmental psychology: Anxiety and depression in children and adolescents. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2:21-36.
Eley, T. C., Lichtenstein, P., and Stevenson, J. (1999). Sex differences in the etiology of aggressive and nonaggressive antisocial behavior: Results from two twin studies. Child Dev. 70:155-168.
Eley, T. C., and Stevenson, J. (1999). Using genetic analyses to clarify the distinction between depressive and anxious symptoms in children. J. Abnor. Child Psychol. 27:105-114.
Feigon, S. A., Waldman, I. D., Levy, F., and Hay, D. A. (2001). Genetic and environmental influences on separation anxiety disorder symptoms and their moderation by age and sex. Behav. Genet. 31:403-411.
Gjone, H., and Novik, T. S. (1995). Parental ratings of behaviour problems: A twin and general population comparison. J. Child Psychol. Psychiat. Allied Discipl. 36:1213-1224.
Gjone, H., Stevenson, J., Sundet, J. M., and Eilertsen, D. E. (1996). Changes in heritability across increasing levels of behavior problems in young twins. Behav. Genet. 26:419-426.
Goldsmith, H. H. (1991). A zygosity questionnaire for young twins: A research note. Behav. Genet. 21:257-270.
Hudziak, J. J. (2001). The role of phenotypes (diagnoses) in genetic studies of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and related child psychopathology. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 10:279-297.
Hudziak, J. J., Rudiger, L. P., Neale, M. C., Heath, A. C., and Todd, R. D. (2000). A twin study of inattentive, aggressive, and anxious/depressed behaviors. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 39:469-476.
Hudziak, J. A., van Beijsterveldt, C. E. M., Bartels, M., Rietveld, M. J. H., Rettew, D. C., Derks, E. M., and Boomsma, D. I. (2003). Individual differences in aggression: Genetic analyses by age, gender, and informant in 3-, 7-, and 10-year-old Dutch twins. Behav. Genet. 33:571-585.
Jöreskog, K. G., and Sörbom, D. I. (1989). LISREL 7: A guide to the Program and Applications. Chicago: SPSS Inc.
Jöreskog, K. G., and Sörbom, D. I. (1999). LISREL 8.3. Chicago: Scientific Software International.
Kuntsi, J., Gayan, J., and Stevenson, J. (2000). Parents' and teachers' ratings of problem behaviours in children: Genetic and contrast effects. Twin Res. 3:251-258.
Leve, L. D., Winebarger, A. A., Fagot, B. I., Reid, J. B., and Goldsmith, H. H. (1998). Environmental and genetic variance in children's observed and reported maladaptive behavior. Child Dev. 69:1286-1298.
Martin, N., Scourfield, J., and McGuffin, P. (2002). Observer effects and heritability of childhood attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder symptoms. Br. J. Psychiatry 180:260-265.
Miles, D. R., and Carey, G. (1997). Genetic and environmental archictecture of human aggression. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 72:207-217.
Nadder, T. S., Silberg, J. L., Eaves, L. J., Maes, H. H., and Meyer, J. M. (1998). Genetic effects on ADHD symptomatology in 7-to 13-year-old twins: Results from a telephone survey. Behav. Genet. 28:83-99.
Nadder, T. S., Silberg, J. L., Rutter, M., Maes, H. H., and Eaves, L. J. (2001). Comparison of multiple measures of ADHD symptomatology: A multivariate genetic analyses. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 42:475-486.
Neale, M. C., Boker, S. M., Xie, G., and Maes, H. H. (1999). Mx: Statistical Modeling, 5th ed. Richmond, VA: Department of Psychiatry, Virginia Commonwealth University.
Neale, M. C., and Cardon, L. R. (1992). Methodology for Genetic Studies of Twins and Families. Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Pfefferbaum, A., Mathalon, D., Sullivan, E., Rawles, J., Zipursky, R., and Lim, K. (1994). A quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study of changes in brain morphology form infancy to late adulthood. Arch. Neurol. 51:874-887.
