Abstract
Background
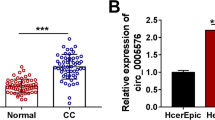
Cervical cancer is a malignant tumor that threatens the life and health of women. Circular RNA (circRNA) is a research hotspot in human diseases including cervical cancer. However, the research of circRNA viral protein R-binding protein (circ_VPRBP) in cervical cancer is blank.
Methods
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was used to detect the expression of target genes in cervical cancer tissues and cells. The expression of related proteins was detected by western blot. The localization of circ_VPRBP was detected by nuclear cytoplasmic separation, and the stability of circ_VPRBP was verified by actinomycin D. After transfection with oligonucleotides and/or plasmids, cell proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis were detected by 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl) -2, 5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT), colony formation, 5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine (EdU), transwell, or flow cytometry assays. Mechanistically, the interaction between microRNA-93-5p (miR-93-5p) and circ_VPRBP/FERM domain containing 6 (FRMD6) was verified by dual luciferase reporter assay. Animal experiment was conducted to investigate the role of circ_VPRBP in vivo.
Results
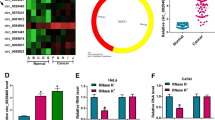
Circ_VPRBP was down-regulated in cervical cancer tissues and cells, and overexpression of circ_VPRBP inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of Caski and C33A cells. MiR-93-5p was a target of circ_VPRBP, and miR-93-5p mimic reversed the effect of circ_VPRBP on cell behavior. FRMD6 was a downstream target of miR-93-5p, and down-regulated FRMD6 reversed the cell viability, migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells inhibited by anti-miR-93-5p. Circ_VPRBP inhibited tumor growth by regulating miR-93-5p and FRMD6 in vivo.
Conclusion
Circ_VPRBP inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion and promoted cell apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by regulating miR-93-5p/FRMD6 axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not Applicable.
Code availability
Not Applicable.
References
Bedell SL, Goldstein LS, Goldstein AR, Goldstein AT. Cervical Cancer Screening: Past, Present, and Future. Sex Med Rev. 2020;8(1):28–37.
Gupta S, Kumar P, Das BC. HPV: Molecular pathways and targets. Curr Probl Cancer. 2018;42(2):161–74.
Estevao D, Costa NR. Gil da Costa RM, Medeiros R: Hallmarks of HPV carcinogenesis: The role of E6, E7 and E5 oncoproteins in cellular malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019;1862(2):153–62.
Thapa N, Maharjan M, Xiong Y, Jiang D, Nguyen TP, Petrini MA, Cai H. Impact of cervical cancer on quality of life of women in Hubei, China. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):11993.
Wright JD, Huang Y, Ananth CV, Tergas AI, Duffy C, Deutsch I, Burke WM, Hou JY, Neugut AI, Hershman DL. Influence of treatment center and hospital volume on survival for locally advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2015;139(3):506–12.
Li XY, Wang X. The role of human cervical cancer oncogene in cancer progression. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(6):8363–8.
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20(11):675–91.
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong F, Ren D, Ye X, Li C, Wang Y, et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):79.
Verduci L, Strano S, Yarden Y, Blandino G. The circRNA-microRNA code: emerging implications for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Mol Oncol. 2019;13(4):669–80.
Chaichian S, Shafabakhsh R, Mirhashemi SM, Moazzami B, Asemi Z. Circular RNAs: A novel biomarker for cervical cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(2):718–24.
Chen RX, Liu HL, Yang LL, Kang FH, Xin LP, Huang LR, Guo QF, Wang YL. Circular RNA circRNA_0000285 promotes cervical cancer development by regulating FUS. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(20):8771–8.
Zhang S, Chen Z, Sun J, An N, Xi Q. CircRNA hsa_circRNA_0000069 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of cervical cancer through miR-873-5p/TUSC3 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:287.
Gao C, Zhou C, Zhuang J, Liu L, Liu C, Li H, Liu G, Wei J, Sun C. MicroRNA expression in cervical cancer: Novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(8):7080–90.
Sun XY, Han XM, Zhao XL, Cheng XM, Zhang Y. MiR-93-5p promotes cervical cancer progression by targeting THBS2/MMPS signal pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(12):5113–21.
