Abstract
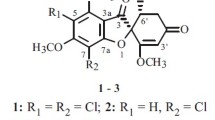
Marine microorganisms have long been recognized as potential sources for drug discovery. Griseofulvin was one of the first antifungal natural products and has been used as an antifungal agent for decades. In this study, 12 new griseofulvin derivatives [(±)-1−2, (+)-3, (±)-4, 10−12, and 14−15] and two new griseofulvin natural products (9 and 16) together with six known analogues [(−)-3, 5−8, and 13] were isolated from the mangrove-derived fungus Nigrospora sp. QQYB1 treated with 0.3% NaCl or 2% NaBr in rice solid medium. Their 2D structures and absolute configurations were established by extensive spectroscopic analysis (1D and 2D NMR, HRESIMS), ECD spectra, computational calculation, DP4 + analysis, and X-ray single-crystal diffraction. Compounds 1−4 represent the first griseofulvin enantiomers with four absolute configurations (2S, 6'S; 2R, 6'R; 2S, 6'R; 2R, 6'S), and compounds 9−12 represent the first successful production of brominated griseofulvin derivatives from fungi via the addition of NaBr to the culture medium. In the antifungal assays, compounds 6 and 9 demonstrated significant inhibitory activities against the fungi Colletotrichum truncatum, Microsporum gypseum, and Trichophyton mentagrophyte with inhibition zones varying between 28 and 41 mm (10 μg/disc). The structure−activity relationship (SAR) was analyzed, which showed that substituents at C-6, C-7, C-6' and the positions of the carbonyl and double bond of griseofulvin derivatives significantly affected the antifungal activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Ali T, Inagaki M, Chai HB, Wieboldt T, Rapplye C, Rakotondraibe LH (2017) Halogenated compounds from directed fermentation of Penicillium concentricum, an endophytic fungus of the liverwort Trichocolea tomentella. J Nat Prod 80:1397–1403
Belofsky GN, Gloer KB, Gloer JB, Wicklow DT, Dowd PF (1998) New p-terphenyl and polyketide metabolites from the sclerotia of Penicillium raistrickii. J Nat Prod 61:1115–1119
Cacho RA, Chooi YH, Zhou H, Tang Y (2013) Complexity generation in fungal polyketide biosynthesis: a spirocycle-forming P450 in the concise pathway to the antifungal drug griseofulvin. ACS Chem Biol 8:2322–2330
Chen SH, Chen DN, Cai RL, Cui H, Long YH, Lu YJ, Li CY, She ZG (2016) Cytotoxic and antibacterial preussomerins from the mangrove endophytic fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae ZJ-HQ1. J Nat Prod 79:2397–2402
Chen Y, Yang WC, Zou G, Wang GS, Kang WY, Yuan J, She ZG (2022) Cytotoxic bromine- and iodine-containing cytochalasins produced by the mangrove endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp. QYM-13 using the OSMAC approach. J Nat Prod 85:1229–1238
Cui H, Liu YN, Li J, Huang XS, Yan T, Cao WH, Liu HJ, Long YH, She ZG (2018) Diaporindenes A-D: four unusual 2,3-dihydro-1H-indene analogues with anti-inflammatory activities from the mangrove endophytic fungus Diaporthe sp. SYSU-HQ3. J Org Chem 83:11804–11813
Dahiya R, Singh S, Sharma A, Chennupati SV, Maharaj S (2016) First total synthesis and biological screening of a proline-rich cyclopeptide from a caribbean marine sponge. Mar Drugs 14:228
Fang CY, Zhang QB, Zhang WJ, Zhang CS, Zhu YG (2022) Discovery of efrotomycin congeners and heterologous expression-based insights into the self-resistance mechanism. J Nat Prod 85:2865–2872
Frank M, Hartmann R, Plenker M, Mándi A, Kurtán T, Özkaya FC, Müller WEG, Kassack MU, Hamacher A, Lin WH, Liu Z, Proksch P (2019) Brominated azaphilones from the sponge-associated fungus Penicillium canescens strain 4.14.6a. J Nat Prod 82:2159–2166
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian HP, Izmaylov AF, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M et al (2009) Gaussian 09, Revision A.1. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT
Gentles JC (1958) Experimental ringworm in guinea pigs: oral treatment with griseofulvin. Nature 182:476–477
Gupta AK, Summerbell RC (2000) Tinea capitis. Med Mycol 38:255–287
Hai Y, Wei MY, Wang CY, Gu YC, Shao CL (2021) The intriguing chemistry and biology of sulfur-containing natural products from marine microorganisms (1987–2020). Mar Life Sci Tech 3:488–518
Kartsev V, Geronikaki A, Petrou A, Lichitsky B, Kostic M (2019) Griseofulvin derivatives: synthesis, molecular docking and biological evaluation. Curr Top Med Chem 19:1145–1161
Levine SG, Hicks RE, Gottlieb HE, Wenkert E (1975) Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of naturally occurring substances. XXX Griseofulvin J Org Chem 40:2540–2542
Li YQ, Tan YH, Liu J, Zhou XF, Zeng SQ, Dong JD, Liu YH, Yang B (2020) A new griseofulvin derivative from a soft coral derived fungus Eupenicillium sp. SCSIO41208. Nat Prod Res 34:2971–2975
