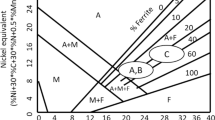
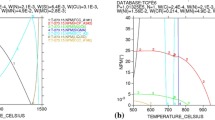
Abstract
Duplex stainless steels consisting of ferrite and austenite are widely used due to their excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Compared with ferritic stainless steels, duplex stainless steels have better plasticity, toughness, and welding performance. They also possess higher strength and better resistance to stress, pitting, and crevice corrosion than austenitic stainless steels. In addition to the above-mentioned properties, there are cost-saving advantages in duplex stainless steels due to their lower nickel content. Today, the types of duplex stainless steel are mainly divided into four categories: lean duplex stainless steel, standard duplex stainless steel, super duplex stainless steel, and hyper duplex stainless steel. Alloying design of duplex stainless steel is an important strategy to achieve high performance. In the last two decades, significant progress has been made in both theoretical calculations and experiments. By adjusting alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, molybdenum, nitrogen, copper, tungsten and rare earth, etc., the mechanical properties and/or corrosion resistance of the duplex stainless steels can be further improved. Summarizing the comprehensive progress of alloying design of duplex stainless steel is of great significance in providing a data basis for establishing the corresponding relationship between chemical compositions and properties. Therefore, this paper reveals the specific roles of alloying elements in the duplex stainless steels and provides a reference for alloying design with different performance requirements.


Copyright 2011 Elsevier

Copyright 2012 Elsevier

Copyright 2012 Elsevier

Copyright 2015 Elsevier

Copyright 2015 Elsevier

Copyright 2013 Elsevier


Copyright 2019 Elsevier

Copyright 2019 Elsevier

Copyright 2019 Elsevier

Copyright 2018 Elsevier


Copyright 2013 Elsevier

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boillot P, Peultier J. Use of stainless steels in the industry: recent and future developments. Procedia Engineering. 2014;83:309.
Michalska J, Sozańska M. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of σ and χ phases in 2205 duplex stainless steel. Mater Charact. 2006;56(4–5):355.
Bae SH, Lee HW. Effect of Mo contents on corrosion behaviors of welded duplex stainless steel. Met Mater Int. 2013;19(3):563.
Gunn R. Duplex stainless steels: microstructure, properties and applications. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing; 1997.
Hsieh YC, Zhang L, Chung TF, Tsai YT, Yang JR, Ohmura T, Suzuki T. In-situ transmission electron microscopy investigation of the deformation behavior of spinodal nanostructured δ-ferrite in a duplex stainless steel. Scripta Mater. 2016;125:44.
Francis R, Byrne G. Duplex stainless steels—alloys for the 21st century. Metals. 2021;11(5):836.
Xu D, Xia J, Zhou E, Zhang D, Li H, Yang C, Li Q, Lin H, Li X, Yang K. Accelerated corrosion of 2205 duplex stainless steel caused by marine aerobic Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Bioelectrochemistry. 2017;113:1.
Gunn R. Duplex stainless steels: microstructure, properties and applications. Anticorros Methods Mater. 2003. https://doi.org/10.1108/acmm.1998.12845bae.001
Lee KM, Cho HS, Choi DC. Effect of isothermal treatment of SAF 2205 duplex stainless steel on migration of δ/γ interface boundary and growth of austenite. J Alloys Compd. 1999;285(1–2):159.
Yang Y, Yan B. The microstructure and flow behavior of 2205 duplex stainless steels during high temperature compression deformation. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2013;579:194.
Zhang W, Jiang L, Hu J, Song H. Effect of ageing on precipitation and impact energy of 2101 economical duplex stainless steel. Mater Charact. 2009;60(1):50.
Lo KH, Shek CH, Lai JKL. Recent developments in stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng, R. 2009;65(4–6):39.
Jiang DW, Ge CS, Zhao XJ, Li J, Shi LI, Xiao XS. 22Cr high-Mn-N low-Ni economical duplex stainless steels. J Iron Steel Res Int. 2012;19(2):50.
Li J, Ma Z, Xiao X, Zhao J, Jiang L. On the behavior of nitrogen in a low-Ni high-Mn super duplex stainless steel. Mater Des. 2011;32(4):2199.
Choi JY, Ji JH, Hwang SW, Park K-T. Strain induced martensitic transformation of Fe–20Cr–5Mn–0.2Ni duplex stainless steel during cold rolling: effects of nitrogen addition. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2011;528(18):6012.
Wang C, Cao W, Shi J, Huang C, Dong H. Deformation microstructures and strengthening mechanisms of an ultrafine grained duplex medium-Mn steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2013;562:89.
Chail G, Kangas P. Super and hyper duplex stainless steels: structures, properties and applications. Procedia Struct Integr. 2016;2:1755.
Wu J, Liu E. Development of duplex stainless steel at home and abroad. Stainless. 2008;8(3):13.
Ezubera HM, El-Houd A, El-Shawesh F. Effects of sigma phase precipitation on seawater pitting of duplex stainless steel. Desalination. 2007;207(1–3):268.
