Abstract
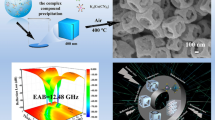
In order to prevent electromagnetic interference, the standards for electromagnetic wave (EMW) absorption materials have tightened with the widespread growth of electrical communication equipment. Optimal EMW absorption performance may be achieved by prudent control of permittivity. Because of its outstanding dielectric property, controlled structure, and low cost of process, NiCo-based materials (NiCo2X4, X = O, S, Se, and Te) have been viewed as potential materials for absorbing electromagnetic waves. In particular, the presence of anionic sites has a significant impact on a material’s permittivity and conductivity. This work reports the effective hydrothermal preparation of NiCo2X4 hollow nanoceras, followed by telluride, vulcanization, selenium, and oxidation processes. Owing to variations in the element electronegativity of anions, NiCo2Se4 and NiCo2Te4 exhibited enhanced conductivity and dielectric loss. An optimal reflection loss (RL) of Mn-NiCo2Se4 at the matching thickness of 2.0 mm can reach −77.57 dB, and the effective absorption bandwidth (EAB) at the matching thickness of 2.0 mm is 4.88 GHz. The RL of Mn-NiCo2Te4 at the matching thickness of 2.1 mm can reach −64.74 dB, and the EAB can reach 5.68 GHz at 2.0 mm. The samples made in this experiment also show maritime anticorrosion capabilities, which offers some research directions for the creation of materials with dual uses. It is anticipated that this research will offer significant new perspectives on the significant impacts of anionic coordination modulation on the EMA characteristics of composites made of transition metal matrix.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the finding of this study are available with the paper.
References
Wu G, Cheng Y, Yang Z et al (2018) Design of carbon sphere/magnetic quantum dots with tunable phase compositions and boost dielectric loss behavior. Chem Eng J 333:519–528
Lan D, Li H, Wang M et al (2024) Recent advances in construction strategies and multifunctional properties of flexible electromagnetic wave absorbing materials. Mater Res Bull 171:112630
Zhang Y, Ruan K, Zhou K et al (2023) Controlled distributed Ti3C2Tx hollow microspheres on thermally conductive polyimide composite films for excellent electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv Mater 35(16):2211642
Fan G, Wang Z, Ren H et al (2021) Dielectric dispersion of copper/rutile cermets: dielectric resonance, relaxation, and plasma oscillation. Scripta Mater 190:1–6
Sun C, Jia Z, Xu S et al (2022) Synergistic regulation of dielectric-magnetic dual-loss and triple heterointerface polarization via magnetic MXene for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J Mater Sci Technol 20:128–137
Zhao T, Jia Z, Zhang Y et al (2023) Multiphase molybdenum carbide doped carbon hollow sphere engineering: the superiority of unique double-shell structure in microwave absorption. Small 19(6):2206323
Jia Z, Lan D, Chang M et al (2023) Heterogeneous interfaces and 3D foam structures synergize to build superior electromagnetic wave absorbers. Mater Today Phys 37:101215
Pan Y, Zhu Q, Zhu J et al (2023) Macroscopic electromagnetic synergy network-enhanced N-doped Ni/C gigahertz microwave absorber with regulable microtopography. Nano Res 16(7):10666–10677
Jia Z, Kong M, Yu B et al (2022) Tunable Co/ZnO/C@MWCNTs based on carbon nanotube-coated MOF with excellent microwave absorption properties. J Mater Sci Technol 127:153–163
Yang J, Wang H, Zhang Y et al (2024) Layered structural PBAT composite foams for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano-Micro Lett 16:31
Zhang Y, Gao S, He J et al (2024) CoFe@C composites decorated with residual carbon as an ultrathin microwave absorber in the X and Ku bands. Diam Relat Mater 141:110666
Yin P, Luo Y, Lan D et al (2024) Structural engineering of porous biochar loaded with ferromagnetic/anti-ferromagnetic NiCo2O4/CoO for excellent electromagnetic dissipation with flexible and self-cleaning properties. J Mater Sci Technol 180:12–22
Guo Y, Ruan K, Wang G et al (2023) Advances and mechanisms in polymer composites toward thermal conduction and electromagnetic wave absorption. Sci Bull 68:1195–1212
Xie P, Zhang Z, Liu K et al (2017) C/SiO2 meta-composite: overcoming the λ/a relationship limitation in metamaterials. Carbon 125:1–8