Lin J, Liu SC, Sun BD, Niu SB, Li EW, Liu XZ, Che YS (2010) Polyketides from the ascomycete fungus Leptosphaeria sp. J Nat Prod 73:905–910
Oxford AE, Raistrick H, Simonart P (1939) Studies in the biochemistry of micro-organisms: griseofulvin, C17H17O6Cl, a metabolic product of Penicillium griseofulvum Dierckx. Biochem J 33:240–248
Pan R, Bai X, Chen JM, Zhang HW, Wang H (2019) Exploring structural diversity of microbe secondary metabolites using OSMAC strategy: a literature review. Front Microbiol 10:294
Panda D, Rathinasamy K, Santra MK, Wilson L (2005) Kinetic suppression of microtubule dynamic instability by griseofulvin: Implications for its possible use in the treatment of cancer. P Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9878–9883
Park JH, Choi GJ, Lee SW, Kim KM, Jung HS, Jang KS, Cho KY, Kim JC (2005) Griseofulvin from Xylaria sp. strain F0010, an endophytic fungus of abies holophylla and its antifungal activity against plant pathogenic fungi. J Microbiol Biotechn 15:112–117
Pinedo-Rivilla C, Aleu J, Durán-Patrón R (2022) Cryptic metabolites from marine-derived microorganisms using OSMAC and epigenetic approaches. Mar Drugs 20:84
Rønnest MH, Rebacz B, Markworth L, Terp AH, Larsen TO, Krämer A, Clausen MH (2009) Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of griseofulvin analogues as inhibitors of centrosomal clustering in cancer cells. J Med Chem 52:3342–3347
Rønnest MH, Raab MS, Anderhub S, Boesen S, Krämer A, Larsen TO, Clausen MH (2012) Disparate SAR data of griseofulvin analogues for the dermatophytes Trichophyton mentagrophytes, T. rubrum, and MDA-MB-231 cancer cells. J Med Chem 55:652–660
Schneck DW, Racz WJ, Hirsch GH, Bubbar GL, Marks GS (1968) Studies of the relationship between chemical structure and porphyria-inducing activity—IV: Investigations in a cell culture system. Biochem Pharmacol 17:1385–1399
Seebacher C, Abeck D, Brasch J, Cornely O, Daeschlein G, Effendy I, Ginter-Hanselmayer G, Haake N, Hamm G, Hipler C, Hof H, Korting HC, Kramer A, Mayser P, Ruhnke M, Schlacke KH, Tietz HJ (2007) Tinea capitis: ringworm of the scalp. Mycoses 50:218–226
Shang Z, Li XM, Li CS, Wang BG (2012) Diverse secondary metabolites produced by marine-derived fungus Nigrospora sp. MA75 on various culture media. Chem Biodivers 9:1338–1348
Wang JF, Cong ZW, Huang XL, Hou CX, Chen WH, Tu ZC, Huang DY, Liu YH (2018) Soliseptide A, a cyclic hexapeptide possessing piperazic acid groups from Streptomyces solisilvae HNM30702. Org Lett 20:1371–1374
Wei MY, Xu RF, Du SY, Wang CY, Xu TY, Shao CL (2016) A new griseofulvin derivative from the marine-derived Arthrinium sp. fungus and its biological activity. Chem Nat Compd 52:1011–1014
Williams DI, Marten RH, Sarkany I (1958) Oral treatment of ringworm with griseofulvin. Lancet 2:1212–1213
Xu WF, Wu NN, Wu YW, Qi YX, Wei MY, Pineda LM, Ng MG, Spadafora C, Zheng JY, Lu L, Wang CY, Gu YC, Shao CL (2022) Structure modification, antialgal, antiplasmodial, and toxic evaluations of a series of new marine-derived 14-membered resorcylic acid lactone derivatives. Mar Life Sci Tech 4:88–97
Yang WC, Yuan J, Tan Q, Chen Y, Zhu YJ, Jiang HM, Zou G, Zang ZM, Wang B, She ZG (2021) Peniazaphilones A-I, produced by co-culturing of mangrove endophytic fungi, Penicillium sclerotiorum THSH-4 and Penicillium sclerotiorum ZJHJJ-18. Chin J Chem 39:3404–3412
Zhang DW, Zhao LL, Wang LN, Fang XM, Zhao JY, Wang XW, Li L, Liu HY, Wei YZ, You XF, Cen S, Yu LY (2017) Griseofulvin derivative and indole alkaloids from Penicillium griseofulvum CPCC 400528. J Nat Prod 80:371–376
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Guangdong Marine Economy Development Special Project (GDNRC[2022]35, GDNRC[2023]39) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U20A2001, 42276114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZG performed the experiments and wrote the paper; LZ provided the pathogenic fungi; YW, CT, and LT participated in the experiments; LZ and CY analyzed the data and discussed the result; SG revised the manuscript; SB and WB reviewed the manuscript and SZ designed and supervised the experiments. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Zhigang She is one of the Editorial Board Members, but he was not involved in the journal’s review of, or decision related to, this manuscript.
Animal and human rights statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by the authors.
Additional information
Edited by Chengchao Chen.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, G., Yang, W., Chen, T. et al. Griseofulvin enantiomers and bromine-containing griseofulvin derivatives with antifungal activity produced by the mangrove endophytic fungus Nigrospora sp. QQYB1. Mar Life Sci Technol 6, 102–114 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-023-00210-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-023-00210-0