Abstract
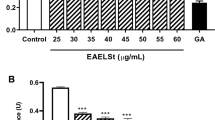
Plumula nelumbinis, the green embryo of the mature seeds of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn., Nelumbonaceae, is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine and possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. However, few reports are available on the anti-inflammatory activity of alkaloids and main contents of alkaloids in P. nelumbinis. This study aims to systematically investigate the anti-inflammatory of total alkaloids fraction and determine the contents of three major alkaloids (liensinine, isoliensinine, and neferine) in P. nelumbinis collected from 13 habitats by ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with triple-quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. Lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced ear edema inflammatory model were used to evaluate in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities, respectively. Histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses were performed to determine histological morphology and related inflammatory factors. The total alkaloids exhibited the best anti-inflammatory activity, thereby significantly inhibiting the nitric oxide release in RAW 264.7 cells. In addition, liensinine (IC 50 5.02 μM), isoliensinine (IC 50 4.36 μM), and neferine (IC 50 4.13 μM) showed excellent anti-inflammatory activity. The total alkaloids reduced ear edema and significantly reduced the expression levels of interleukin 6, interleukin 1β, tumor necrosis factor α, and nuclear factor-kappa B in a dose-dependent manner. Total alkaloids in P. nelumbinis exhibited good anti-inflammatory activity, suggesting that they might act as anti-inflammatory agents.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper.
References
Agrawal V, Sawhney N, Hickey E (2016) Loss of presenilin 2 function is associated with defective LPS-mediated innate immune responsiveness. Mol Neurobiol 53:3428–3438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9285-0
Bai RR, Yao CS, Zhong ZC, Ge JM, Bai ZQ, Ye XY, Xie T, Xie YY (2021) Discovery of natural anti-inflammatory alkaloids: potential leads for the drug discovery for the treatment of inflammation. Eur J Med Chem 213:113165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113165
Cassiano DSA, Reis IMA, Estrela ID, de Freitas HF, Pita SSD, David JM, Branco A (2019) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities and bioguided fractionation of the Ocotea percoriacea extracts: HPLC-DAD-MS/MS characterization and molecular modeling of their alkaloids in the active fraction. Comput Biol Chem 83:107129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2019.107129
Chen L, Teng H, Jia Z, Battino M, Miron A, Yu ZL, Cao H, Xiao JB (2018) Intracellular signaling pathways of inflammation modulated by dietary flavonoids: the most recent evidence. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:2908–2924. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1345853
Chen GL, Fan MX, Wu JL, Li N, Guo MQ (2019) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of flavonoids from lotus plumule. Food Chem 277:706–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.040
Chen SX, Li XP, Wu JX, Li JY, Xiao MZ, Yang Y, Liu ZQ, Cheng YY (2021) Plumula nelumbinis: a review of traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and safety. J Ethnopharmacol 266:113429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.113429
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (2020) Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China 2020, vol 1. China Medical Science Press, Beijing, pp 285–286
Debnath B, Singh WS, Das M, Goswami S, Singh MK, Maiti D, Manna K (2018) Role of plant alkaloids on human health: a review of biological activities. Mater Today Chem 9:56–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2018.05.001
Eid W, Abdel-Rehim W (2017) Neferine enhances the antitumor effect of mitomycin-C in Hela cells through the activation of p38-MAPK pathway. J Cell Biochem 118:3472–3479. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26006
Elnahasa EM, Zeida MSA, Kawya HAS, Hendawy N, Baher W (2016) Celecoxib attenuates depressive-like behavior associated with immunological liver injury in C57BL/6 mice through TNF-α and NF-κb dependent mechanisms. Life Sci 163:23–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.08.027
Epstein FH, Barnes PJ, Karin M (1997) Nuclear factor-κB — a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. New Engl J Med 336:1066–1071. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199704103361506
Feng CY, Li SS, Yin DD, Zhang HJ, Tian DK, Wu Q, Wang LJ, Su S, Wang LS (2016) Rapid determination of flavonoids in plumules of sacred lotus cultivars and assessment of their antioxidant activities. Ind Crops Prod 87:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.04.030
Fioranelli M, Bottaccioli AG, Bottaccioli F, Bianchi M, Rovesti M, Roccia MG (2018) Stress and inflammation in coronary artery disease: a review psychoneuroendocrineimmunology-based. Front Immunol 6:2031. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02031
Hu Y, Tao LJ, Tan H, Zhang M, Shimizu K, Zhang F, Zhang CF (2017) An active drimane-type lactone from Polygonum jucundum attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice through TLR4-MAPKs signaling pathway. Inflamm 40:1204–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0563-z
