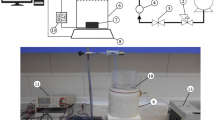
Abstract
Purpose
Due to the advantages of aeroponic compared to other cultivation systems, the advantages of piezoelectric ultrasonic compared to other mist makers, and lack of research done to study the parameters affecting the misting rate of nutrient solutions with the approach used in aeroponic systems, the current work was carried out.
Methods
The effects of dosage of nutrient solution, voltage, horn diameter, and horn height on the misting rate, circuit current, power consumption, amplitude of sound waves, Δ pH, Δ EC (electrical conductivity), and Δ TDS (total dissolved solids) were investigated. Physical properties of the solution (density, viscosity, surface tension, and speed of sound) were measured. Moreover, optimization was performed to determine suitable ranges of independent variables.
Results
Obtained results showed that the four mentioned independent variables significantly affect the six dependent variables (P<1%). The misting rate was in the range of 96 to 411.6 g h−1. At the temperature of 25 °C and for different concentrations of fertilizer, the density, surface tension, viscosity, speed of sound in the solution, initial TDS, and initial pH varied between 1002.3–1004.8 kg m−3, 73.33–74.42 mN m−1, 1.009–1.395 mPa s, 1489–1502 m s−1, 1323–8865 mg L−1, and 6.18–6.84, respectively. Also, theoretically calculated mist mean droplet diameter was in the range of 2.868 to 2.880 μm for different fertilizer doses.
Conclusion
Mist generation by piezoelectric ceramics is an efficient method for use in aeroponic systems. Although the obtained misting rates in this study differ from the industrial values, the use of several piezoelectric ceramics is the simplest solution to this problem.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedi, K. J., & Mesforoush, M. (2009). Evaluation of superabsorbent polymer application on yield, water and fertilizer use efficiency in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Iranian Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2(3), 100–111.
Amdoun, R., Khelifi, L., Khelifi-Slaoui, M., Amroune, S., Asch, M., Assaf-Ducrocq, C., & Gontier, E. (2018). The desirability optimization methodology; a tool to predict two antagonist responses in biotechnological systems: Case of biomass growth and hyoscyamine content in elicited datura starmonium hairy roots. Iranian Journal of Biotechnology, 16(1), 11–19.
Arcas-Pilz, V., Parada, F., Villalba, G., Rufí-Salis, M., Rosell-Melé, A., & Gabarrell Durany, X. (2021). Improving the fertigation of soilless urban vertical agriculture through the combination of struvite and rhizobia inoculation in Phaseolus vulgaris. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 952. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.649304
Avvaru, B., Patil, M. N., Gogate, P. R., & Pandit, A. B. (2006). Ultrasonic atomization: effect of liquid phase properties. Ultrasonics, 44(2), 146–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2005.09.003
Badjakov, I., Georgiev, V., Georgieva, M., Dincheva, I., Vrancheva, R., Ivanov, I., Georgiev, D., Hristova, D., Kondakova, V., & Pavlov, A. (2021). Bioreactor technology for in vitro berry plant cultivation. Plant Cell and Tissue Differentiation and Secondary Metabolites: Fundamentals and Applications, 383–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30185-9_18
Baganz, G. F. M., Junge, R., Portella, M. C., Goddek, S., Keesman, K. J., Baganz, D., Staaks, G., Shaw, C., Lohrberg, F., & Kloas, W. (2021). The aquaponic principle—It is all about coupling. Reviews in Aquaculture, 14, 252–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12596
Barla, S.-A., Salachas, G., & Abeliotis, K. (2020). Assessment of the greenhouse gas emissions from aeroponic lettuce cultivation in Greece. Euro-Mediterranean Journal for Environmental Integration, 5(2), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-020-00168-w
Barreras, F., Amaveda, H., & Lozano, A. (2002). Transient high-frequency ultrasonic water atomization. Experiments in Fluids, 33(3), 405–413.