Tani J-I, Mayuzumi M, Hara N. Stress corrosion cracking of stainless-steel canister for concrete cask storage of spent fuel. J Nucl Mater. 2008;379(13):42.
Bello J, Wood R, Wharton J. Synergistic effects of micro-abrasion–corrosion of UNS S30403, S31603 and S32760 stainless steels. Wear. 2007;263(1–6):149.
Nelson DE, Baeslack Iii WA, Lippold JC. Characterization of the weld structure in a duplex stainless steel using color metallography. Mater Charact. 1997;39(2–5):467.
Xiang H, Huang W, Liu D, He F. Effect of N content on microstructure and properties of 29Cr casting super duplex stainless steel. Acta Metall Sin. 2010;46(3):304.
Aval HJ. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of friction stir-welded C71000 copper–nickel alloy and 304 austenitic stainless steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater. 2018;25(11):1294.
Wan J, Ran Q, Li J, Xu Y, Xiao X, Yu H, Jiang L. A new resource-saving, low chromium and low nickel duplex stainless steel 15Cr–xAl–2Ni–yMn. Mater Des. 2014;53:43.
Yang Y, Cao J, Gu Y. Investigation on the solution treated behavior of economical 19Cr duplex stainless steels by Mn addition. Mater Des. 2015;83:820.
Papula S, Anttila S, Talonen J, Sarikka T, Virkkunen I, Hänninen H. Strain hardening of cold-rolled lean-alloyed metastable ferritic-austenitic stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2016;677:11.
Ryś J, Cempura G. Microstructure and deformation behavior of metastable duplex stainless steel at high rolling reductions. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2017;700:656.
Ha H-Y, Lee T-H, Kim S-J. Effect of C fraction on corrosion properties of high interstitial alloyed stainless steels. Metall Mater Trans A. 2012;43(9):2999.
Dong F, Zhang H, Wu ZX, Chen JZ. Research progress on erosion-corrosion and cavitation erosion of duplex stainless steel. Total Corros Contr. 2009;4(1):15.
Dyja D, Stradomski Z. Solidification model of highly alloyed FE-Cr-Ni cast steels. Arch Foundry. 2006;6(19):81.
Stradomski Z, Dyja D,Stachura S. Technological problem in elaboration of massive casting from duplex cast steel. Stainless Steel World. 2005: 363.
Stradomski Z, Dyja D. Influence of carbon content on the segregation process in duplex cast steel. Arch Foundry Eng. 2007;7(1):139.
Dyja D, Stradomski Z, Stachura S. Solidification structure of massive castings from duplex cast steel. Arch Foundry. 2005;5(15):79.
Li Y, Jiang W, Feng Y, Guo E, Jiang Y. Effect of C content on microstructure and properties of 00Cr22Ni5Mo3N duplex stainless steel. Heat Treat Met. 2015;40(7):55.
Nilsson J-O. Super duplex stainless steels. Mater Sci Technol. 1992;8(8):685.
Tomota Y, Tokuda H, Adachi Y, Wakita M, Minakawa N, Moriai A, Morii Y. Tensile behavior of TRIP-aided multi-phase steels studied by in situ neutron diffraction. Acta Mater. 2004;52(20):5737.
Cai ZH, Ding H, Misra RDK, Ying ZY. Austenite stability and deformation behavior in a cold-rolled transformation-induced plasticity steel with medium manganese content. Acta Mater. 2015;84:229.
Blondé R, Jimenez-Melero E, Zhao L, Wright JP, Brück E, van der Zwaag S, van Dijk NH. High-energy X-ray diffraction study on the temperature-dependent mechanical stability of retained austenite in low-alloyed TRIP steels. Acta Mater. 2012;60(2):565.
Yan K, Liss K-D, Timokhina IB, Pereloma EV. In situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction studies of the effect of microstructure on tensile behavior and retained austenite stability of thermo-mechanically processed transformation induced plasticity steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2016;662:185.
Tissier J, Balloy D, Dairon J, Dorlencourt S, Ninin J. Vacuum decarburization: a solution within reach of small foundries. Fonderie Fondeur d’Aujourd’hui. 2005;246:28.
Levey P, Van Bennekom A. A mechanistic study of the effects of nitrogen on the corrosion properties of stainless steels. Corrosion. 1995;51(12):911.
Hendry A. Developments in high-nitrogen stainless steels. Wire J Int. 1994;27(4):140.
Moverare JJ, Oden M. Influence of elastic and plastic anisotropy on the flow behavior in a duplex stainless steel. Metall Mater Trans A. 2002;33(1):57.
Fujisawa M, Mauchi R, Morikawa T, Tanaka M, Higashida K. Influence of strain-induced martensite on tensile properties of metastable duplex stainless steels consisting of Fe-Cr-Mn-Ni and Fe-Cr-Mn-N. Tetsu-to-Hagané. 2014;100(9):1140.
Choi JY, Ji JH, Hwang SW, Park K-T. Effects of nitrogen content on TRIP of Fe–20Cr–5Mn–xN duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2012;534:673.
