Abstract
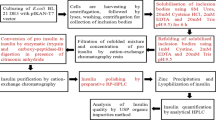
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that has affected approximately 463 million populations till date and this number is expected to exponentially rise in the coming decade. Majority of diabetic patients require multiple insulin injections regularly, at the risk of hypoglycemia. As an alternative to conventional insulin, glargine insulin, a long-acting insulin analog that helps in maintaining blood glucose levels, is being preferred. Hence, the present work focuses on glargine insulin production using recombinant E. coli BL-21(DE3) cells through fed-batch fermentation. After fermentation, the cells were lysed through high pressure homogenization to release inclusion bodies containing insulin glargine precursor and the major impurities like Arg (B31)-insulin were reduced by incorporating citraconylation in appropriate concentration. These steps are novel which makes the present study distinct from the other. Furthermore, refolding and enzymatic digestion of insulin glargine precursor was carried out to obtain glargine insulin. Consequently, purification and polishing of glargine insulin were performed by loading onto cation exchange chromatography and reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatography which fetched 98.6% pure product. Through the aforementioned process, from 20 L of culture broth, nearly 0.3 g/L of recombinant glargine insulin with high purity was obtained in two purification steps. Hence, the present study devises an efficient and economical process for large-scale production of glargine insulin.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are recorded in the manuscript and any further information will be made available on request from the first author.
The authors express their consent for communicating this manuscript to your journal and moreover confirm that this article has not been communicated to any other journal for publication.
Abbreviations
- Gly:
-
Glycine
- Ile:
-
Isoleucine
- Val:
-
Valine
- Glu:
-
Glutamic acid
- Gln:
-
Glutamine
- Cys:
-
Cysteine
- Thr:
-
Threonine
- Ser:
-
Serine
- Leu:
-
Leucine
- Tyr:
-
Tyrosine
- Asn:
-
Asparagine
- Phe:
-
Phenylalanine
- His:
-
Histidine
- Ala:
-
Alanine
- Arg:
-
Arginine
- Pro:
-
Proline
- Lys:
-
Lysine
- Da:
-
Dalton
References
E. Haythorne, M. Rohm, M. van de Bunt, M.F. Brereton, A.I. Tarasov, T.S. Blacker, F.M. Ashcroft, Diabetes causes marked inhibition of mitochondrial metabolism in pancreatic β-cells. Nat Commun 10(1), 1–17 (2019)
C.F. Deacon, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 16(11), 642–653 (2020)
M.J. Kim, S.H. Min, S.Y. Shin, M.N. Kim, H. Lee, J.Y. Jang, H.S. Jung, Attenuation of PERK enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in islets. J Endocrinol 236, 125–136 (2018)
T.N. Vinther, M. Norrman, U. Ribel, K. Huss, M. Schlein, D.B. Steensgaard, F. Hubalek, Insulin analog with additional disulfide bond has increased stability and preserved activity. Protein Sci 22, 296–305 (2013)
Y. Kollati, R.R. Ambati, P.N. Reddy, N.S.S. Kumar, R.K. Patel, V.R. Dirisala, Congenital hypothyroidism: facts, facets & therapy. Curr Pharm Des 23(16), 2308–2313 (2017)
S. Khan, M.W. Ullah, R. Siddique, G. Nabi, S. Manan, M. Yousaf, H. Hou, Role of recombinant DNA technology to improve life. International Journal of Genomics, 2016(2405954), 14 (2016)
R. Patra, Y. Kollati, N.S. Sampath Kumar, V.R. Dirisala, Valsartan in combination with metformin and gliclazide in diabetic rat model using developed RP-HPLC method. Future J Pharma Sci 7(1), 1–10 (2021)
P. Hazra, S. Sreenivas, K. Venkatesan, M.B. Patale, A. Chatterjee, N. Ramprabu, M. Kusumanchi, A novel peptide design aids in the expression and its simplified process of manufacturing of Insulin Glargine in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 105, 3061–3074 (2021)
A. Lapolla, M.G. Dalfra, Hundred Years of Insulin Therapy: Purified Early Insulins. Am J Ther 27, e24–e29 (2020)
X. Zhao, H. Zong, A. Abdulla, E.S. Yang, Q. Wang, J.Y. Ji, F. Yang, Inhibition of SREBP transcriptional activity by a boron-containing compound improves lipid homeostasis in diet-induced obesity. Diabetes 63, 2464–2473 (2014)
G.E. Umpierrez, D.C. Klonoff, Diabetes technology update: use of insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring in the hospital. Diabetes Care 41, 1579–1589 (2018)
P. Sonksen, J. Sonksen, Insulin: understanding its action in health and disease. Br J Anaesth 85(1), 69–79 (2000)
H.G. Hwang, K.J. Kim, S.H. Lee, C.K. Kim, C.K. Min, J.M. Yun, S.U. Lee, Y.J. Son, Recombinant glargine insulin production process using Escherichia coli. J Microbiol Biotechnol 26, 1781–1789 (2016)
A. Bera, S. Herbert, A. Jakob, W. Vollmer, F. Götz, Why are pathogenic staphylococci so lysozyme resistant? The peptidoglycan O-acetyltransferase OatA is the major determinant for lysozyme resistance of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 55, 778–787 (2005)
R. Patra, P.N. Reddy, N.S. Kumar, V.R. Dirisala, Novel Validated RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Valsartan & Gliclazide in Bulk and Dosage Forms. Curr Pharm Anal 14(4), 412–418 (2018)
R.A. Nazeer, R. Kavitha, R.J. Ganesh, S.Y. Naqash, N.S. Kumar, R. Ranjith, Detection of collagen through FTIR and HPLC from the body and foot of Donax cuneatus Linnaeus, 1758. J Food Sci Technol 51(4), 750–755 (2014)