Biswas, A. K., & Tortajada, C. (2019). Water crisis and water wars: Myths and realities. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2019.1636502
Chang, Y.-Y., Wu, M.-Y., Hung, Y.-L., & Lin, S.-Y. (2011). Accurate surface tension measurement of glass melts by the pendant drop method. Review of Scientific Instruments, 82(5), 55107.
Chaudhry, A. R., & Mishra, V. P. (2019). A comparative analysis of vertical agriculture systems in residential apartments. 2019 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASET.2019.8714358
Chowdhury, M., Islam, M. N., Reza, M. N., Ali, M., Rasool, K., Kiraga, S., Lee, D., & Chung, S.-O. (2021). Sensor-based nutrient recirculation for aeroponic lettuce cultivation. Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 46(1), 81–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-021-00089-8
Cooper, A. (1988). 1. The system. 2. Operation of the system. The ABC of NFT. Nutrient Film Technique. .
Corzo, O., & Gomez, E. R. (2004). Optimization of osmotic dehydration of cantaloupe using desired function methodology. Journal of Food Engineering, 64(2), 213–219.
Dalmoro, A., Barba, A. A., & D’Amore, M. (2013). Analysis of size correlations for microdroplets produced by ultrasonic atomization. The Scientific World Journal, 2013, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/482910
Demirbaş, N. (2019). Vertical agriculture: A review of developments. Cataloging-In-Publication Data, 633–639.
Donnelly, T. D., Hogan, J., Mugler, A., Schubmehl, M., Schommer, N., Bernoff, A. J., Dasnurkar, S., & Ditmire, T. (2005). Using ultrasonic atomization to produce an aerosol of micron-scale particles. Review of Scientific Instruments, 76(11), 113301. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2130336
Drews, M., Larsen, M. A. D., & Balderrama, J. G. P. (2020). Projected water usage and land-use-change emissions from biomass production (2015–2050). Energy Strategy Reviews, 29, 100487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2020.100487
Dritsa, V., Rigas, F., Doulia, D., Avramides, E. J., & Hatzianestis, I. (2009). Optimization of culture conditions for the biodegradation of lindane by the polypore fungus Ganoderma australe. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 204(1), 19–27.
Dupuis, E. D., Momen, A. M., Patel, V. K., & Shahab, S. (2018). Ultrasonic piezoelectric atomizers: Electromechanical modeling and performance testing. Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, 51944, V001T04A027. https://doi.org/10.1115/SMASIS2018-8262
Faraway, J. J. (2002). Practical regression and ANOVA using R (Vol. 168).
Forde, G., Friend, J., & Williamson, T. (2006). Straightforward biodegradable nanoparticle generation through megahertz-order ultrasonic atomization. Applied Physics Letters, 89(6), 64105.
Ghatee, M. H., Zare, M., Zolghadr, A. R., & Moosavi, F. (2010). Temperature dependence of viscosity and relation with the surface tension of ionic liquids. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 291(2), 188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2010.01.010
Gianino, C. (2006). Measurement of surface tension by the dripping from a needle. Physics Education, 41(5), 440–444. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9120/41/5/010
He, L., Du, Y., Wu, S., & Zhang, Z. (2021). Evaluation of the agricultural water resource carrying capacity and optimization of a planting-raising structure. Agricultural Water Management, 243, 106456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106456
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water (Vol. 2254). Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey. Google Books URL: https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=1k9GAAAAYAAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR3&dq=%3Cdiv+class%3D%22NodiCopyInline%22%3E+%3Ci%3EStudy+and+interpretation+of+the+chemical+characteristics+of+natural+water%3C/i%3E+(Vol.+2254).%3C/div%3E&ots=RYM_uLgvUe&sig=TnvtP7VqWiDSHqE3tKXA9udlC2o#v=onepage&q&f=false
Hoagland, D. R., & Arnon, D. I. (1938). Growing plants without soil by the water-culture method. Growing Plants without Soil by the Water-Culture Method.