Speidel M. New nitrogen-bearing austenitic stainless steels with high strength and ductility. Met Sci Heat Treat. 2005;47(11–12):489.
Simmons J. Overview: high-nitrogen alloying of stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng, A. 1996;207(2):159.
Fujisawa M, Kato Y, Ujiro T. Mechanical properties and stress corrosion cracking receptivity of metastable Cr-Mn-N duplex stainless steels. CAMP-ISIJ. 2009;22:1163.
Remy L, Pineau A. Twinning and strain-induced F.C.C. ~ H.C.P. transformation in the Fe-Mn-Cr-C System. Mater Sci Eng. 1997;28(1):99.
Byun TS. On the stress dependence of partial dislocation separation and deformation microstructure in austenitic stainless steels. Acta Mater. 2003;51(11):3063.
Park K-T, Kim G, Kim SK, Lee SW, Hwang SW, Lee CS. On the transitions of deformation modes of fully austenitic steels at room temperature. Met Mater Int. 2010;16(1):1.
Herrera C, Ponge D, Raabe D. Design of a novel Mn-based 1GPa duplex stainless TRIP steel with 60% ductility by a reduction of austenite stability. Acta Mater. 2011;59(11):4653.
Choi JH, Jo MC, Lee H, Zargaran A, Song T, Sohn SS, Kim NJ, Lee S. Cu addition effects on TRIP to TWIP transition and tensile property improvement of ultra-high-strength austenitic high-Mn steels. Acta Mater. 2019;166:246.
Choi JY, Hwang SW, Ha MC, Park K-T. Extended strain hardening by a sequential operation of twinning induced plasticity and transformation induced plasticity in a low Ni duplex stainless steel. Met Mater Int. 2014;20(5):893.
Choi JY, Hwang SW, Park K-T. Twinning-induced plasticity aided high ductile duplex stainless steel. Metall Mater Trans A. 2012;44(2):597.
Choi JY, Ji JH, Hwang SW, Park K-T. TRIP aided deformation of a near-Ni-free, Mn–N bearing duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2012;535:32.
Vasilakos AN, Ohlert J, Giasla K, Haidemenopoulos GN, Bleck W. Low-alloy TRIP steels: a correlation between mechanical properties and the retained austenite stability. Steel Res Int. 2002;73(67):245.
Grässel O, Krüger L, Frommeyer G, Meyer LW. High strength Fe–Mn–(Al, Si) TRIP/TWIP steels development—properties—application. Int J Plast. 2000;16(10–11):1391.
Sabzi HE, Zarei Hanzaki A, Abedi HR, Soltani R, Mateo A, Roa JJ. The effects of bimodal grain size distributions on the work hardening behavior of a TRansformation-TWinning induced plasticity steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2016;678:23.
Allain S, Chateau JP, Bouaziz O, Migot S, Guelton N. Correlations between the calculated stacking fault energy and the plasticity mechanisms in Fe–Mn–C alloys. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2004;387–389:158.
Lee T-H, Oh C-S, Kim S-J. Effects of nitrogen on deformation-induced martensitic transformation in metastable austenitic Fe–18Cr–10Mn–N steels. Scripta Mater. 2008;58(2):110.
Galindo-Nava EI, Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo PEJ. Understanding martensite and twin formation in austenitic steels: a model describing TRIP and TWIP effects. Acta Mater. 2017;128:120.
Ding H, Ding H, Song D, Tang Z, Yang P. Strain hardening behavior of a TRIP/TWIP steel with 18.8% Mn. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2011;528(3):868.
Frommeyer G, Brüx U, Neumann P. Supra-ductile and high-strength manganese-TRIP/TWIP steels for high energy absorption purposes. ISIJ Int. 2003;43(3):438.
Tang ZY, Misra RDK, Ma M, Zan N, Wu ZQ, Ding H. Deformation twinning and martensitic transformation and dynamic mechanical properties in Fe–0.07C–23Mn–3.1Si–2.8Al TRIP/TWIP steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2015;624:186.
Sahraoui T, Hadji M, Yahi M. Design and deformation behavior of high strength Fe–Mn–Al–Cr–C duplex steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2009;523(1–2):271.
Rahimi R, Ullrich C, Rafaja D, Biermann H, Mola J. Microstructural evolution of an Al-alloyed duplex stainless steel during tensile deformation between 77 and 473 K (−196 and 200 °C). Metall Mater Trans A. 2016;47(6):2705.
Hutchinson WB, Ushioda K, Runnsjö G. Anisotropy of tensile behaviour in a duplex stainless steel sheet. Mater Sci Technol. 2013;1(9):728.
Hilkhuijsen P, Geijselaers HJM, Bor TC, Perdahcıoğlu ES, vd Boogaard AH, Akkerman R. Strain direction dependency of martensitic transformation in austenitic stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2013;573:100.
Chou S-L, Tsai M-J, Tsai W-T, Lee J-T. Effect of nitrogen on the electrochemical behavior of 301LN stainless steel in H2SO4 solutions. Mater Chem Phys. 1997;51(2):97.
