Abstract
Introduction
The aim of systematic review and meta-analysis was to find out whether minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) is better than open reduction and internal plate fixation (ORIF) in terms of functional outcome, achieving union (union time and incidence of non-union), intraoperative parameters (surgical duration, blood loss, and radiation exposure), and complications (iatrogenic radial nerve palsy and infection) for humeral shaft fractures.
Materials and Methods
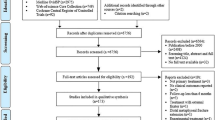
We searched online databases (Pubmed, Embase, Scopus, and The Cochrane Library) from inception till 3rd September 2020 for articles comparing MIPO with ORIF for humeral shaft fractures. The methodological quality of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) was done by Cochrane Risk of Bias assessment tool 2 (RoB2) and of non-randomized studies (case–control and cohort studies) by Methodological Index for non-randomized studies (MINORS). Meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager 5.4 software.
Results
11 studies (5 RCTs and 6 non-randomized comparative studies) involving a total of 582 patients (MIPO-290, ORIF-292) meeting our inclusion criteria were included in the study. There was no statistically significant difference in pooled analysis of functional outcome scores between MIPO and ORIF. Union time was significantly lesser (mean difference = 3.12 weeks) and incidence of non-union lower (odd’s ratio = 0.27) in MIPO group. Surgical duration and intraoperative blood loss were significantly lesser in MIPO group. Iatrogenic radial nerve palsy and infection were higher in ORIF group.
Conclusions
This study showed that MIPO gives similar functional outcomes as compared to ORIF but causes significantly lesser blood loss, requires lesser operative duration and has a lesser incidence of major complications.
Trial Registration
International prospective register of systematic reviews (PROSPERO)—CRD42020208346, Date of registration 09/10/2020








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perez, E. A. (2017). Fractures of the shoulder, arm and forearm. In F. M. Azar, J. H. Beaty, & S. T. Canale (Eds.), Campbell’s Operative Orthopaedics. (13th ed., pp. 2951–2955). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
Ekholm, R., Tidermark, J., Törnkvist, H., Adami, J., & Ponzer, S. (2006). Outcome after closed functional treatment of humeral shaft fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 20(9), 591–596. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.bot.0000246466.01287.04
Papasoulis, E., Drosos, G. I., Ververidis, A. N., & Verettas, D.-A. (2010). Functional bracing of humeral shaft fractures A review of clinical studies. Injury, 41(7), e21-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2009.05.004
Harkin, F. E., & Large, R. J. (2017). Humeral shaft fractures: union outcomes in a large cohort. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, 26(11), 1881–1888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2017.07.001
Zhang, B. S., Li, W. Y., Liu, X. H., Wei, J., He, L., & Wang, M. Y. (2017). Comparative results of non-operative and operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 49(5), 851–854 PMID: 29045968.
Chapman, J. R., Henley, M. B., Agel, J., & Benca, P. J. (2000). Randomized prospective study of humeral shaft fracture fixation: intramedullary nails versus plates. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 14(3), 162–166. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131-200003000-00002
Bhandari, M., Devereaux, P. J., McKee, M. D., & Schemitsch, E. H. (2006). Compression plating versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures–a meta-analysis. Acta Orthopaedica, 77(2), 279–284. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453670610046037
Hohmann, E., Glatt, V., & Tetsworth, K. (2016). Minimally invasive plating versus either open reduction and plate fixation or intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, 25(10), 1634–1642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2016.05.014
Hu, X., Xu, S., Lu, H., Chen, B., Zhou, X., He, X., Dai, J., Zhang, Z., & Gong, S. (2016). Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis vs conventional fixation techniques for surgically treated humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 11(1), 59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-016-0394-x
Zhang, Q., Sun, N., Huang, Q., Zhu, S., & Wu, X. (2017). Minimally Invasive Plating Osteosynthesis in the Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Investigative Surgery, 30(2), 133–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941939.2016.1215581
Zhao, J. G., Wang, J., Meng, X. H., Zeng, X. T., & Kan, S. L. (2017). Surgical interventions to treat humerus shaft fractures: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE, 12(3), e0173634. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173634
Zhiquan, A., Bingfang, Z., Yeming, W., Chi, Z., & Peiyan, H. (2007). Minimally Invasive Plating Osteosynthesis (MIPO) of Middle and Distal Third Humeral Shaft Fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 21(9), 628–633. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e31815928c2
Kini, A., Kumar, M. A., Shetty, M. S., Sujay, K., & Kanthi, K. (2011). Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for humerus diaphyseal fractures. Indian Jounal of Orthopaedics, 45(6), 520 PMID: 22144745.
