Abstract
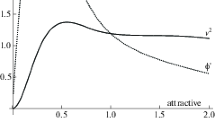
If one attributes to each component i of a gravitational system a dimensionless parameter ψ i equal to the ratio of its relative mass (with respect to the mass of the system) to its relative position (with respect to a generally defined radius) and sums up the ψ i values of all components outside the central core, one obtains a mass distribution index Σψ of the order of unity irrespective of the size or the type of the system. In the case of spiral galaxies (and probable other galactic systems) this property applies not only to the whole galaxy, but also to the matter inside any radius larger than the core radius. The mass distribution index in these systems has a maximum Σψ* at a certain radius r *, which strongly correlates with the surface brightness at r * in galaxies with similar mass to light ratio. The gravitational acceleration of all galaxies at r * divided by (Σψ*)2 is constant and approximately equal to MOND acceleration parameter. Also, at this radius all galaxies have a surface temperature of the order of the temperature of the cosmic microwave background radiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buote, D.A. and Canizalez, C.R.: 1994, Astrophys. J. 427, 86.
Cretton, N., Rix, H.W. and de Zeeuw, P.T.: 2000, Preprintastro-ph/0001506.
Geller, M.J., Diaferio, A. and Kurtz, M.J.: 1999, Preprintastro-ph/ 9903305.
Gerbal, D., Durret, F., Lachiere-Rey, M. and Lima-Neto, G.: 1992, Astron. Astrophys. 262, 395.
Harrison, E.R.: 1987, Darkness at Night, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Knutsen, H.: 1997, Eur. J. Phys. 18, 295.
Krauss, L.M.: 2003, Preprintastro-ph/0301012.
Lang, K.R.: 1992, Astrophysical Data Planets and Stars, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Leonard, P.J.T., Richer, B.H. and Fahlman, G.G.: 1992, Astron. J. 104, 2104.
Lynden-Bell, D. and Wood, R.: 1968, Mon. Not. R. Astr. Soc. 138, 495.
Mathewson, D.S., Ford, V.L. and Buchhorn, M.: 1992, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 81, 413.
McGaugh, S.S., Rubin, V.C. and de Blok, W.J.G.: 2001, Preprintastro-ph/0107326.
Milgrom, M.: 1983, Astrophys. J. 270, 365.
Peebles, P.J.E.: 1993, Principles of Physical Cosmology, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ.
Persic, M. and Salucci, P.: 1995, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 99, 501.
Persic, M., Salucci, P. and Stel, F.: 1996, MNRAS 281, 27.
Saslaw, W.C.: 1985, Gravitational Physics of Stellar and Galactic Systems, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Swaters, R.A., Madore, B.F. and Trewhella, M.: 2000, Preprintastro-ph/0001277.
Tully, R.B. and Fisher, J.R.: 1977, Astron. Astrophy s. 54, 661.
Turner, M.S.: 1999, Preprintastro-ph/ 9904051.
van den Bosch, F.C. and Swaters, R.A.: 2000, Preprintastro-ph/0006048.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinculescu, A. On a Property of Gravitational Systems. Astrophysics and Space Science 293, 423–432 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ASTR.0000044621.34621.8c
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:ASTR.0000044621.34621.8c