E.J. Bennett, N.F. Bence, R. Jayakumar, R.R. Kopito, Global impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome system by nuclear or cytoplasmic protein aggregates precedes inclusion body formation. Mol Cell 17, 351–365 (2005)
G.L. Rosano, E.A. Ceccarelli, Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Front Microbiol 5, 172 (2014)
M.M. Carrio, A. Villaverde, Role of molecular chaperones in inclusion body formation. FEBS Lett 537, 215–221 (2003)
A. Singh, V. Upadhyay, A.K. Upadhyay, S.M. Singh, A.K. Panda, Protein recovery from inclusion bodies of Escherichia coli using mild solubilization process. Microb Cell Factories 14, 1–10 (2015)
A. Sarker, A.S. Rathore, R.D. Gupta, Evaluation of scFv protein recovery from E. coli by in vitro refolding and mild solubilization process. Microb Cell Factories 18, 5 (2019)
K. Ashutosh, K.A. Dinesh, K. Sunil, Y. Mohan Reddy, A.D. Chintagunta, K.V. Saritha, P. Govind, S.P. Jeevan Kumar, Nutraceuticals derived from seed storage proteins: Implications for health wellness. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 17, 710–719 (2019)
P. Singhvi, A. Saneja, S. Srichandan, A.K. Panda, Bacterial inclusion bodies: a treasure trove of bioactive proteins. Trends Biotechnol 38, 474–486 (2020)
N. Venkata Raju, K. Sukumar, G.R. Babul, P.K. Pankaj, G. Muralitharan, A. Shanti, D. Teja Sai, A.D. Chintagunta, In-Vitro Studies on Antitumour and Antimicrobial Activities of Methanolic Kernel Extract of MangiferaIndica L. Cultivar Banganapalli. Biomed Pharmacol J 12(1), 357–362 (2019)
C.K. Kim, S.B. Lee, Y.J. Son, Large-scale refolding and enzyme reaction of human preproinsulin for production of human insulin. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(10), 1742–1750 (2015)
H.K.S. Leiros, B.O. Brandsdal, O.A. Andersen, V. Os, I. Leiros, R. Helland, A.O. Smalas, Trypsin specificity as elucidated by LIE calculations, X-ray structures, and association constant measurements. Protein Sci 13, 1056–1070 (2004)
Y. Xie, S. Min, N.P. Harte, H. Kirk, J.E. Obrien, H.P. Voorheis, K. Hun Mok, Electrostatic interactions play an essential role in the binding of oleic acid with α‐lactalbumin in the HAMLET‐like complex A study using charge‐specific chemical modifications. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf 81, 1–17 (2013)
M. Thevis, A. Thomas, W. Schanzer, Mass spectrometric determination of insulins and their degradation products in sports drug testing. Mass Spectrom Rev 27, 35–50 (2008)
T. Arakawa, K. Tsumoto, K. Nagase, D. Ejima, The effects of arginine on protein binding and elution in hydrophobic interaction and ion-exchange chromatography. Protein Expr Purif 54, 110–116 (2007)
M.Weiss, D.F. Steiner, L.H. Philipson, Insulin biosynthesis, secretion, structure, and structure-activity relationships (2015)
D. LeRoith, H. Werner, D. Beitner-Johnson, C.T. Roberts, Molecular and cellular aspects of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Endocr Rev 16, 143–163 (1995)
N.S. Sampath Kumar, S. NorizahMhd, S.R. Sandeep, A.D. Chintagunta, S. Prathibha, I. Satheesh Kumar, S.P. Jeevan Kumar, B. Sai Anvesh, D. VijayaRamu, Extraction of bioactive compounds from Psidium guajava leaves and its utilization in preparation of jellies. AMB Express 11, 36 (2021)
M. Zielinski, A. Romanik-Chruscielewska, D. Mikiewicz, N. Lukasiewicz, I. Sokolowska, J. Antosik, A. Plucienniczak, Expression and purification of recombinant human insulin from E. coli 20 strain. Protein Expr Purif 157, 63–69 (2019)
K. Govender, T. Naicker, J. Lin, S. Baijnath, A.A. Chuturgoon, N.S. Abdul, T. Docrat, H.G. Kruger, T. Govender, A novel and more efficient biosynthesis approach for human insulin production in Escherichia coli (E. coli). AMB Express 10, 1–9 (2020)
S. Polez, D. Origi, S. Zahariev, C. Guarnaccia, S.G. Tisminetzky, N. Skoko, M. Baralle, A simplified and efficient process for insulin production in Pichia pastoris 11, e0167207 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This is a part of the PhD work carried by the first author SBK. The first author gratefully acknowledges the support extended by Nanogen Biopharmaceutical, Vietnam, for providing no objection certificate to execute the PhD work along with publishing articles. In addition to it, help extended by Vcare Biolabs Pvt. Ltd., Hyderabad, for slight improvement of the work is also acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Satish Babu Kaki: designed and executed the work and drafted the manuscript; Anjani Devi Chintagunta: reviewing the manuscript; A. Naga Prasad: supported in executing the work; N.S. Sampath Kumar: valuable insights during periodic reviews of the work and helped in drafting the manuscript; Vijaya R. Dirisala: reviewing the manuscript, M. Sai Krishna: provided inputs in drafting the manuscript; S.J.K. Naidu and B. Ramesh: supported with resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Consent for publication
The authors express their consent for communicating this manuscript to your journal and moreover confirm that this article has not been communicated to any other journal for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaki, S.B., Chintagunta, A.D., Prasad, A.N. et al. Production and purification of recombinant glargine insulin from Escherichia coli BL-21 strain. emergent mater. 5, 335–346 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00313-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00313-3