Rice, F., Gordon, H., and Thapar, A. (2002). The genetic aetiology of childhood depression: A review. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 43:65-79.
Rietveld, M. J. H., Hudziak, J. J., Bartels, M., Van Beijsterveldt, C. E. M., and Boomsma, D. I. (2003). Heritability of attention problems in children. I. Cross-sectional results from a study of twins, age 3–12 years. Am. J. Med. Genet. 117:102-113.
Rietveld, M. J. H., Hudziak, J. A., Bartels, M., van Beijsterveldt, C. E. M., and Boomsma, D. I. Heritability of attention problems in children. II. Longitudinal results from a study of twins, age 3 to 12. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry.Author: Please supply missing information.
Rietveld, M. J. H., Vander Valk, J. C., Bongers, I. L., Stroet, T. M., Slagboom, P. E., and Boomsma, D. I. (2000). Zygosity diagnosis in young twins by parental report. Twin Res. 3:134-141.
Rutter, M., Silberg, J., O'Connor, T., and Simonoff, E. (1999). Genetics and child psychiatry. I advances in quantitative and molecular genetics. J. Child Psychol. Psychiat. Allied Discipl. 40:3-18.
Schmitz, S., Fulker, D. W., and Mrazek, D. A. (1995). Problem behavior in early and middle childhood: An initial behavior genetic analysis. J. Child Psychol. Psychiat. Allied Discipl. 36:1443-4458.
Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Hervas, A., Silberg, J. L., Rutter, M., and Eaves, L. (1998). Genetic influences on childhood hyperactivity: Contrast effects imply parental rating bias, not sibling interaction. Psychol. Med. 28:825-837.
Simonoff, E., Pickles, A., Hewitt, J., Silberg, J., Rutter, M., Loeber, R., Meyer, J., Neale, M., and Eaves, L. (1995). Multiple raters of disruptive child behavior: Using a genetic strategy to examine shared views and bias. Behav. Genet. 25:311-326.
Spivack, G., and Spotts, J. (1966). The Devereux Child Behavior (DCB) Rating Scale. Devon, A: The Devereux Foundation.
Thapar, A., and McGuffin, P. (1995). Are anxiety symptoms in childhood heritable? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 36:439-447.
van Baal, G. C., Boomsma, D. I., and de Geus, E. J. (2001). Longitudinal genetic analysis of EEG coherence in young twins. Behav. Genet. 31:637-651.
Van den Oord, E. J., Verhulst, F. C., and Boomsma, D. I. (1996). A genetic study of maternal and paternal ratings of problem behaviors in 3-year-old twins. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 105:349-357.
Van der Valk, J. C., Van den Oord, E., Verhulst, F. C., and Boomsma, D. I. (2003). Genetic and environmental contributions to stability and change in children's internalizing and externalizing problems. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 42:1-9.
Van der Valk, J. C., Van den Oord, E. J., Verhulst, F. C., and Boomsma, D. (2001). Using parental ratings to study the etiology of 3-year-old twins' problem behaviors: Different views or rater bias? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 42:921-931.
Van der Valk, J. C., Verhulst, F. C., Stroet, T. M., and Boomsma, D. I. (1998). Quantitative genetic analysis of internalising and externalising problems in a large sample of 3-year-old twins. Twin Res. 1:25-33.
Verhulst, F., and Van der Ende, J. (2001). Rating scales. In M., Rutter and E. A., Taylor (eds.), Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 4th ed. (pp. 70-86). Oxford: Blackwell Science.
Zahn-Waxler, C., Schmitz, S., Fulker, D., Robinson, J., and Emde, R. (1996). Behavior problems in 5-year-old monozygotic and dizygotic twins: Genetic and environmental influences, patterns of regulation, and internalization of control. Dev. Psychopathol. 8:103-122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Beijsterveldt, C.E.M., Verhulst, F.C., Molenaar, P.C.M. et al. The Genetic Basis of Problem Behavior in 5-Year-Old Dutch Twin Pairs. Behav Genet 34, 229–242 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BEGE.0000017869.30151.fd
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BEGE.0000017869.30151.fd