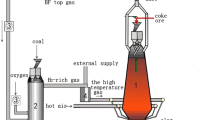
Abstract
The changes in the softening and melting behaviors of ferrous burden in the cohesive zone and the characteristics of the slag–iron–coke interface in a blast furnace were investigated by simulating an actual blast furnace under hydrogen-rich conditions. According to the variation in the transient shrinkage of the burden under different atmospheres, the shrinkage start temperature of the sinter was higher than that of the pellets. The negative shrinkage rate of the pellets was greater than that of the sinter. Additionally, the softening start temperature in the blast furnace decreased under hydrogen-rich conditions, giving the blast furnace a broader range of softening zones. The softening start temperatures of the pellets and sinter decreased from 1102 to 949 °C and 1152 to 1080 °C, respectively. The hydrogen-rich traditional blast furnace conditions narrowed the melting zone temperature range and shifted it toward the high-temperature zone, significantly improving the burden layer permeability. However, under the hydrogen-rich oxygen blast furnace conditions, there were a decrease in the melting start temperature, a shift of the melting zone location to the low-temperature zone, and an increase in the burden layer permeability and pressure difference. A comparison of the slag–iron–coke interface characteristics under different atmospheric conditions showed that the carbon content in metallic iron decreased under hydrogen-rich traditional blast furnace conditions compared with traditional blast furnace conditions. Contrastingly, under hydrogen-rich oxygen blast furnace conditions, the carbon content in metallic iron increased compared with oxygen blast furnace conditions. These findings provide guidance for the development of low-carbon ironmaking processes in blast furnaces.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.Q. Xu, B. Wan, T.Y. Zhu, M.P. Shao, J. Clean. Prod. 139 (2016) 1504–1511.
K.D. Xu, Iron and Steel 45 (2010) No. 3, 1–12.
X.C. Tan, H. Li, J.X. Guo, B.H. Gu, Y. Zeng, J. Clean. Prod. 222 (2019) 823–834.
K.H. Ma, J.Y. Deng, G. Wang, Q. Zhou, J. Xu, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 46 (2021) 26646–26664.
Y.B. Chen, H.B. Zuo, Ironmak. Steelmak. 48 (2021) 749–768.
J. Tang, M.S. Chu, F. Li, C. Feng, Z.G. Liu, Y.S. Zhou, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 27 (2020) 713–723.
X.Y. Zhang, K.X. Jiao, J.L. Zhang, Z.Y. Guo, J. Clean. Prod. 306 (2021) 127259.
G.Y. Sun, B. Li, W.S. Yang, J. Guo, H.J. Guo, Energies 13 (2020) 1986.
Z.J. Liu, J.L. Zhang, T.J. Yang, ISIJ Int. 55 (2015) 1146–1156.
A. Heidari, N. Niknahad, M. Iljana, T. Fabritius, Materials 14 (2021) 7540.
J. Zhao, H.B. Zuo, C. Ling, W.T. Guo, J.S. Wang, Q.G. Xue, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27 (2020) 743–754.
X.L. Liu, T. Honeyands, G. Evans, P. Zulli, D. O’Dea, Ironmak. Steelmak. 46 (2019) 953–967.
Y.N. Qie, Q. Lyu, X.J. Liu, J.P. Li, C.C. Lan, S.H. Zhang, C.J. Yan, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 2622–2632.
C.C. Lan, S.H. Zhang, X.J. Liu, Q. Lyu, M.F. Jiang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 45 (2020) 14255–14265.
Y.Z. Pan, H.B. Zuo, B.X. Wang, J.S. Wang, G. Wang, Y.L. Liu, Q.G. Xue, Ironmak. Steelmak. 47 (2020) 322–327.
J. Li, S.B. Kuang, R.P. Zou, A.B. Yu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 53 (2022) 4124–4137.
J. Li, S.B. Kuang, L.L. Jiao, L.L. Liu, R.P. Zou, A.B. Yu, Fuel 323 (2022) 124368.
J. Tang, M.S. Chu, F. Li, Z.D. Zhang, Y.T. Tang, Z.G. Liu, J. Yagi, J. Clean. Prod. 278 (2021) 123191.
Y.H. Han, J.S. Wang, Y.Z. Li, X.F. She, L.T. Kong, Q.G. Xue, J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 33 (2011) 1280–1286.
K.H. Ma, J. Xu, J.Y. Deng, D.D. Wang, Y. Xu, Z.H. Liao, C.F. Sun, S.F. Zhang, L.Y. Wen, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 2308–2321.
X.W. An, J.S. Wang, R.Z. Lan, Y.H. Han, Q.G. Xue, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 20 (2013) No. 5, 11–16.
M. Hayashi, K. Suzuki, Y. Maeda, T. Watanabe, ISIJ Int. 56 (2016) 220–225.
S. Hayashi, Y. Iguchi, Ironmak. Steelmak. 32 (2005) 353–358.
H.T. Wang, H.Y. Sohn, Ironmak. Steelmak. 38 (2011) 447–452.
L.Y. Yi, Z.C. Huang, T. Jiang, L.N. Wang, T. Qi, Powder Technol. 269 (2015) 290–295.
F. Li, M.S. Chu, J. Tang, Z.G. Liu, C. Feng, Y.T. Tang, JOM 69 (2017) 1751–1758.
H.C. Chuang, W.S. Hwang, S.H. Liu, Mater. Trans. 50 (2009) 1448–1456.
S. Ueda, T. Kon, T. Miki, S.J. Kim, H. Nogami, ISIJ Int. 55 (2015) 2098–2104.
P. Wang, Y.Q. Zhang, H.M. Long, R.F. Wei, J.X. Li, Q.M. Meng, S.C. Yu, ISIJ Int. 57 (2017) 643–648.
P. Wang, S. Yu, H. Long, R. Wei, Q. Meng, Y. Zhang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 44 (2017) 595–600.
W.T. Guo, Q.G. Xue, Y.L. Liu, Z.C. Guo, X.F. She, J.S. Wang, Q.Q. Zhao, X.W. An, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 40 (2015) 13306–13313.
C.C. Lan, Q. Lyu, X.J. Liu, M.F. Jiang, Y.N. Qie, S.H. Zhang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43 (2018) 19405–19413.
Z.G. Zhao, X.B. Yu, Y.S. Shen, Y.T. Li, H. Xu, Z.J. Hu, Energy Fuels 34 (2020) 15048–15060.
G.Q. Yang, J.L. Zhang, Y.X. Chen, Q.Y. Wu, Z.Y. Zhao, J. Zhao, Iron and Steel 47 (2012) No. 9, 14–18.
K. Zhou, J.Q. Song, Z.X. You, H.E. Xie, X.W. Lv, ISIJ Int. 60 (2020) 1409–1415.
T. Umadevi, P. Kumar, N.F. Lobo, M. Prabhu, P.C. Mahapatra, M. Ranjan, ISIJ Int. 51 (2011) 14–20.
H.S. Kim, J.G. Kim, Y. Sasaki, ISIJ Int. 50 (2010) 1099–1106.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. U1960205 and 51804024), China Baowu Low Carbon Metallurgy Innovation Foundation (BWLCF202101 and BWLCF202104) and China Minmetals Science and Technology Special Plan Foundation (2020ZXA01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, Bb., Wang, G., Yang, F. et al. Softening and melting behaviors of ferrous burden in hydrogen-rich blast furnace cohesive zone. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30, 2366–2377 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-00951-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-00951-3