Ha H-Y, Lee T-H, Kim S-J. Role of nitrogen in the active–passive transition behavior of binary Fe–Cr alloy system. Electrochim Acta. 2012;80:432.
Ha H, Jang H, Kwon H, Kim S. Effects of nitrogen on the passivity of Fe–20Cr alloy. Corros Sci. 2009;51(1):48.
Jargelius-Pettersson R. Electrochemical investigation of the influence of nitrogen alloying on pitting corrosion of austenitic stainless steels. Corros Sci. 1999;41(8):1639.
Ha H-Y, Lee C-H, Lee T-H, Kim S. Effects of nitrogen and tensile direction on stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of Ni-free FeCrMnC-based duplex stainless steels. Materials. 2017;10(3):294.
Matsunaga H, Sato Y, Kokawa H, Kuwana T. Effect of nitrogen on corrosion of duplex stainless steel weld metal. Sci Technol Weld Join. 1998;3(5):225.
Fang YL, Liu ZY, Xue WY, Song HM, Jiang LZ. Precipitation of secondary phases in lean duplex stainless steel 2101 during isothermal ageing. ISIJ Int. 2010;50(2):286.
Huang C-S, Shih C-C. Effects of nitrogen and high temperature aging on σ phase precipitation of duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2005;402(1–2):66.
Merello R, Botana F, Botella J, Matres M, Marcos M. Influence of chemical composition on the pitting corrosion resistance of non-standard low-Ni high-Mn–N duplex stainless steels. Corros Sci. 2003;45(5):909.
Park Y-H, Lee Z-H. The effect of nitrogen and heat treatment on the microstructure and tensile properties of 25Cr–7Ni–1.5 Mo–3W–xN duplex stainless steel castings. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2001;297(12):78.
Wei Z, Chen X, Zhong H, Zhai Q. Effect of N content on microstructure of Fe-21Cr-3Ni-1Mo-N duplex stainless steel. J Shanghai Univ (Nat Sci). 2018;24(6):955.
Charles J. Duplex stainless steels-a review after DSS ‘07 held in Grado. Steel Res Int. 2008;79(6):455.
Nilsson J, Wilson A, Josefsson B, Thorvaldsson T. Proceedings of the applications of stainless steel. Mater Sci Technol. 1992;8:685.
Mozhi TA, Clark W, Nishimoto K, Johnson W, Macdonald D. The effect of nitrogen on the sensitization of AISI 304 stainless steel. Corrosion. 1985;41(10):555.
Sedriks A. 1989 speller award lecture: new stainless steels for seawater service. Corrosion. 1989;45(6):510.
Pramanik A, Littlefair G, Basak A. Weldability of duplex stainless steel. Mater Manuf Process. 2015;30(9):1053.
Kim S-C, Zhang Z, Furuya Y, Kang C-Y, Sung J-H, Ni Q-Q, Watanabe Y, Kim I-S. Effect of precipitation of σ-phase and N addition on the mechanical properties in 25Cr–7Ni–4Mo–2W super duplex stainless steel. Mater Trans. 2005;46(7):1656.
Palit G, Kain V, Gadiyar H. Electrochemical investigations of pitting corrosion in nitrogen-bearing type 316LN stainless steel. Corrosion. 1993;49(12):977.
Newman R, Shahrabi T. The effect of alloyed nitrogen or dissolved nitrate ions on the anodic behaviour of austenitic stainless steel in hydrochloric acid. Corros Sci. 1987;27(8):827.
Potgieter J, Olubambi P, Cornish L, Machio C, Sherif E-SM. Influence of nickel additions on the corrosion behaviour of low nitrogen 22% Cr series duplex stainless steels. Corros Sci. 2008;50(9):2572.
Oblonsky L, Devine T. A surface enhanced Raman spectroscopic study of the passive films formed in borate buffer on iron, nickel, chromium and stainless steel. Corros Sci. 1995;37(1):17.
Alvarez-Armas I. Duplex stainless steels: brief history and some recent alloys. Recent Pat Mech Eng. 2008;1(1):51.
Pilhagen J, Sandström R. Influence of nickel on the toughness of lean duplex stainless steel welds. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2014;602:49.
Kang D, Lee H. Study of the correlation between pitting corrosion and the component ratio of the dual phase in duplex stainless steel welds. Corros Sci. 2013;74:396.
Miura M, Koso M, Kudo T, Tsuge H. The effects of nickel and nitrogen on the microstructure and corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steel weldments. Weld Int. 1990;4(3):200.
Shek C, Wong K, Lai J, Li D. Hot tensile properties of 25Cr-8Ni duplex stainless steel containing cellular (σ+ γ2) structure after various thermal treatments. Mater Sci Eng, A. 1997;231(1–2):42.
Pohl M, Storz O. Sigma-phase in duplex-stainless steels. Int J Mater Res. 2004;95(7):631.
Komizo Y, Ogawa K, Azuma S. HAZ embrittlement in high Cr-Mo duplex stainless steel and the effects of Ni and N. Weld Int. 1991;5(4):277.
Ha H-Y, Lee T-H, Kim S-D, Jang JH, Moon J. Improvement of the corrosion resistance by addition of Ni in lean duplex stainless steels. Metals. 2020;10(7):891.