Zhang P-F, Wei C-Y, Huang X-Y, Peng R, Yang X, Lu J-C, Zhang C, Gao C, Cai J-B, Gao P-T, et al. Circular RNA circTRIM33-12 acts as the sponge of MicroRNA-191 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):105.
Cao Z, Zhang G, Xie C, Zhou Y. MiR-34b regulates cervical cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):2042–7.
Li X, Li Y, Han Y, Dong B, Liu D, Che L, Liu Y, Wang Y. miR-205 Promotes Apoptosis of Cervical Cancer Cells and Enhances Drug Sensitivity of Cisplatin by Inhibiting YAP1. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2020;35(5):338–44.
Li P, Wang J, Zhi L, Cai F. Linc00887 suppresses tumorigenesis of cervical cancer through regulating the miR-454-3p/FRMD6-Hippo axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):33.
Patop IL, Kadener S. circRNAs in Cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018;48:121–7.
Chen S, Yang X, Yu C, Zhou W, Xia Q, Liu Y, Chen Q, Chen X, Lv Y, Lin Y. The Potential of circRNA as a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker in Cervical Cancer. J Oncol. 2021;2021:5529486.
Yi Y, Liu Y, Wu W, Wu K, Zhang W. Reconstruction and analysis of circRNAmiRNAmRNA network in the pathology of cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(4):2209–25.
Chen X, Liu J, Zhang Q, Liu B, Cheng Y, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Ge H, Liu Y. Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-93-5p from cancer-associated fibroblasts confer radioresistance in colorectal cancer cells by downregulating FOXA1 and upregulating TGFB3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):65.
Cai Y, Ruan W, Ding J, Wei N, Wang J, Zhang H, Ma N, Weng G, Su WK, Lin Y, et al. miR‑93‑5p regulates the occurrence and development of esophageal carcinoma epithelial cells by targeting TGFβR2. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(3).
Yang Y, Jia B, Zhao X, Wang Y, Ye W. miR-93-5p may be an important oncogene in prostate cancer by bioinformatics analysis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):10463–83.
Beck J, Kressel M. FERM domain-containing protein 6 identifies a subpopulation of varicose nerve fibers in different vertebrate species. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;381(1):13–24.
Haldrup J, Strand SH, Cieza-Borrella C, Jakobsson ME, Riedel M, Norgaard M, Hedensted S, Dagnaes-Hansen F, Ulhoi BP, Eeles R, et al. FRMD6 has tumor suppressor functions in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2021;40(4):763–76.
Guan C, Chang Z, Gu X, Liu R. MTA2 promotes HCC progression through repressing FRMD6, a key upstream component of hippo signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;515(1):112–8.
Xu Y, Wang K, Yu Q. FRMD6 inhibits human glioblastoma growth and progression by negatively regulating activity of receptor tyrosine kinases. Oncotarget. 2016;7(43):70080–91.
Wang W, Zhao C, Quan F, Zhang P, Shao Y, Liu L. FERM domain-containing protein 6 exerts a tumor-inhibiting role in thyroid cancer by antagonizing oncogenic YAP1. 2021.
Li P, Wang J, Zhi L, Cai F. Linc00887 suppresses tumorigenesis of cervical cancer through regulating the miR-454–3p/FRMD6-Hippo axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):33.
Funding
This work was supported by:
1. A special free exploration basic project for local science and technology development guided by the central government in 2020 (2020ZYD056).
2. Nanchong City School Science and Technology Strategic Cooperation Special Fund Project (18SXHZ0126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants, and this study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College.
Consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlight
(1) Circ_VPRBP was down-regulated in cervical cancer tissue and cells.
(2) Circ_VPRBP functioned as a sponge of miR-93-5p.
(3) FRMD6 was a target of miR-93-5p.
(4) Circ_VPRBP regulated FRMD6 expression by sponging miR-93-5p.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., Dang, J., Liu, S. et al. CircRNA VPRBP inhibits tumorigenicity of cervical cancer via miR-93-5p/FRMD6 axis. Reprod. Sci. 29, 2251–2264 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-022-00923-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-022-00923-0