Abstract
Introduction
The treatment of late-presenting Perthes disease with extrusion is controversial and debatable. One of the options available is the labral shelf acetabuloplasty (LSA).
Aim
The aim of the study was to evaluate the results of LSA in late-presenting Perthes disease in terms of clinic-radiological outcome measures.
Materials and Methods
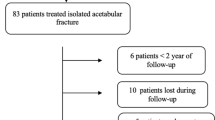
A retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data of patients with late presenting Perthes disease (Elizabethtown stage 2B onwards) treated by LSA by 2 experienced paediatric orthopaedic surgeons was performed. Data was collected of clinical parameters such as hip range of motion(ROM) and Harris Hip score and radiological parameters such as acetabular height, width and volume, shelf width, Centre Edge angle(CEA) and the lateral extrusion.
Results
Thirty-five patients (28 males and 7 females) treated between 2012 to 2019 were analyzed. Majority were in Elizabethtown stage 3A (23) followed by 2B and 3B (12 each). At a mean follow up of 36 months, the hip ROM and the Harris Hip Score (from 65 ± 3.5 to 81.33 ± 7.12) improved significantly and there was a statistically significant improvement in terms of all radiological parameters. Majority of the hips were in Stulberg grade 3 (20) followed by grade 1 and 2 (7 each) and Stulberg 4 (1). There were no major complications in any of the patients of the series.
Conclusion
Labral support shelf acetabuloplasty is a valuable surgery for late presenting Perthes disease and helps in maintenance of good coverage and allows restoration of range of motion over time.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joseph, B., & Price, C. T. (2011). Principles of the containment treatment aimed at preventing femoral head deformation in perthes disease. Orthopedic Clinics of North America, 42(3), 317–327.
Stulberg, S. D., Cooperman, D. R., & Wallensten, R. (1981). The natural historyof Legg Calve Perthes disease. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume, 63, 1095.
Joseph, B., Varghese, G., Mulpuri, K., et al. (2003). Natural evaolution of Perthes disease: A study of 610 children under 12 years of age at disease onset. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 23, 590–600.
Herring, J. A., Neustadt, J. B., Williams, J. J., et al. (1992). The lateral pillar classification of Leg-Calve-Perthes disease. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 12, 143.
Staheli, L. T. (1981). Slotted acetabular augmentation. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 1(3), 321–327.
Konishi, N., & Mieno, T. (1993). Determination of acetabular coverage of the femoral head with use of a single Anteroposterior radiograph. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery., 75, 1318–1333.
Humbert, L., Carlioz, H., Baudoin, A., et al. (2008). 3D evaluation of the acetabular coverage assessed by biplanar X-rays or single anteroposterior X-ray compared with CT-scan. Computer methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical engineering., 11(3), 257–262.
Sundt, H. (1949). Further investigation respecting malum coxae Calvé-Legg-Perthes’ disease with special regard to the prognosis and treatment. Acta Chir Scand., suppl 148, 1–101.
Bellamy, N., Buchanan, W. W., Goldsmith, C. H., et al. (1988). Validation study of WOMAC: A health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient- relevant outcomes following total hip or knee arthroplasty in osteoarthritis. Journal of Orthopedics Rheum, 1, 95.
Bowen, J. R., Guille, J. T., Jeong, C., Worananarat, P., et al. (2011). Labral support shelf arthroplasty for containment in early stages of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 31, S206–S211.
Wright, D., Perry, D., & Bruce, C. (2013). Shelf acetabuloplasty for perthes disease in patients older than eight years of age: An observational cohort study. JPO B, 22, 96–100.
Yoo, W. J., Moon, H. J., Cho, T., & Choi, I. H. (2012). Does Shelf acetabuloplasty influence acetabular growth and remodelling? Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 470, 2411–2420.
Price, C. T., Thompson, G. H., & Wegner, D. R. (2011). Containment methods for treatment of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Orthopedic Clinics of North America, 42(3), 329–340.
Chang, J. H., Kuo, K. N., & Huang, S. C. (2011). Outcomes in advanced Legg-CalvePerthes disease treated with the Staheli procedure. Journal of Surgical Research, 168, 237–242.
Li, W. C., & Xu, R. J. (2016). Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty for severe Legg-Calve-Perthes disease in patients older than 8 years. A mean eleven-year folloe up. Medicine, 95(45), e5272.
Huang, M. J., & Huang, S. C. (1999). Surgical treatment of severe perthes disease: Comparison of triple osteotomy and shelf augmentation. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association, 98(3), 183–189.
Bulut, M., Demerits, A., Ucar, B. Y., et al. (2014). Salter pelvic osteotomy in the treatment of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease: The medium-term results. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica, 80, 56–62.
Salter, R. B. (1984). The present status of surgical treatment for Legg-Perthes disease. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume, 66, 961–966.
Sponseller, P. D., Desai, S. S., & Millis, M. B. (1988). Comparison of femoral and innominate osteotomies for the treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume, 70(8), 1131–1139.
Noonan, K. J., Price, C. T., Kupiszewski, S. J., et al. (2001). Results of femoral varus osteotomy in children older than 9 years of age with Perthes disease. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 21, 198–204.
Kruse, R. W., Guille, J. T., & Bowen, J. R. (1991). Shelf arthroplasty in patients who have Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. A study of long-term results. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery America, 73, 1338–1347.
Daly, K., Bruce, C., & Catterall, A. (1999). Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes’ disease. A review of the end of growth. The Journal of Bone Joint Surgery British, 81, 380–384.
Van der Haven, I., Kooijman, M. A., Havinga, M. E., van der Geest, I. C., Jacobs, W., & Anderson, P. G. (2003). Teardrop-femoral head distance after shelf acetabuloplasty for Perthes’ disease. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica, 69(2), 157–161.
Freeman, R. T., Wainwright, A. M., Theologis, T. N., & Benson, M. K. (2008). The outcome of patients with hinge abduction in severe Perthes disease treated by shelf acetabuloplasty. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics, 28, 619–625.
Jacobs, R., Moens, P., & Fabry, G. (2004). Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in the early stage of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease with special emphasis on the remaining growth of the acetabulum: A preliminary report. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics. Part B, 13, 21–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Standard Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vinayak, U., Gundawar, C., Shyam, A. et al. Labral Support Shelf Acetabuloplasty for Late Presenting Perthes Disease: Outcomes in Indian Patients. JOIO 57, 1785–1792 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-023-00978-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-023-00978-4