Malhan, S., Thomas, S., Srivastav, S., Agarwal, S., Mittal, V., Nadkarni, B., & Gulati, D. (2012). Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Locking Compression Plate for Diaphyseal Humeral Fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery (Hong Kong), 20(3), 292–296. https://doi.org/10.1177/230949901202000305
An, Z., Zeng, B., He, X., Chen, Q., & Hu, S. (2010). Plating osteosynthesis of mid-distal humeral shaft fractures: minimally invasive versus conventional open reduction technique. International Orthopaedics, 34(1), 131–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-009-0753-x
Oh, C. W., Byun, Y. S., Oh, J. K., Kim, J. J., Jeon, I. H., Lee, J. H., & Park, K. H. (2012). Plating of humeral shaft fractures: comparison of standard conventional plating versus minimally invasive plating. Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Surgery and Research, 98(1), 54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2011.09.016
Shen, L., Qin, H., An, Z., Zeng, B., & Yang, F. (2013). Internal fixation of humeral shaft fractures using minimally invasive plating: comparative study of two implants. European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology, 23(5), 527–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-012-1039-3
Wang, C., Li, J., Li, Y., Dai, G., & Wang, M. (2015). Is minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture advantageous compared with the conventional open technique? Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, 24(11), 1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2015.07.032
Kim, J. W., Oh, C. W., Byun, Y.-S., Kim, J. J., & Park, K. C. (2015). A prospective randomized study of operative treatment for noncomminuted humeral shaft fractures: conventional open plating versus minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, 29(4), 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000232
Hadhoud, M., Darwish, A., & Mesriga, M. K. (2015). Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus open reduction and plate fixation of humeral shaft fractures. Menoufia Medical Journal, 28(1), 154. https://doi.org/10.4103/1110-2098.155974
Esmailiejah, A. A., Abbasian, M. R., Safdari, F., & Ashoori, K. (2015). Treatment of humeral shaft fractures: minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus open reduction and internal fixation. Trauma Monthly. https://doi.org/10.5812/traumamon.26271v2
Lee, T., & Yoon, J. (2016). Newly designed minimally invasive plating of a humerus shaft fracture; a different introduction of the plate. International Orthopaedics, 40(12), 2597–2602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-3097-8
Ko, S. H., Cha, J. R., Lee, C. C., Joo, Y. T., & Eom, K. S. (2017). Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Using a Screw Compression Method for Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures. Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery, 9(4), 506–513. https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.506
Kulkarni, V. S., Kulkarni, M. S., Kulkarni, G. S., Goyal, V., & Kulkarni, M. G. (2017). Comparison between antegrade intramedullary nailing (IMN), open reduction plate osteosynthesis (ORPO) and minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in treatment of humerus diaphyseal fractures. Injury, 48(Suppl 2), S8–S13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-1383(17)30487-4
Sri, S. P., & Subash, Y. (2019). Comparison of outcome in mipo versus orif with plate osteosynthesis in the management of fractures of the shaft of humerus. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology, 12, 3933–3937. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-360X.2019.00677.2
Wang, Z., Song, S., Guo, Q., Yang, D., Chen, X., Ling, J., Chen, P., Zhen, X. (2019). Therapeutic effect of anterior approach mipo combined with LCP in the treatment of humeral shaft fracture. Acta Medica Mediterranea 35:2765–2768. https://doi.org/10.19193/0393-6384_2019_5_434
Keshav, K., Baghel, A., Mishra, P., Kumar, V., Neradi, D., Kaustubh, K. (2020). Is minimally invasive plating osteosynthesis (MIPO) better than conventional open plating for humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PROSPERO 2020 CRD42020208346 Available at: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42020208346. Accessed 10 September 2020.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., & Altman, D. G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 62(10), 1006–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005
Higgins, J. P. T., Savovic, J., Page, M. J., Elbers, R. G., & Sterne, J. A. C. (2019). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In J. P. T. Higgins, J. Thomas, J. Chandler, M. Cumpston, T. Li, M. J. Page, & V. A. Welch (Eds.), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. (2nd ed., pp. 205–228). Chichester (UK): John Wiley & Sons.
Slim, K., Nini, E., Forestier, D., Kwiatkowski, F., Panis, Y., & Chipponi, J. (2003). Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ Journal of Surgery, 73(9), 712–716. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1445-2197.2003.02748.x
McGuinness, L. A., & Higgins, J. P. T. (2020). Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Research Synthesis Method JRSM. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1411
Higgins JPT, Li T, Deeks JJ (ed) (2019) Chapter 6: Choosing effect measures and computing estimates of effect. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (ed). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester (UK), pp. 143–176
Centre for Evidence Based Medicine. Available at https://www.cebm.ox.ac.uk/resources/levels-of-evidence/oxford-centre-for-evidence-based-medicine-levels-of-evidence-march-2009 Accessed 15 October 2020.
