Abstract
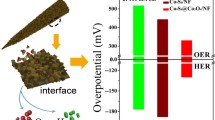
Constructing hetero-structured catalyst is promising but still challenging to achieve overall water splitting for hydrogen production with high efficiency. Herein, we developed a sulfide-based MoS2/Co1−xS@C hetero-structure for highly efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER). The carbon derived from the filter paper acts as a conducting carrier to ensure adequate exposure of the active sites guaranteed with improved catalytic stability. The unique hierarchical nano-sheets facilitate the charge and ion transfer by shortening the diffusion path during electro-catalysis. Meanwhile, the robust hetero-interfaces in MoS2/Co1−xS@C can expose rich electrochemical active sites and facilitate the charge transfer, which further cooperates synergistically toward electro-catalytic reactions. Consequently, the optimal MoS2/Co1−xS@C hetero-structures present small over-potentials toward HER (135 mV @ 10 mA·cm−2) and OER (230 mV @ 10 mA·cm−2). The MoS2/Co1−xS@C electrolyzer requires an ultralow voltage of 1.6 V at the current density of 10 mA·cm−2 with excellent durability, outperforming the state-of-the-art electro-catalysts. This work sheds light on the design of the hetero-structured catalysts with interfacial engineering toward large-scale water splitting.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Huang J, Sheng H, Ross RD, Han J, Wang X, Song B, Jin S. Modifying redox properties and local bonding of Co3O4 by CeO2 enhances oxygen evolution catalysis in acid. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):3036.
Huo WY, Wang SQ, Zhu WH, Zhang ZL, Fang F, Xie ZH, Jiang JQ. Recent progress on high-entropy materials for electrocatalytic water splitting applications. Tungsten. 2021;3(2):161.
Song Y, Ji K, Duan H, Shao M. Hydrogen production coupled with water and organic oxidation based on layered double hydroxides. Exploration. 2021;1(3):20210050.
Luo M, Liu S, Zhu W, Ye G, Wang J, He Z. An electrodeposited MoS2-MoO3−x/Ni3S2 heterostructure electrocatalyst for efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. Chem Eng J. 2022;428: 131055.
Dai L, Chen ZN, Li L, Yin P, Liu Z, Zhang H. Ultrathin Ni(0)-embedded Ni(OH)2 heterostructured nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical overall water splitting. Adv Mater. 2020;32(8):1906915.
Jin H, Guo C, Liu X, Liu J, Vasileff A, Jiao Y, Zheng Y, Qiao SZ. Emerging two-dimensional nanomaterials for electrocatalysis. Chem Rev. 2018;118(13):6337.
Wu Y, Li F, Chen W, Xiang Q, Ma Y, Zhu H, Tao P, Song C, Shang W, Deng T, Wu J. Coupling interface constructions of MoS2/Fe5Ni4S8 heterostructures for efficient electrochemical water splitting. Adv Mater. 2018;30(38):1803151.
Qin C, Fan A, Zhang X, Wang S, Yuan X, Dai X. Interface engineering: few-layer MoS2 coupled to a NiCo-sulfide nanosheet heterostructure as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. J Mater Chem A. 2019;7(48):27594.
Hu F, Yu D, Ye M, Wang H, Hao Y, Wang L, Li L, Han X, Peng S. Lattice-matching formed mesoporous transition metal oxide heterostructures advance water splitting by active Fe–O–Cu bridges. Adv Energy Mater. 2022;12(19):2200067.
Xi W, Ren Z, Kong L, Wu J, Du S, Zhu J, Xue Y, Meng H, Fu H. Dual-valence nickel nanosheets covered with thin carbon as bifunctional electrocatalysts for full water splitting. J Mater Chem A. 2016;4(19):7297.
Shit S, Chhetri S, Jang W, Murmu NC, Koo H, Samanta P, Kuila T. Cobalt sulfide/nickel sulfide heterostructure directly grown on nickel foam: an efficient and durable electrocatalyst for overall water splitting application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(33):27712.
Niu Y, Gong S, Liu X, Xu C, Xu M, Sun S-G, Chen Z. Engineering iron-group bimetallic nanotubes as efficient bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts for flexible Zn–air batteries. eScience. 2022;2(5):546.
Xin Y, Kan X, Gan LY, Zhang Z. Heterogeneous bimetallic phosphide/sulfide nanocomposite for efficient solar-energy-driven overall water splitting. ACS Nano. 2017;11(10):10303.
Zhang W, Han N, Luo J, Han X, Feng S, Guo W, Xie S, Zhou Z, Subramanian P, Wan K, Arbiol J, Zhang C, Liu S, Xu M, Zhang X, Fransaer J. Critical role of phosphorus in hollow structures cobalt-based phosphides as bifunctional catalysts for water splitting. Small. 2022;18(4):2103561.