Javidan, S. M., & Mohamadzamani, D. (2021). Design, construction, and evaluation of automated seeder with ultrasonic sensors for row detection. Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 46, 365–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-021-00113-x
Jung, C. G. H., Waldeck, P., Petrick, I., Braune, S., Küpper, J.-H., & Jung, F. (2021). Bioreactor for the cultivation of Arthrospira platensis under controlled conditions. Journal of Cellular Biotechnology, Preprint, 1–6, 7, 35–40. https://doi.org/10.3233/JCB-210032
Jůza, J. (2019). Surface tension measurements of viscous materials by pendant drop method: Time needed to establish equilibrium shape. Macromolecular Symposia, 384(1), 1800150.
Kanakoudis, V., Papadopoulou, A., Tsitsifli, S., Curk, B. C., Karleusa, B., Matic, B., Altran, E., & Banovec, P. (2017). Policy recommendation for drinking water supply cross-border networking in the Adriatic region. Journal of Water Supply: Research and Technology--AQUA, 66(7), 489–508. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2017.079
Karuniawati, S., Putrada, A. G., & Rakhmatsyah, A. (2021). Optimization of grow lights control in IoT-based aeroponic systems with sensor fusion and random forest classification. International Symposium on Electronics and Smart Devices (ISESD), 2021, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISESD53023.2021.9501863
Khmelev, V. N., Shalunov, A. V., Golykh, R. N., Nesterov, V. A., Dorovskikh, R. S., & Shalunova, A. V. (2017). Providing the efficiency and dispersion characteristics of aerosols in ultrasonic atomization. Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics, 90(4), 831–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10891-017-1632-8
Kim, J. Y. (2020). Roadmap to high throughput phenotyping for plant breeding. Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 45(1), 43–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-020-00043-0
Kim, G., Cho, B.-K., Oh, S. H., & Kim, K.-B. (2020). Feasibility study for the evaluation of chicken meat storage time using surface acoustic wave sensor. Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 45(4), 261–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-020-00066-7
Klarin, B., Garafulić, E., Vučetić, N., & Jakšić, T. (2019). New and smart approach to aeroponic and seafood production. Journal of Cleaner Production, 239, 117665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117665
Kozuka, T., Ando, J., Sato, M., Hatanaka, S.-I., & Yasui, K. (2019). Effect of horn and liquid height in ultrasonic atomization. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 58(SG), SGGD18. https://doi.org/10.7567/1347-4065/ab1bd4
Lakhiar, I. A., Gao, J., Syed, T. N., Chandio, F. A., & Buttar, N. A. (2018). Modern plant cultivation technologies in agriculture under controlled environment: A review on aeroponics. Journal of Plant Interactions, 13(1), 338–352. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2018.1472308
Lakhiar, I. A., Gao, J., Syed, T. N., Chandio, F. A., Tunio, M. H., Ahmad, F., & Solangi, K. A. (2020). Overview of the aeroponic agriculture–An emerging technology for global food security. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 13(1), 1–10.
Lang, R. J. (1962). Ultrasonic atomization of liquids. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 34(1), 6–8. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1909020
Li, Q., Li, X., Tang, B., & Gu, M. (2018). Growth responses and root characteristics of lettuce grown in aeroponics, hydroponics, and substrate culture. Horticulturae, 4(4), 35.
Liu, X., Wang, G., & Gao, J. (2018). Experimental study of ultrasonic atomizer effects on values of EC and pH of nutrient solution. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 11(5), 59–64.
Loudari, A., Benadis, C., Naciri, R., Soulaimani, A., Zeroual, Y., El Gharous, M., Kalaji, H. M., & Oukarroum, A. (2020). Salt stress affects mineral nutrition in shoots and roots and chlorophyll a fluorescence of tomato plants grown in hydroponic culture. Journal of Plant Interactions, 15(1), 398–405. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2020.1841842
Manaa, A., Mimouni, H., Terras, A., Chebil, F., Wasti, S., Gharbi, E., & Ben Ahmed, H. (2014). Superoxide dismutase isozyme activity and antioxidant responses of hydroponically cultured Lepidium sativum L. to NaCl stress. Journal of Plant Interactions, 9(1), 440–449. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2013.850596
Martinez-Ruiz, A., Lopez-Cruz, I. L., Ruiz-Garcia, A., Pineda-Pineda, J., Sanchez-Garcia, P., & Mendoza-Perez, C. (2021). Uncertainty analysis of the HORTSYST model applied to fertigated tomatoes cultivated in a hydroponic greenhouse system. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 19(3).