Wessman S, Hertzman S, Pettersson R, Lagneborg R, Liljas M. On the effect of nickel substitution in duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Technol. 2008;24(3):348.
Sohn SS, Hong S, Lee J, Suh B-C, Kim S-K, Lee B-J, Kim NJ, Lee S. Effects of Mn and Al contents on cryogenic-temperature tensile and Charpy impact properties in four austenitic high-Mn steels. Acta Mater. 2015;100:39.
Li J, Xu Y, Xiao X, Zhao J, Jiang L, Hu J. A new resource-saving, high manganese and nitrogen super duplex stainless steel 25Cr–2Ni–3Mo–xMn–N. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2009;527(1–2):245.
Liljas M, Johansson P, Liu HP, Olsson COA. Development of a lean duplex stainless steel. Steel Res Int. 2008;79(6):466.
Yang Y, Ni K. Investigation on the precipitation and corrosion behaviour of 19% Cr economical duplex stainless steel with Mn addition by aging at 800 °C. Ironmaking Steelmaking. 2021;48(2):200.
Feng Z, Yang Y, Wang J. Effect of Mn addition on the precipitation and corrosion behaviour of 22% Cr economical duplex stainless steel after isothermal aging at 800 °C. J Alloys Compd. 2017;699:334.
Wang L, Dong W, Guo E, Jiang W, Feng Y. Effect of Mn content on microstructure and properties of 00Cr22Ni5Mo3Mnx duplex stainless steel. Hot Work Technol. 2013;42(2):63.
Jang YH, Kim SS, Lee JH. Effect of different Mn contents on tensile and corrosion behavior of CD4MCU cast duplex stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2005;396(1–2):302.
Park J-Y, Ahn Y-S. Effect of Ni and Mn on the mechanical properties of 22Cr micro-duplex stainless steel. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (Engl Lett). 2015;28(1):32.
Toor I-U-H, Hyun PJ, Kwon HS. Development of high Mn–N duplex stainless steel for automobile structural components. Corros Sci. 2008;50(2):404.
Ran Q, Peng W, Xu Y, Li J, Xiao X, Yu H, Jiang L. Self-repairing behavior of oxidation diffusion layer and phase transformation mechanism during tensile test of 19Cr duplex stainless steels with various Mn content. Corros Sci. 2015;90:535.
Kubaschewski O, Smith JF, Bailey DM. A thermodynamic analysis of phase relationships in the iron-copper system/eine thermodynamische analyse der phasenbeziehungen in dem system eisen-kupfer. Int J Mater Res. 1977;68(7):495.
Banas J, Mazurkiewicz A. The effect of copper on passivity and corrosion behaviour of ferritic and ferritic–austenitic stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2000;277(1–2):183.
de Lima HMLF, Tavares SSM, Martins M, Araujo WS. The effect of copper addition on the corrosion resistance of cast duplex stainless steel. J Market Res. 2019;8(2):2107.
Smuk O, Selleby M, Bergman B. The effect of copper on secondary phase precipitation in duplex stainless steel–a thermodynamic calculations approach. Int J Mater Res. 2005;96(8):918.
Zhao Y, Liu X, Li X, Wang Y, Zhang W, Liu Z. Pitting corrosion behavior in novel Mn–N alloyed lean duplex stainless steel containing Cu. J Mater Sci. 2018;53(1):824.
Fuertes N, Pettersson R. Passive film properties and electrochemical response of different phases in a Cu-alloyed stainless steel after long term heat treatment. J Electrochem Soc. 2016;163(7):C377.
Weber L, Uggowitzer P. Partitioning of chromium and molybdenum in super duplex stainless steels with respect to nitrogen and nickel content. Mater Sci Eng, A. 1998;242(1–2):222.
O’gorman J, Humphreys H. Application of copper to prevent and control infection. Where are we now? J Hosp Infect. 2012;81(4):217.
Monzen R, Jenkins M, Sutton A. The bcc-to-9R martensitic transformation of Cu precipitates and the relaxation process of elastic strains in an Fe-Cu alloy. Philos Mag A. 2000;80(3):711.
Bajguirani HH. The effect of ageing upon the microstructure and mechanical properties of type 15–5 PH stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2002;338(1–2):142.
Holzer I, Kozeschnik E. Computer simulation of the yield strength evolution in Cu-precipitation strengthened ferritic steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2010;527(15):3546.
Stechauner G, Kozeschnik E. Simulation of Cu precipitation in the Fe-Cu binary system. Adv Mater Res. 2014;922:728.
Primig S, Leitner H. Transformation from continuous-to-isothermal aging applied on a maraging steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2010;527(16–17):4399.
Zhao J, Yang C, Zhang D, Zhao Y, Khan MS, Xu D, Xi T, Li X, Yang K. Investigation on mechanical, corrosion resistance and antibacterial properties of Cu-bearing 2205 duplex stainless steel by solution treatment. RSC Adv. 2016;6(114): 112738.