Chen D, Lu R, Pu Z, Zhu J, Li H-W, Liu F, Hu S, Luo X, Wu J, Zhao Y, Mu S. Ru-doped 3D flower-like bimetallic phosphide with a climbing effect on overall water splitting. Appl Catal B: Environ. 2020;279: 119396.
Guo X, Wan X, Liu Q, Li Y, Li W, Shui J. Phosphated IrMo bimetallic cluster for efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. eScience. 2022;2(3):304.
Li L, Yu D, Li P, Huang H, Xie D, Lin CC, Hu F, Chen HY, Peng S. Interfacial electronic coupling of ultrathin transition-metal hydroxide nanosheets with layered MXenes as a new prototype for platinum-like hydrogen evolution. Energy Environ Sci. 2021;14(12):6419.
Jiao C, Bo X, Zhou M. Electrocatalytic water splitting at nitrogen-doped carbon layers-encapsulated nickel cobalt selenide. J Energy Chem. 2019;34:161.
Deng L, Hu F, Ma M, Huang SC, Xiong Y, Chen HY, Li L, Peng S. Electronic modulation caused by interfacial Ni–O–M (M = Ru, Ir, Pd) bonding for accelerating hydrogen evolution kinetics. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2021;60(41):22276.
Zhou YN, Zhu YR, Chen XY, Dong B, Li QZ, Chai YM. Carbon–based transition metal sulfides/selenides nanostructures for electrocatalytic water splitting. J Alloys Compd. 2021;852: 156810.
Guo Y, Park T, Yi JW, Henzie J, Kim J, Wang Z, Jiang B, Bando Y, Sugahara Y, Tang J, Yamauchi Y. Nanoarchitectonics for transition-metal-sulfide-based electrocatalysts for water splitting. Adv Mater. 2019;31(17):1807134.
Wang M, Zhang L, He Y, Zhu H. Recent advances in transition-metal-sulfide-based bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. J Mater Chem A. 2021;9(9):5320.
Xiong Q, Wang Y, Liu PF, Zheng LR, Wang G, Yang HG, Wong PK, Zhang H, Zhao H. Cobalt covalent doping in MoS2 to induce bifunctionality of overall water splitting. Adv Mater. 2018;30:1801450.
Zhang J, Wang T, Pohl D, Rellinghaus B, Dong R, Liu S, Zhuang X, Feng X. Interface engineering of MoS2/Ni3S2 heterostructures for highly enhanced electrochemical overall-water-splitting activity. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016;55(23):6702.
Li Z, Hu M, Wang P, Liu J, Yao J, Li C. Heterojunction catalyst in electrocatalytic water splitting. Coord Chem Rev. 2021;439: 213953.
Xiong P, Zhang X, Wan H, Wang S, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Zhou D, Gao W, Ma R, Sasaki T, Wang G. Interface modulation of two-dimensional superlattices for efficient overall water splitting. Nano Lett. 2019;19(7):4518.
Jiao J, Yang W, Pan Y, Zhang C, Liu S, Chen C, Wang D. Interface engineering of partially phosphidated Co@Co-P@NPCNTs for highly enhanced electrochemical overall water splitting. Small. 2020;16(41):2002124.
Wang W, Dong J, Ye X, Li Y, Ma Y, Qi L. Heterostructured TiO2 nanorod@nanobowl arrays for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Small. 2016;12(11):1469.
Zhang J, Zhang Q, Feng X. Support and interface effects in water-splitting electrocatalysts. Adv Mater. 2019;31(31):1808167.
Li Y, Yin J, An L, Lu M, Sun K, Zhao YQ, Gao D, Cheng F, Xi P. FeS2/CoS2 Interface nanosheets as efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Small. 2018;14(26):1801070.
Shit S, Bolar S, Murmu NC, Kuila T. Tailoring the bifunctional electrocatalytic activity of electrodeposited molybdenum sulfide/iron oxide heterostructure to achieve excellent overall water splitting. Chem Eng J. 2021;417: 129333.
Liu J, Wang J, Zhang B, Ruan Y, Wan H, Ji X, Xu K, Zha D, Miao L, Jiang J. Mutually beneficial Co3O4@MoS2 heterostructures as a highly efficient bifunctional catalyst for electrochemical overall water splitting. J Mater Chem A. 2018;6(5):2067.
Wang L, Hao Y, Deng L, Hu F, Zhao S, Li L, Peng S. Rapid complete reconfiguration induced actual active species for industrial hydrogen evolution reaction. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5785.
Aftab U, Tahira A, Mazzaro R, Morandi V, Abro MI, Baloch MM, Syed JA, Nafady A, Ibupoto ZH. Facile NiCo2S4/C nanocomposite: an efficient material for water oxidation. Tungsten. 2020;2(4):403.
An K, Zheng Y, Xu X, Wang Y. Filter paper derived three-dimensional mesoporous carbon with Co3O4 loaded on surface: an excellent binder-free air-cathode for rechargeable Zinc-air battery. J Solid State Chem. 2019;270:539.