Zhang S, Lan D, Chen X et al (2023) Three-dimensional macroscopic absorbents: from synergistic effects to advanced multifunctionalities. Nano Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-023-6120-1
Chang Q, Liang H, Shi B et al (2021) Sodium oxalate-induced hydrothermal synthesis of wood-texture-column-like NiCo2O4 with broad bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorption performance. J Colloid Interface Sci 600:49–57
Zhou Z, Zhou X, Di L et al (2023) Modulation engineering of electromagnetic wave absorption performance of layered double hydroxides derived hollow metal carbides integrating corrosion protection. Small. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202305849
Zhao S, Refaai M, Salman S et al (2023) Investigations of physicochemical and microwave absorption performance of NiCo2S4/AgBr nanocomposite in X-band frequency. Surf Interfaces 37:102684
Dong Y, Zhu X, Pan F et al (2022) Implanting NiCo2O4 equalizer with designable nanostructures in agaric aerogel-derived composites for efficient multiband electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 190:68–79
Zhou X, Jia Z, Zhang X et al (2021) Electromagnetic wave absorption performance of NiCo2X4 (X = O, S, Se, Te) spinel structures. Chem Eng J 420:129907
Liu J, Jia Z, Dong Y et al (2022) Structural engineering and compositional manipulation for high-efficiency electromagnetic microwave absorption. Mater Today Phys 27:100801
Rathore D, Ghosh S, Chowdhury J et al (2023) Fe-doped NiCo2Se4 nanorod arrays as electrocatalysts for overall electrochemical water splitting. ACS Appl Nano Mater 6(4):3095–3110
Tao L, Huang M, Guo S et al (2019) Surface modification of NiCo2Te4 nanoclusters: a highly efficient electrocatalyst for overall water-splitting in neutral solution. Appl Catal B Environ 254:424–431
Gao Q, Wang X, Shi Z et al (2018) Synthesis of porous NiCo2S4 aerogel for supercapacitor electrode and oxygen evolution reaction electrocatalyst. Chem Eng J 331:185–193
Huang P, Zhang S, Ying H et al (2021) Few-layered Ti3C2 MXene anchoring bimetallic selenide NiCo2Se4 nanoparticles for superior sodium-ion batteries. Chem Eng J 417:129161
Li L, Zhao J, Zhu Y et al (2020) Bimetallic Ni/Co-ZIF-67 derived NiCo2Se4/N-doped porous carbon nanocubes with excellent sodium storage performance. Electrochim Acta 353:136532
Yang J, Gao H, Men S et al (2018) Chen, CoSe2 nanoparticles encapsulated by N-doped carbon framework intertwined with carbon nanotubes: high-performance dual-role anode materials for both Li- and Na-ion batteries. Adv Sci 5(12):1800763
Jiang Y, Zou G, Hou H et al (2019) Composition engineering boosts voltage windows for advanced sodium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 13(9):10787–10797
Majumdar A, Dutta P, Sikdar A et al (2022) Impact of atomic rearrangement and single atom stabilization on MoSe2@NiCo2Se4 heterostructure catalyst for efficient overall water splitting. Small 18(19):2200622
Wang Y, Shi Y, Zhang X et al (2022) Atomically dispersed manganese sites embedded within nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption. Carbon 198:382–391
Janani G, Yuvaraj S, Surendran S et al (2020) Enhanced bifunctional electrocatalytic activity of Ni-Co bimetallic chalcogenides for efficient water-splitting application. J Alloys Compd 846:156389
Chen G, Zhang L, Lou B et al (2022) Optimal control of the compositions, interfaces, and defects of hollow sulfide for electromagnetic wave absorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 607:24–33
Sun M, Zhao D, Zhang F et al (2023) Expanded graphite and thermally reduced graphene oxide filled with NiCo2O4 for improve microwave absorption. Mater Chem Phys 305:127898
Long F, Wei L, Rehman S et al (2023) Honeycomb-like structured ZnFe2O4@C derived from ZnFe2O4@ZIF-8 for electromagnetic wave absorption. J Magn Magn Mater 568:170253
Cheng X, Zhou X, Wang S et al (2019) Fabrication of NiO/NiCo2O4 mixtures as excellent microwave absorbers. Nanoscale Res Lett 14:1–9
Zhou C, Yao Z, Wei B et al (2022) Facile synthesis of ZIF-67 derived dodecahedral C/NiCO2S4 with broadband microwave absorption performance. Nanoscale 14(29):10375
Zhang X, Jia Z, Zhang F et al (2022) MOF-derived NiFe2S4/porous carbon composites as electromagnetic wave absorber. J Colloid Interface Sci 610:610–620
Zhao H, Gao H, Jin S et al (2023) Exploring interfacial engineering in 3D porous, lightweight ZnFe2O4/rGO aerogel for electromagnetic wave absorption. J Alloy Compd 957:170326