Ellman, H., Hanker, G., & Bayer, M. (1986). Repair of the rotator cuff. End-result study of factors influencing reconstruction. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume, 68(8), 1136–1144
Morrey, B. F., & Adams, R. A. (1992). Semiconstrained arthroplasty for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis of the elbow. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume, 74(4), 479–490 PMID: 1583042.
Hudak, PL., Amadio, PC., Bombardier, C. (1996). Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: the DASH (disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand) [corrected]. The Upper Extremity Collaborative Group (UECG). American Journal of Industrial Medicine 29(6):602–608. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0274(199606)29:6<602::AID-AJIM4>3.0.CO;2-L
Michener, L. A., McClure, P. W., & Sennett, B. J. (2002). American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons Standardized Shoulder Assessment Form, patient self-report section: reliability, validity, and responsiveness. Journal of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, 11(6), 587–594. https://doi.org/10.1067/mse.2002.127096
Yu, B.-F., Liu, L., Yang, G.-J., Zhang, L., & Lin, X.-P. (2016). Comparison of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and conventional plate osteosynthesis for humeral shaft fracture: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore), 95(39), e4955. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000004955 PMID: 27684839.
Qiu, H., Wei, Z., Liu, Y., Dong, J., Zhou, X., Yin, L., Zhang, M., & Lu, M. (2016). A Bayesian network meta-analysis of three different surgical procedures for the treatment of humeral shaft fractures. Medicine (Baltimore), 95(51), e5464. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000005464 PMID: 28002327.
Beeres, F. J., Diwersi, N., Houwert, M. R., Link, B. C., Heng, M., Knobe, M., Groenwold, R. H., Frima, H., Babst, R., & Jm van de Wall, B. (2020). ORIF versus MIPO for humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis and systematic review of randomized clinical trials and observational studies. Injury. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2020.11.016
Bhandari, M., Devereaux, P. J., Mckee, D., & M, H Schemitsch E, . (2006). Compression plating versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures—a meta-analysis. Acta Orthopaedica, 77(2), 279–284. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453670610046037
Baumgaertel, F. (2019). Bridge plating. In R. E. Buckley, C. G. Moran, & T. Apivatthakakul (Eds.), AO Principles of Fracture Management. (3rd ed., pp. 241–252). New York: Thieme Publishing.
Matsunaga, F. T., Tamaoki, M. J. S., Matsumoto, M. H., Netto, N. A., Faloppa, F., & Belloti, J. C. (2017). Minimally Invasive Osteosynthesis with a Bridge Plate Versus a Functional Brace for Humeral Shaft Fractures: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American Volume, 99(7), 583–592. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.16.00628
Xue, Z., Jiang, C., Hu, C., Qin, H., Ding, H., & An, Z. (2016). Effects of different surgical techniques on mid-distal humeral shaft vascularity: open reduction and internal fixation versus minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 17(1), 370. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-016-1224-3
Paris, H., Tropiano, P., Clouet Dorval, B., Chaudet, H., & Poitout, D. G. (2000). Fractures of the shaft of the humerus systematic plate fixation. Anatomic and functional results in 156 cases and a review of the literature. Revue de chirurgie orthopedique et reparatrice de l’appareil moteur, 86(4), 346–359
Lim, K. E., Yap, C. K., Ong, S. C., & Aminuddin null. (2001). Plate osteosynthesis of the humerus shaft fracture an its association with radial nerve injury–a retrospective study in Melaka General Hospital. The Medical journal of Malaysia , 56C, 8–12
Apivatthakakul, T., Arpornchayanon, O., & Bavornratanavech, S. (2005). Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture. Is it possible? A cadaveric study and preliminary report. Injury, 36(4), 530–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2004.05.036
Tetsworth, K., Hohmann, E., & Glatt, V. (2018). Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis of Humeral Shaft Fractures: Current State of the Art. Journal of American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 26(18), 652–661. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-17-00238
Boileau, P., Bicknell, R. T., Mazzoleni, N., Walch, G., & Urien, J. P. (2008). CT scan method accurately assesses humeral head retroversion. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 466(3), 661–669. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-007-0089-z
Acknowledgements
The work was conducted at- Sanjay Gandhi Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Rae Bareli Road, Lucknow, U.P., PIN-226029
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by the any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keshav, K., Baghel, A., Kumar, V. et al. Is Minimally Invasive Plating Osteosynthesis Better Than Conventional Open Plating for Humeral Shaft Fractures? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Comparative Studies. JOIO 55 (Suppl 2), 283–303 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-021-00413-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43465-021-00413-6