Xu B, Chen Z, Yang X, Wang X, Huang Y, Li C. Electronic modulation of carbon-encapsulated NiSe composites via Fe doping for synergistic oxygen evolution. Chem Commun. 2018;54(65):9075.
Wang W, Wang Z, Hu Y, Liu Y, Chen S. A potential-driven switch of activity promotion mode for the oxygen evolution reaction at Co3O4/NiOxHy interface. eScience. 2022;2(4):438.
Li Y, Liu Y, Xing D, Wang J, Zheng L, Wang Z, Wang P, Zheng Z, Cheng H, Dai Y, Huang B. 2D/2D heterostructure of ultrathin BiVO4/Ti3C2 nanosheets for photocatalytic overall Water splitting. Appl Catal B: Environ. 2021;285: 119855.
Wang J, Du CF, Xue Y, Tan X, Kang J, Gao Y, Yu H, Yan Q. MXenes as a versatile platform for reactive surface modification and superior sodium-ion storages. Exploration. 2021;1(2):20210024.
Li Q, Li L, Yu X, Wu X, Xie Z, Wang X, Lu Z, Zhang X, Huang Y, Yang X. Ultrafine platinum particles anchored on porous boron nitride enabling excellent stability and activity for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem Eng J. 2020;399: 125827.
Wang L, Yu H, Zhao S, Ma H, Li L, Hu F, Li L, Pan H, El-Khatib KM, Peng S. Electronic modulation of cobalt–molybdenum oxide via Te doping embedded in a carbon matrix for superior overall water splitting. Inorg Chem Front. 2022;9(15):3788.
Pan ZY, Tang Z, Zhan YZ, Sun D. Three-dimensional porous CoNiO2@reduced graphene oxide nanosheet arrays/nickel foam as a highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Tungsten. 2020;2(4):390.
Babar P, Patil K, Mahmood J, Kim S-J, Kim JH, Yavuz CT. Low-overpotential overall water splitting by a cooperative interface of cobalt-iron hydroxide and iron oxyhydroxide. Cell Rep Phys Sci. 2022;3(2):100762.
Yin D, Cao YD, Chai DF, Fan LL, Gao GG, Wang ML, Liu H, Kang Z. A WOx mediated interface boosts the activity and stability of Pt-catalyst for alkaline water splitting. Chem Eng J. 2022;431: 133287.
Yu D, Ma Y, Hu F, Lin CC, Li L, Chen HY, Han X, Peng S. Dual-sites coordination engineering of single atom catalysts for flexible metal–air batteries. Adv Energy Mater. 2021;11(30):2101242.
Wang A, Cheng L, Shen X, Chen X, Zhu W, Zhao W, Lv C. Porphyrin coordination polymer/Co1−xS composite electrocatalyst for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Chem Eng J. 2020;400: 125975.
Xue Y, Min S, Meng J, Liu X, Lei Y, Tian L, Wang F. Light-induced confined growth of amorphous Co doped MoSx nanodots on TiO2 nanoparticles for efficient and stable in situ photocatalytic H2 evolution. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2019;44(16):8133.
Liu R, Fei HL, Ye GL. Recent advances in single metal atom-doped MoS2 as catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Tungsten. 2020;2(2):147.
Li XX, Liu XC, Liu C, Zeng JM, Qi XP. Co3O4/stainless steel catalyst with synergistic effect of oxygen vacancies and phosphorus doping for overall water splitting. Tungsten. 2023;5:100.
Shit S, Bolar S, Murmu NC, Kuila T. Minimal lanthanum-doping triggered enhancement in bifunctional water splitting activity of molybdenum oxide/sulfide heterostructure through structural evolution. Chem Eng J. 2022;428: 131131.
Han WK, Wei JX, Xiao K, Ouyang T, Peng X, Zhao S, Liu ZQ. Activating lattice oxygen in layered lithium oxides through cation vacancies for enhanced urea electrolysis. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2022;61:202206050.
Wei JX, Xiao K, Chen YX, Guo XP, Huang B, Liu ZQ. In-situ precise anchoring of Pt single atoms in spinel Mn3O4 for a highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ Sci. 2022;15:4592.
Xiao K, Lin RT, Wei JX, Li N, Li H, Ma T, Liu ZQ. Electrochemical disproportionation strategy to in-situ fill cation vacancies with Ru single atoms. Nano Res. 2022;15:4980.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51871119, 22075141, and 22101132), Scientific and Technological Innovation Special Fund for Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutrality of Jiangsu Province (BK20220039), Jiangsu Provincial Founds for Natural Science Foundation (BK20180015 and BK20210311), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M691561 and 2021T140319), Jiangsu Postdoctoral Research Fund (2021K547C) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (kfjj20180605).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, MY., Yu, HZ., Deng, LM. et al. Interfacial engineering of heterostructured carbon-supported molybdenum cobalt sulfides for efficient overall water splitting. Tungsten 5, 589–597 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-023-00212-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-023-00212-6