Hou T, Wang B, Ma M et al (2020) Preparation of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx) and NiCo2O4 composites to achieve excellent microwave absorption properties. Compos Part B Eng 180:107577
Shen Z, Lan D, Cong Y et al (2024) Tailored heterogeneous interface based on porous hollow In-Co-C nanorods to construct adjustable multi-band microwave absorber. J Mater Sci Technol 181:128–137
Wang J, Jia Z, Liu X et al (2021) Construction of 1D heterostructure NiCo@C/ZnO nanorod with enhanced microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett 13:175
Xu J, Liu Z, Chen Y et al (2023) Carbon-based cages with hollow confined structures for efficient microwave absorption: state of the art and prospects. Carbon 201(5):1090–1114
Li W, Xu M, Xu H et al (2022) Metamaterial absorbers: from tunable surface to structural transformation. Adv Mater 34(38):2202509
Zhao Z, Zhang L, Wu H et al (2022) Hydro/organo/ionogels: “controllable” electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv Mater 34(43):2205376
Zhang S, Cheng B, Gao Z et al (2022) Two-dimensional nanomaterials for high-efficiency electromagnetic wave absorption: an overview of recent advances and prospects. J Alloy Compd 893:16234
Liu Y, Wei X, He X et al (2023) Multifunctional shape memory composites for joule heating, self-healing, and highly efficient microwave absorption. Adv Funct Mater 33(5):2211352
Wang C, Liu Y, Jia Z et al (2023) Multicomponent nanoparticles synergistic one-dimensional nanofibers as heterostructure absorbers for tunable and efficient microwave absorption. Nano-Micro Lett 15(1):13
Manna R, Srivastava SK (2021) Reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4/polyaniline ternary composites as a superior microwave absorber in the shielding of electromagnetic pollution. ACS Omega 13(6):9164–9175
Zhao T, Jia Z, Liu J et al (2024) Multiphase interfacial regulation based on hierarchical porous molybdenum selenide to build anticorrosive and multiband tailorable absorbers. Nano-Micro Letters 16(1):6
Mohd N, Gaurav M, Yogendra K et al (2015) Ultra-wide bandwidth with enhanced microwave absorption of electroless Ni–P coated tetrapod-shaped ZnO nano- and microstructures. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:22923–22933
Feng A, Lan D, Liu J et al (2024) Dual strategy of A-site ion substitution and self-assembled MoS2 wrapping to boost permittivity for reinforced microwave absorption performance. J Mater Sci Technol 180:1–11
Lv H, Zhou X, Wu G et al (2021) Engineering defects in 2D g-C3N4 for wideband, efficient electromagnetic absorption at elevated temperature. J Mater Chem A 9:19710–19718
Huang M, Lou C, Sun C et al (2023) Achieving absorption-type microwave shielding performance in polydimethylsiloxane/carbon nanotube sandwiched composites via regulating microwave interference effect. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 169:107532
Zhou Z, Lan D, Ren J et al (2024) Controllable heterogeneous interfaces and dielectric modulation of biomass-derived nanosheet metal-sulfide complexes for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J Mater Sci Technol 185:165–173
Hu W, Yin H, Yuan H et al (2023) Microwave absorption and mechanical properties of glass fiber/polyamide 6 composites containing carbon black by microstructural design. Compos Sci Technol 233:109927
Lu S, Wan L, Zheng S et al (2024) Effect of austenitizing temperature on martensitic transformation in SA508Gr.4N steel. J Mater Sci Technol 186:244–255
Liang L, Liu Z, Xie L et al (2021) Bamboo-like N-doped carbon tubes encapsulated CoNi nanospheres towards efficient and anticorrosive microwave absorbents. Carbon 171:142–153
Gao F, Liu Y, Jiao C et al (2023) Fluorine-phosphate copolymerization waterborne acrylic resin coating with enhanced anticorrosive performance. J Polym Sci 61:2677–2687
Xie T, Li S, Ma L et al (2023) Bimetallic MOF-derived composites with broad electromagnetic wave absorption and strong corrosion resistance. Carbon 208:33–42
Zheng C, Ning M, Zou Z et al (2023) Two birds with one stone: broadband electromagnetic wave absorption and anticorrosion performance in 2–18 GHz for prussian blue analog derivatives aimed for practical applications. Small 19(32):2208211
Jalgham R, Roymahapatra G, Dash M et al (2023) In silico studies on triazole derivatives as corrosion inhibitors on mild steel in acidic media. ES Mater Manuf 21:867
Tong Z, Liao Z, Liu Y et al (2021) Hierarchical Fe3O4/Fe@C@MoS2 core-shell nanofibers for efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 179:646–654