Meneghelli, C. M., Fontes, P. C. R., Milagres, C. d. C., da Silva, J. M., & Junior, E. G. (2021). Zinc-biofortified lettuce in aeroponic system. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 44, 2146–2156. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2021.1889587
Mirzabe, A. H., Hajiahmad, A., Fadavi, A., & Rafiee, S. (2020). Ultrasonic production of plant nutrients mist to use in aeroponic systems: Feasibility and investigation of some effective parameters. Iranian Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 51(3), 585–598. https://doi.org/10.22059/IJBSE.2020.295739.665263
Misak, M. D. (1968). Equations for determining 1/H versus S values in computer calculations of interfacial tension by the pendent drop method. JCIS, 27(1), 141–142.
Niam, A. G., & Sucahyo, L. (2020). Ultrasonic atomizer application for low cost aeroponic chambers (LCAC): A review. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 542(1), 12034. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/542/1/012034
Niederhauser, D. O., & Bartell, F. E. (1950). Report of progress-fundamental research on the occurrence and recovery of petroleum (p. 114).
Oladejo, A. O. (2020). Process optimization of ultrasound-assisted osmotic dehydration of yellow cassava using response surface methodology. Journal of Biosystems Engineering, 45(3), 167–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-020-00058-7
Ozdemir, O., Karakashev, S. I., Nguyen, A. V, & Miller, J. D. (2009). Adsorption and surface tension analysis of concentrated alkali halide brine solutions. Minerals Engineering, 22(3), 263–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2008.08.001
Pfister, S., Bayer, P., Koehler, A., & Hellweg, S. (2011). Projected water consumption in future global agriculture: scenarios and related impacts. Science of the Total Environment, 409(20), 4206–4216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.019
Phanphanit, P., & Cooper, D. (2005). Ultrasonic atomization of salt water. ILASS Conference, Sept, 8–10.
Rainwater, F. H., & Thatcher, L. L. (1960). Methods for collection and analysis of water samples (Issues 1454–1458). US Government Printing Office.
Ramisetty, K. A., Pandit, A. B., & Gogate, P. R. (2013). Investigations into ultrasound induced atomization. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 20(1), 254–264.
Rooney, J. A. (1981). 6. Nonlinear phenomena. In Methods in Experimental physics (Vol. 19, pp. 299–353). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-695X(08)60337-3
Rusydi, A. F. (2018). Correlation between conductivity and total dissolved solid in various type of water: A review. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 118(1), 12019. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/118/1/012019
Saufie, S., Estim, A., Shaleh, S. R. M., & Mustafa, S. (2020). Production efficiency of green beans integrated with tilapia in a circular farming system of media-filled aquaponics. Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 18(3), 26.
Shajari, M. A., Fallahi, H.-R., Sahabi, H., Kaveh, H., & Branca, F. (2021). Production systems and methods affect the quality and the quantity of saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 19(1), 901.
Simon, J. C., Sapozhnikov, O. A., Khokhlova, V. A., Crum, L. A., & Bailey, M. R. (2015). Ultrasonic atomization of liquids in drop-chain acoustic fountains. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 766, 129–146. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2015.11
Song, J.-S., Jung, S., Jee, S., Yoon, J. W., Byeon, Y. S., Park, S., & Kim, S. B. (2021). Growth and bioactive phytochemicals of Panax ginseng sprouts grown in an aeroponic system using plasma-treated water as the nitrogen source. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-82487-8
Stauffer, C. E. (1965). The measurement of surface tension by the pendant drop technique. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 69(6), 1933–1938.