Xu D, Zhou E, Zhao Y, Li H, Liu Z, Zhang D, Yang C, Lin H, Li X, Yang K. Enhanced resistance of 2205 Cu-bearing duplex stainless steel towards microbiologically influenced corrosion by marine aerobic Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J Mater Sci Technol. 2018;34(8):1325.
Ressel G, Gsellmann M, Brandl D, Landefeld A, Keplinger A, Zhang Z, Maier-Kiener V, Schnitzer R. Copper and its effects on microstructure and correlated tensile properties of super duplex stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2021;821: 141544.
Pan M, Zhang X, Misra R. Effect of Cu on phase proportion, mechanical properties and corrosion properties of Fe-Cr-Mn-Al duplex stainless steel. SSRN J. 2022. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4010407.
Ran Q, Li J, Xu Y, Xiao X, Yu H, Jiang L. Novel Cu-bearing economical 21Cr duplex stainless steels. Mater Des. 2013;46:758.
Shu J, Bi H, Li X, Xu Z. The effect of copper and molybdenum on pitting corrosion and stress corrosion cracking behavior of ultra-pure ferritic stainless steels. Corros Sci. 2012;57:89.
Jeon S-H, Park I-J, Kim H-J, Kim S-T, Lee Y-K, Park Y-S. Effect of Cu on the precipitation of deleterious phases and the mechanical properties of 27Cr–7Ni hyper duplex stainless steels. Mater trans. 2014;55(6):971.
Jeon S-H, Kim S-T, Lee I-S, Kim J-S, Kim K-T, Park Y-S. Effects of Cu on the precipitation of intermetallic compounds and the intergranular corrosion of hyper duplex stainless steels. Corros Sci. 2013;66:217.
Jeon S-H, Kim S-T, Kim J-S, Kim J-S, Kim K-T, Park Y-S. Effects of copper addition on the precipitation of chromium nitrides and the associated pitting corrosion resistance of the hyper duplex stainless steels. Mater Trans. 2012;53(12):2129.
Jeon S-H, Kim S-T, Lee I-S, Park J-H, Kim K-T, Kim J-S, Park Y-S. Effects of copper addition on the formation of inclusions and the resistance to pitting corrosion of high performance duplex stainless steels. Corros Sci. 2011;53(4):1408.
Kong K-H, Jeon S-H, Kim S-T, Kim D-H, Kim B-J, Guim H-U, Moon M-B, Park Y-S. Effects of Cu addition on the microstructure and localized corrosion resistance of hyper duplex stainless steels aged at 748 K. Mater trans. 2015;56(5):749.
Li X, Zhang D, Liu Z, Li Z, Du C, Dong C. Materials science: share corrosion data. Nature. 2015;527(7579):441.
AlAbbas FM, Bhola SM, Spear JR, Olson DL, Mishra B. The shielding effect of wild type iron reducing bacterial flora on the corrosion of linepipe steel. Eng Fail Anal. 2013;33:222.
Ha H-Y, Jang M-H, Lee T-H, Moon J. Interpretation of the relation between ferrite fraction and pitting corrosion resistance of commercial 2205 duplex stainless steel. Corros Sci. 2014;89:154.
Olsson J, Snis M. Duplex—A new generation of stainless steels for desalination plants. Desalination. 2007;205(1–3):104.
Sowards JW, Williamson C, Weeks TS, McColskey JD, Spear JR. The effect of Acetobacter sp and a sulfate-reducing bacterial consortium from ethanol fuel environments on fatigue crack propagation in pipeline and storage tank steels. Corros Sci. 2014;79:128.
Liu D, Jia R, Xu D, Yang H, Zhao Y, Saleem Khan M, Huang S, Wen J, Yang K, Gu Y. Biofilm inhibition and corrosion resistance of 2205-Cu duplex stainless steel against acid producing bacterium Acetobacter aceti. J Mater Sci Technol. 2019;35(11):2494.
Sun D, Babar Shahzad M, Li M, Wang G, Xu D. Antimicrobial materials with medical applications. Mater Technol. 2015;30(sup6):B90.
Xia J, Yang C, Xu D, Sun D, Nan L, Sun Z, Li Q, Gu T, Yang K. Laboratory investigation of the microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) resistance of a novel Cu-bearing 2205 duplex stainless steel in the presence of an aerobic marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Biofouling. 2015;31(6):481.
Ravindranath K, Malhotra S. The influence of aging on the intergranular corrosion of 22 chromium-5 nickel duplex stainless steel. Corros Sci. 1995;37(1):121.
Iacoviello F, Casari F, Gialanella S. Effect of “475 C embrittlement” on duplex stainless steels localized corrosion resistance. Corros Sci. 2005;47(4):909.
Lee J-B. Effects of alloying elements, Cr, Mo and N on repassivation characteristics of stainless steels using the abrading electrode technique. Mater Chem Phys. 2006;99(2–3):224.
Brooks A, Clayton C, Doss K, Lu Y. On the role of Cr in the passivity of stainless steel. J Electrochem Soc. 1986;133(12):2459.