Hwang JS, Kwon MY, Kim KH, Lee Y, Lyoo IK, Kim JE, Oh ES, Han IO (2017) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated iNOS induction is increased by glucosamine under normal glucose conditions but is inhibited by glucosamine under high glucose conditions in macrophage cells. J Biol Chem 292:1724–1736. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.737940
Jia D, Li S, Xiao L (2009) Supercritical co 2 extraction of Plumula nelumbinis oil: experiments and modeling. J Supercrit Fluids 50:229–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu.2009.06.005
Jiang YP, Zi W, Pei ZF, Liu S (2018) Characterization of polysaccharides and their antioxidant properties from Plumula nelumbinis. Saudi Pharm J 26:656–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2018.02.026
Klimczak I, Gliszczyńska WA (2015) Comparison of UPLC and HPLC methods for determination of vitamin C. Food Chem 175:100–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.104
Korhonen R, Lahti A, Kankaanranta H, Moilanen E (2005) Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr Drug Targets 4:471–479. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568010054526359
Li SC, Liu X, Chen XR, Bi L (2020) Research progress on anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of alkaloids from Chinese medical herbs. Evid-Based Compl Alt 2020:1303524. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1303524
Lin Z, Yang R, Guan Z, Chen AL, Li W (2014) Ultra-performance LC separation and quadrupole time-of-flight ms identification of major alkaloids in Plumula nelumbinis. Phytochem Anal 25:485–494. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2517
Liu S, Wang B, Li XZ, Qi LF, Liang YZ (2009) Preparative separation and purification of liensinine, isoliensinine and neferine from seed embryo of Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. using high-speed counter-current chromatography. J Sep Sci 32:2476–2481. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.200800766
Liu SJ, Huang ZS, Wu QG, Huang ZJ, Wu LR, Yan WL, Chang DL, Yang Z, Wang ZW (2014) Quantization and diagnosis of Shanghuo (heatiness) in Chinese medicine using a diagnostic scoring scheme and salivary biochemical parameters. Chin Med 9:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8546-9-2
Liu WY, Li YL, Zheng X, Zhang K, Du ZY (2015) Potent inhibitory effect of silibinin from milk thistle on skin inflammation stimuli by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Food Funct 6:3712–3719. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5FO00899A
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo DH, Sun SC (2017) NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Tar 2:17023. https://doi.org/10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Meng XL, Chen ML, Chen CL, Gao CC, Li C, Wang D, Liu HS, Xu C (2019) Bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) seed embryo inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage activation via suppression of Ca2+-CaM/CaMKII pathway. Food Agr Immunol 30:878–896. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2019.1638889
Meng XL, Zheng LC, Liu J, Gao CC, Qiu MC, Liu YY, Lu J, Wang D, Chen CL (2017) Inhibitory effects of three bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids on lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation RSC Adv 7:18347-18357. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA01882G
Milani GB, Camponogara C, Piana M, Silva CR, Oliveira SM (2019) Cariniana domestica fruit peels present topical anti-inflammatory efficacy in a mouse model of skin inflammation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 392:513–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1594-1
Moon SW, Ahn CB, Oh Y, Je JY (2019) Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seed protein isolate exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in LPS-stimulated raw264.7 macrophages via inhibiting nf-κb and mapk pathways, and upregulating catalase activity. Int J Bio Macromol 134:791–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.094
Naveen P, Lingaraju HB, Anitha PKS (2017) Simultaneous determination of rutin, isoquercetin, and quercetin flavonoids in Nelumbo nucifera by high-performance liquid chromatography method. Int J Pharm Investig 7:94–100. https://doi.org/10.4103/jphi.JPHI_33_17
Priya LB, Baskaran R, Huang CY, Padma VV (2018) Neferine modulates IGF-1R/Nrf2 signaling in doxorubicin treated H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. J Cell Biochem 119:1441–1452. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26305
Sharma BR, Gautam L, Adhikari D, Karki R (2017) A comprehensive review on chemical profiling of Nelumbo nucifera: potential for drug development. Phytother Res 31:3–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5732
Shen YT, Bian R, Li YX, Gao Y, Liu YB, Xu YZ, Song XL, Zhang YJ (2019) Liensinine induces gallbladder cancer apoptosis and G2/M arrest by inhibiting ZFX-induced PI3K/AKT pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 51:607–614. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmz041
Singsai K, Charoongchit P, Chaikaew W, Boonma N, Fhanjaksai P, Chaisatan K (2020) Antilipoxygenase and anti-inflammatory activities of Streblus asper leaf extract on xylene-induced ear edema in mice. Adv Pharm Pharm Sci 2020:3176391. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3176391