Steiner, A. A. (1984). The universal nutrient solution, International Congress on Soilless Culture. ISOSC The Netherlands.
Su, M. H., Azwar, E., Yang, Y., Sonne, C., Yek, P. N. Y., Liew, R. K., Cheng, C. K., Show, P. L., & Lam, S. S. (2020). Simultaneous removal of toxic ammonia and lettuce cultivation in aquaponic system using microwave pyrolysis biochar. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 396, 122610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122610
Sulistyowati, C. A., & Nurhasana, R. (2022). Food crisis transformation to sustainable urban agriculture in Cuba: Lessons for Indonesia. In Sustainable Architecture and Building Environment (Vol. 161, pp. 161–169). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-2329-5_18
Tafesse, E. G., Aidoo, M. K., Lazarovitch, N., & Rachmilevitch, S. (2021). Aeroponic systems: A unique tool for estimating plant water relations and NO3 uptake in response to salinity stress. Plant Direct, 5(4), e00312. https://doi.org/10.1002/pld3.312
Tunio, M H, Gao, J., Lakhiar, I. A., Solangi, K. A., Qureshi, W. A., Shaikh, S. A., & Chen, J. (2021a). Influence of atomization nozzles and spraying intervals on growth, biomass yield, and nutrient uptake of butter-head lettuce under aeroponics system. Agronomy 2021, 11, 97 (pp. 1–17). Agronomy.
Tunio, M. H., Gao, J., Lakhiar, I. A., Solangi, K. A., Qureshi, W. A., Shaikh, S. A., & Chen, J. (2021b). Influence of atomization nozzles and spraying intervals on growth, biomass yield, and nutrient uptake of butter-head lettuce under aeroponics system. Agronomy, 11(1), 97.
Uddin, M. R., & Suliaman, M. F. (2021). Energy efficient smart indoor fogponics farming system. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 673(1), 12012. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/673/1/012012
Walton, N. R. G. (1989). Electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids—What is their precise relationship? Desalination, 72(3), 275–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/0011-9164(89)80012-8
Yang, T., & Kim, H.-J. (2020). Comparisons of nitrogen and phosphorus mass balance for tomato-, basil-, and lettuce-based aquaponic and hydroponic systems. Journal of Cleaner Production, 274, 122619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122619
Yasuda, K., Honma, H., Asakura, Y., & Koda, S. (2010). 2P-37 Effect of frequency on ultrasonic atomization. Proceedings of Symposium on Ultrasonic Electronics, 31, 363–364. https://doi.org/10.24492/use.31.0_363
Zheng, M., Tian, J., & Mulero, Á. (2013). New correlations between viscosity and surface tension for saturated normal fluids. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 360, 298–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2013.09.045
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the University of Tehran and Farvardin Azma Tajhiz Co. for supporting this work. The authors would also like to thank Prof. Ali Rajabipour and Dr. Mohammad Hassan Torabi for their technical support.
Funding
This work is based upon research funded by Iran National Science Foundation under project number 99022977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Amir Hossein Mirzabe: software, visualization, providing setup, acquisition of data; data analysis, drafting of the manuscript.
Ali Hajiahmad: providing setup, data analysis, supervising the work.
Ali Fadavi: revision of the manuscript, technical support.
Shahin Rafiee: revision of the manuscript, technical support.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Highlights
1. Designing aeroponic cultivation system based on the ultrasonic technology was investigated.
2. Effects of nutrient solution dosage, voltage, and horn dimensions on misting rate were studied.
3. Density, viscosity, surface tension, and speed of sound of the solutions were measured.
4. Modeling of mechanical properties of the solutions as well as misting rate has been performed.
5. Optimization of the ultrasonic mist making process was performed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirzabe, A.H., Hajiahmad, A., Fadavi, A. et al. Ultrasonic Atomizer for Aeroponic Cultivation: Effect of Nutrient Solution Dosage, Voltage, and Horn Dimensions. J. Biosyst. Eng. 47, 130–151 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-022-00135-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42853-022-00135-z