Zhang S, Li H, Jiang Z, Zhang B, Li Z, Wu J, Fan S, Feng H, Zhu H. Effects of Cr and Mo on precipitation behavior and associated intergranular corrosion susceptibility of superaustenitic stainless steel S32654. Mater Charact. 2019;152:141.
Chandra K, Singhal R, Kain V, Raja V. Low temperature embrittlement of duplex stainless steel: correlation between mechanical and electrochemical behavior. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2010;527(16–17):3904.
Yoshiie T, Xu Q. Effects of alloying elements Mn, Mo, Ti, Si, P and C on the incubation period of void swelling in austenitic stainless steels. Tungsten. 2021;3(1):3.
Zhao P. Application of molybdenum in stainless steel. China Molybd Ind. 2004;28(5):3.
Dong Y, Lin X, Jiang X. Effect of Cr, Mo on resistance to the corrosion and corrosion wear of stainless steels. Mater Mech Eng. 1997;21(6):29.
Kim N-H, Gil W, Lim H-D, Choi C-H, Lee H-W. Variation of mechanical properties and corrosion properties with Mo contents of hyper duplex stainless-steel welds. Metals Mater Int. 2019;25(1):193.
Sun Y-T, Tan X, Lei L-L, Li J, Jiang Y-M. Revisiting the effect of molybdenum on pitting resistance of stainless steels. Tungsten. 2021;3(3):329.
Schweitzer PA. Metallic materials: physical, mechanical, and corrosion properties. Florida: CRC Press; 2003.
Roberge PR. Corrosion engineering handbook. Florida: CRC Press; 1996.
Tian H, Cheng X, Wang Y, Dong C, Li X. Effect of Mo on interaction between α/γ phases of duplex stainless steel. Electrochim Acta. 2018;267:255.
Martins M, Casteletti LC. Heat treatment temperature influence on ASTM A890 GR 6A super duplex stainless steel microstructure. Mater Charact. 2005;55(3):225.
Sieurin H, Sandström R. Sigma phase precipitation in duplex stainless steel 2205. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2007;444(1–2):271.
Jiménez JA, Frommeyer G, Carsı́ M, Ruano OA,. Superplastic properties of a δ/γ stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2001;307(1–2):134.
Clayton C, Lu Y. A bipolar model of the passivity of stainless steel: the role of Mo addition. J Electrochem Soc. 1986;133(12):2465.
Yoon B-J, Ahn Y-S. Effect of Mo addition on aging behavior of TRIP-aided duplex stainless steel. Mater Charact. 2021;173: 110946.
Malta PO, Dias FL, de Souza ACM, Santos DB. Microstructure and texture evolution of duplex stainless steels with different molybdenum contents. Mater Charact. 2018;142:406.
Yan H, Bi H, Li X, Xu Z. Microstructure and texture of Nb+ Ti stabilized ferritic stainless steel. Mater Charact. 2008;59(12):1741.
Jang Y, Kim S, Lee J. Effect of different Mo contents on tensile and corrosion behaviors of CD4MCU cast duplex stainless steels. Metall Mater Trans A. 2005;36(5):1229.
Kim J-S, Kwon H-S. Effects of tungsten on corrosion and kinetics of sigma phase formation of 25% chromium duplex stainless steels. Corrosion. 1999;55(5):512.
Kim J, Xiang P, Kim K. Effect of tungsten and nickel addition on the repassivation behavior of stainless steel. Corrosion. 2005;61(2):174.
Jeon S-H, Kim S-T, Lee I-S, Kim J-S, Kim K-T, Park Y-S. Effects of W substitution on the precipitation of secondary phases and the associated pitting corrosion in hyper duplex stainless steels. J Alloys Compd. 2012;544:166.
Kim K, Zhang P, Ha T, Lee Y. Electrochemical and stress corrosion properties of duplex stainless steels modified with tungsten addition. Corrosion. 1998;54(11):910.
Liu H, Zheng J, Ma M, Wei L, Chen L. Structure-mechanical property–formability relationships for 444-type W-containing ferritic stainless steels. J Mater Eng Perform. 2021;30(1):467.
Wei L, Chen L, Liu H, Misra R. Significant grain refinement in the simulated heat-affected zone (HAZ) of ferritic stainless steels by alloying with tungsten. Metall Mater Trans A. 2020;51(6):2719.
Liu H, Wei L, Ma M, Zheng J, Chen L, Misra RDK. Laves phase precipitation behavior and high-temperature strength of W-containing ferritic stainless steels. J Market Res. 2020;9(2):2127.
Ma M, He C, Chen L, Wei L, Misra RDK. Effect of W and Ce additions on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of 444-type ferritic stainless steel. Corros Eng, Sci Technol. 2018;53(3):199.
Wei L, Zheng J, Chen L, Misra RDK. High temperature oxidation behavior of ferritic stainless steel containing W and Ce. Corros Sci. 2018;142:79.
Ogawa K, Okamoto H, Ueda M, Igarashi M, Mori T, Kobayashi T. Effects of tungsten on pitting corrosion resistance and impact toughness in the HAZ of duplex stainless steel-study of weldability of high-tungsten duplex stainless steel (1st Report). Weld Int. 1996;10(6):466.