Sui Y, He XS, WangSC, (2018) Quantitative assay and optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of three main alkaloids from Plumula nelumbinis. Chin Pharm J 53:1901–1907
Tao W, Yang N, Duan JA, Wu DK, Guo JM, Tang YP, Qian DW, Zhu ZH (2011) Simultaneous determination of eleven major flavonoids in the pollen of Typha angustifolia by HPLC-PDA-MS. Phytochem Anal 22:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.1302
Tian WY, Zhi H, Yang C, Wang LK, Long JT, Xiao LM, Liang JZ, Huang Y, Zheng X, Zhao SQ, Zhang K, Zheng JX (2018) Chemical composition of alkaloids of Plumula nelumbinis and their antioxidant activity from different habitats in China. Ind Crops Prod 125:537–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.09.045
Wu XX, Guo YL, Min XJ, Pei LX, Chen XP (2018) Neferine, a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid, ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis. Am J Chinese Med 46:1263–1279. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X18500660
Xie Y, Zhang Y, Zhang LT, Zeng SX, Guo ZB, Zheng BD (2013) Protective effects of alkaloid compounds from Nelumbinis plumula on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress. Molecules 18:10285–10300. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules180910285
Xie Y, Zhang Y, Guo ZB, Zeng HL, Zheng BD (2016) Effect of alkaloids from Nelumbinis plumula against insulin resistance of high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. J Diabetes Res 2016:3965864. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3965864
Yang L, Jiang H, Hou AJ, Guo XY, Man WJ, Yan ML, Xing XD, Yang BY, Wang QH, Kuang HX (2019) Simultaneous determination of thirteen Q-markers in raw and processed Tussilago farfara L. by UPLC-QQQ-MS/MS coupled with mhemometrics. Molecules 24:598. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030598
Yao XL, Pei CY, Wang ZQ (2012) Determination of calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside and formononetin in crude drugs and slices of astragalus from different habitats and gathering periods. Chin J Pharm Anal 32:797–805
Ye LH, He XX, Yan MZ, Chang Q (2014) Identification of in vivo components in rats after oral administration of lotus leaf flavonoids using ultra fast liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Methods 6:6088–6094. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AY00652F
Zhang XX, Ma SC, Mao P, Wang YD (2016) A new bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid from Plumula nelumbinis. Chin Chem Lett 27:1755–1758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2016.06.051
Zhang LY, Yang ZW, Wei JW, Su P, Pan WY, Zheng X, Zhang K, Lin L, Tang J, Fang YX, Du Z (2017) Essential oil composition and bioactivity variation in wild-growing populations of Curcuma phaeocaulis Valeton collected from China. Ind Crops Prod 103:272–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.04.019
Zhao X, Shen J, Chang KJ, Kim SH (2014) Comparative analysis of antioxidant activity and functional components of the ethanol extract of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) from various growing regions. J Agric Food Chem 62:6227–6235. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf501644t
Zheng JX, Tian WY, Yang C, Shi WP, Cao PH, Long JT, Xiao LM, Wu Y, Liang JZ, Li XB, Zhao SQ, Zhang K, Zhi H, Sun PH (2019) Identification of flavonoids in Plumula nelumbinis and evaluation of their antioxidant properties from different habitats. Ind Crops Prod 127:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.08.020
Zhong JS, Wan JZ, Ding WJ, Wu XF, Xie ZY (2015) Multi-responses extraction optimization combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry and chemometrics techniques for the fingerprint analysis of Aloe barbadensis Miller. J Pharmaceut Biomed 107:31–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2014.12.032
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the generous support from the Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Sun Yat-sen University Sixth Affiliated Hospital, and Jinan University, Guangzhou P. R. China.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant numbers 82073977, 81773593, 81803378, 81872759, and Key Platform and Characteristic Innovation Project of Guangdong Education Department, grant number 21815073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Investigation, writing original draft, conceptualization: JX and TS. Methodology, formal analysis: WT. Writing review and editing: LW and JC. Software: JH. Data curation: ZX and KL. Methodology: PS and HF. Second writing review and editing: WW. Resources: LW. Conceptualization, project administration: JZ. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Jinan University (Approval no. 20200723–03), and the animal experiments were carried out according to the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Juntao Xie and Tianjian Sha contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, J., Sha, T., Tian, W. et al. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Total Alkaloids in Nelumbo nucifera and Simultaneous Determination of Major Bisbenzylisoquinolines. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 33, 353–363 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-023-00373-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-023-00373-y