Yao L, Wang Y, Zhao J et al (2023) Multifunctional nanocrystalline-assembled porous hierarchical material and device for integrating microwave absorption, electromagnetic interference shielding, and energy storage. Small 19(25):2208101
Hou T, Jia Z, Feng A et al (2021) Hierarchical composite of biomass derived magnetic carbon framework and phytic acid doped polyanilne with prominent electromagnetic wave absorption capacity. J Mater Sci Technol 68:61–69
Ma Z, Xiang X, Shao L et al (2022) Multifunctional wearable silver nanowire decorated leather nanocomposites for joule heating, electromagnetic interference shielding and piezoresistive sensing. Angew Chem Int Ed 61(15):202200705
Zhou X, Jia Z, Zhang X et al (2021) Controllable synthesis of Ni/NiO@porous carbon hybrid composites towards remarkable electromagnetic wave absorption and wide absorption bandwidth. J Mater Sci Technol 87:120–132
Lv H, Yao Y, Li S et al (2023) Staggered circular nanoporous graphene converts electromagnetic waves into electricity. Nat Commun 14(1):1982
Wang J, Wang B, Wang Z et al (2021) Synthesis of 3D flower-like ZnO/ZnCo2O4 composites with the heterogeneous interface for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J Colloid Interface Sci 586:479–490
Li M, Zhu W, Li X et al (2022) Ti3C2Tx/MoS2 self-rolling rod-based foam boosts interfacial polarization for electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Sci 9(16):2201118
Zhai N, Luo J, Mei J et al (2023) Interface engineering of heterogeneous NiSe2-CoSe2@C@MoSe2 for high-efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Adv Funct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202312237
Lv H, Yang Z, Liu B et al (2021) A flexible electromagnetic wave-electricity harvester. Nat Commun 12:834
Zhong X, He M, Zhang C et al (2024) Heterostructured BN@Co-C@C endowing polyester composites excellent thermal conductivity and microwave absorption at C band. Adv Funct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202313544
Wang C, Wang B, Cao X et al (2021) 3D flower-like Co-based oxide composites with excellent wideband electromagnetic microwave absorption. Compos Part B Eng 205:108529
He M, Hu J, Yan H et al (2024) Shape anisotropic chain-like CoNi/polydimethylsiloxane composite films with excellent low-frequency microwave absorption and high thermal conductivity. Adv Funct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202316691
Wang C, Jia Z, He S et al (2022) Metal-organic framework-derived CoSn/NC nanocubes as absorbers for electromagnetic wave attenuation. J Mater Sci Technol 108:236–243
Li F, Wu N, Kimura H et al (2023) Initiating binary metal oxides microcubes electromagnetic wave absorber toward ultrabroad absorption bandwidth through interfacial and defects modulation. Nano-Micro Letters 15:220
Wei C, Shi L, Li M et al (2024) Hollow engineering of sandwich NC@Co/NC@MnO2 composites toward strong wideband electromagnetic wave attenuation. J Mater Sci Technol 175:194–203
Han Y, He M, Hu J et al (2023) Hierarchical design of FeCo-based microchains for enhanced microwave absorption in C band. Nano Res 16:1773–1778
Funding
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52377026 and No. 52301192), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2019YQ24), the Taishan Scholars and Young Experts Program of Shandong Province (No. tsqn202103057), the Qingchuang Talents Induction Program of Shandong Higher Education Institution (Research and Innovation Team of Structural-Functional Polymer Composites), and the Special Financial of Shandong Province (Structural Design of High-Efficiency Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing Composite Materials and Construction of Shandong Provincial Talent Teams).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuelei Pan: related literature and writing, original draft preparation. Di Lan: complete drawings. Xing Feng: data curation. Zirui Jia, Ailing Feng, Pengfei Yin, and Guanglei Wu: some great enlightenment and helpful advices during the writing process.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Y., Lan, D., Jia, Z. et al. Multi-mode tunable electromagnetic wave absorber based on hollow nano-cage structure and self-anticorrosion performance. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 7, 40 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-024-00851-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-024-00851-4