Haugan EB, Næss M, Rodriguez CT, Johnsen R, Iannuzzi M. Effect of tungsten on the pitting and crevice corrosion resistance of type 25Cr super duplex stainless steels. Corrosion. 2017;73(1):53.
Torres C, Hazarabedian M-S, Quadir Z, Johnsen R, Iannuzzi M. The role of tungsten on the phase transformation kinetics and its correlation with the localized corrosion resistance of 25Cr super duplex stainless steels. J Electrochem Soc. 2020;167(8):081510.
Ahn Y, Kang J. Effect of aging treatments on microstructure and impact properties of tungsten substituted 2205 duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Technol. 2000;16(4):382.
Ha H-Y, Lee T-H, Kim S. Effect of W on stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of newly developed Ni-saving duplex stainless steels. Met Mater Int. 2017;23(1):115.
Oh B, Kim J, Jeong S, Kwon H-S, Hong S, Kim Y. The influence of tungsten on corrosion resistance and sigma phase formation in duplex stainless steels. Process Mater: Innov Stainl Steel. 1993;3:3.
Tan H, Wang Z, Jiang Y, Yang Y, Deng B, Song H, Li J. Influence of welding thermal cycles on microstructure and pitting corrosion resistance of 2304 duplex stainless steels. Corros Sci. 2012;55:368.
Zhang ZX, Ran QX, Xu YL, Yu XJ, Jiang DW, Xiao XS. A new series of Mo-free 21.5 Cr-3.5 Ni-x W-0.2 N economical duplex stainless steels. J Iron Steel Res Int. 2014;21(1):69.
Chi RA, Li ZJ, Peng C, Zhu GC, Xu SM. Partitioning properties of rare earth ores in China. Rare Met. 2005;24(3):205.
Ma X, An Z, Chen L, Mao T, Wang J, Long H, Hongyan X. The effect of rare earth alloying on the hot workability of duplex stainless steel—a study using processing map. Mater Des. 2015;86:848.
Kim SM, Kim JS, Kim KT, Park K-T, Lee CS. Effect of Ce addition on secondary phase transformation and mechanical properties of 27Cr–7Ni hyper duplex stainless steels. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2013;573:27.
Park Y-S, Kim S-T, Lee I-S, Song C-B. Effects of rare earth metals addition and aging treatment on the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of super duplex stainless steels. Met Mater Int. 2002;8(3):309.
Xiaofeng W, Weiqing C. Influence of cerium on hot workability of 00Cr25Ni7Mo4N super duplex stainless steel. J Rare Earths. 2010;28(2):295.
Kim S-T, Jeon S-H, Lee I-S, Park Y-S. Effects of rare earth metals addition on the resistance to pitting corrosion of super duplex stainless steel–Part 1. Corros Sci. 2010;52(6):1897.
Wang L, Lin Q, Ji J, Lan D. New study concerning development of application of rare earth metals in steels. J Alloys Compd. 2006;408:384.
Yoo Y-H, Choi Y-S, Kim J-G, Park Y-S. Effects of Ce, La and Ba addition on the electrochemical behavior of super duplex stainless steels. Corros Sci. 2010;52(4):1123.
Shim S-I, Park Y-S, Kim S-T, Song C-B. Effects of rare earth metal addition on the cavitation erosion-corrosion resistance of super duplex stainless steels. Met Mater Int. 2002;8(3):301.
Ha H, Park C, Kwon H. Effects of misch metal on the formation of non-metallic inclusions and the associated resistance to pitting corrosion in 25% Cr duplex stainless steels. Scripta Mater. 2006;55(11):991.
Xiaoshen Z. Effect of Ce on inclusion and properties in medium plate of heat resisting steel 253MA. Special Steel. 2008;29(2):56.
Sun W, Ding G, Luo M, Wang Z, Song A. Behaviour of Ce in duplex stainless steel. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (China). 1996;32:245.
Sun W. Progress in duplex stainless steel and its application in ordnance industry. Mater Sci Eng. 2001;24(4):49.
Gong W, Wang P, Zhang L, Jiang Z. Effects of Ce on microstructure and mechanical properties of LDX2101 duplex stainless steel. Metals. 2020;10(9):1233.
Liu X, Wang LM. Effects of rare earth addition on the inclusions and mechanical properties of 2205 duplex stainless steel. Trans Tech Publ. 2012;503:463.
Choi Y, Moon BM, Sohn D-S. Fabrication of Gd containing duplex stainless steel sheet for neutron absorbing structural materials. Nucl Eng Technol. 2013;45(5):689.
Khan Z. Influence of gadolinium on the microstructure and mechanical properties of steel and stainless steel. J South Afr Inst Min Metall. 2012;112(4):309.
Ahn J-H, Jung H-D, Im J-H, Jung KH, Moon B-M. Influence of the addition of gadolinium on the microstructure and mechanical properties of duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2016;658:255.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51974032, 52174355, 51604034, and 51701021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Liu, ZH., Wu, CB. et al. A short review on the role of alloying elements in duplex stainless steels. Tungsten 5, 419–439 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-022-00168-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42864-022-00168-z