Abstract
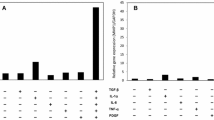
To gain a better understanding of the mechanisms that control the repair process in the injured liver, the actions of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and protein kinase A (PKA) were studied. Normal rat liver cells (clone 9) were grown to confluence. Standardized excisional wounds were made with a razor blade. The extent of hepatocyte migration into the wound was measured and determined at specific time intervals using a computerized digital analyzing system. Immunostaining of F-actin was performed with a fluorescein-labeled phalloidin. EGF significantly stimulated liver cell migration, whereas specific EGF-neutralizing antibody inhibited the EGF-induced migration. Agents that activate PKA at different stages of the PKA activation pathway, including 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX), forskolin, and cholera toxin, inhibited EGF-induced migration. EGF triggered formation of actin stress fibers. PKA-activating agents inhibited actin stress fiber formation and stretching of cells at the wound margin. The following conclusions were drawn: (1) In excisional wounds of hepatocyte monolayers, both EGF and PKA exert action on actin microfilaments, which are stretched by EGF and inhibited by PKA; (2) the enhanced repair of wounded hepatocyte monolayers by EGF is blocked by activation of the PKA pathway at various levels; and (3) these actions of EGF and PKA indicate their important regulatory roles in controlling the rate of hepatocyte migration and restitution following the creation of excisional wounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bade EG, Feindler S. Liver epithelial cell migration induced by epidermal growth factor or transforming growth factor-a is associated with change in the gene expression of secreted proteins. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 1988;24:149–154.
Tomiya T, Fujiwara K. Serum levels of transforming growth factor-α in patients after partial hepatectomy as determined with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Hepatology 1993;18:304–308.
Michalopoulos GK, Zarnegav R. Hepatocyte growth factor. Hepatology 1992;15:149–155.
Fujiwara K, Nagoshi S, Ohno A, Hirata K, Ohta Y, Mochida S, Tomiya T, Higashio K, Kurokawa K. Stimulation of liver growth by exogenous human hepatocyte growth factor in normal and partially hepatectomized rats. Hepatology 1991;14:901–905.
Nakamura T, Teramoto H, Ichihara A. Partial purification and characterization of a growth factor from rat platelets in primary culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986;83:6489–6493.
Strain AJ, McGuinness G, Rubin JS, Aaronson SA. Keratinocyte growth factor and fibroblast growth factor action on DNA synthesis in rat and human hepatocytes: Modulation by heparin. Exp Cell Res 1994;210:253–259.
Leffert HL, Koch KS, Moran T, Rubalcava B. Hormonal control of rat liver regeneration. Gastroenterology 1979;76:1470–1482.
Massagure J, Blinderman LA, Czech MP. The high affinity insulin receptor mediates growth stimulation in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 1982;257:13958–13963.
Kvietys PR, Specian RD, Grisham MB, Tso P. Jejunal mucosal injury and restitution: Role of hydrolytic products of food digestion. Am J Physiol 1991;261:G384-G391.
MacCormack SA, Viar MJ, Johnson LR. Migration of IEC-6 cells: A model for mucosal healing. Am J Physiol 1992;263:G422-G435.
Fujiwara Y, Tarnawski A, Fujiwara K, Arakawa T, Kobayashi K. Inhibitory effects of indomethacin on growth and proliferation of gastric carcinoma cells KATO III. J Physiol Pharmacol 1993;44:147–153.
Nusrat A, Delp C, Madara JL. Intestinal epithelial restitution. J Clin Invest 1992;89:1501–1511.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Medical Research Service of the Veterans Affairs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kikuchi, M., Ma, T.Y., Tarnawski, A.S. et al. Role of protein kinase a pathway in epidermal growth factor-induced liver cell repair. J Gastrointest Surg 1, 132–137 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(97)80100-X
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1091-255X(97)80100-X