Abstract
Purpose
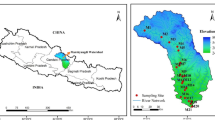
The aim of this study is to assess the seasonal variation in major ion distribution patterns and identify the origin and geochemical behavior of some trace metals of streamwaters bathing the mineralized Lom Basin.
Methods
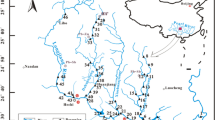
Eighty-one water samples were collected during the dry and wet seasons and analyzed for major ions using AAS and 12 trace metals (Fe, Mn, V, Cr, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Pb, Hg) by ICP-MS.
Results
All physicochemical parameters besides pH and Cl– varied narrowly between both seasons. No seasonal variability was observed for Cl– given its conservative nature, while NO3 – levels decreased in the wet period due to the dilution effect. Similarly, SO4 2– concentrations were low for both seasons reflecting the dissolution of low sulphide minerals associated with gold deposits. In contrast, the concentration of Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+ and HCO3 – slightly increased during the wet season as they are flushed from the soil layers by rain. Water samples had very low concentrations (< 1 µg/l) of V, Cr, Co, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb and significant concentrations of Fe and Mn.
Conclusions
The seasonal regime of streamwater chemistry is controlled by groundwater supply of major cations and HCO3 – from chemical weathering, leaching of ions from surface soil layers during precipitation and dilution of nitrate by surface runoff during the wet season. In this tropical basin, low acidity and trace metal loadings revealed lateritic weathering of sulphides, entrapment of trace metals in Fe and Mn oxides and leaching into deep groundwater. Although the streams have not been impacted, these findings may guide policymakers for water chemistry evaluation in Cameroon.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agyarko K, Dartey E, Kuffour RAW, Sarkodie PA (2014) Assessment of trace elements levels in sediment and water in some artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) localities in Ghana. Current World Environ 9(1):07–16
Ako TA, Onoduku US, Oke SA, Adamu IA, Ali SE, Mamodu A, Ibrahim AT (2014) Environmental impact of artisanal gold mining in Luku, Minna, Niger State, North Central Nigeria. J Geosci Geomat 2(1):28–37
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (1996) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. AA Balkema, Leiden
Ashley RP (2002) Geoenvironmental model for low-sulfide gold-quartz vein deposits. U.S. Geological Survey Open-file Report 02–195 K, 2002, pp 176–195. https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2002/of02-195/OF02-195K.pdf. Accessed 21 February 2017
Bortey-Sam N, Nakayama SMM, Ikenaka Y, Akoto O, Baidoo E, Mizukawa H, Ishizuka M (2015) Health risk assessment of heavy metals and metalloid in drinking water from communities near gold mines in Tarkwa, Ghana. Environ Monit Assess 187:397
Braun JJ, Viers J, Dupré B, Polve M, Ndam J, Muller JP (1998) Solid/Liquid REE fractionation in the lateritic system of Goyoum, East Cameroon: the implication for the present dynamics of the soil covers of the humid tropical regions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62:273–299
Cheng H, Hu Y, Luo J, Xu B, Zhao J (2009) Geochemical processes controlling fate and transport of arsenic in acid mine drainage (AMD) and natural systems. J Hazard Mater 165:13–26
Cravotta CAIII (2000) Relations among sulfate, metals and stream flow data for a stream draining a coal-mined watershed in east-central Pennsylvania. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acid Rock Drainage (ICARD), Denver, Colorado: Soc Mining Metallur Explor vol 1:p 401–410
Dan SF, Umoh UU, Osabor VN (2014) Seasonal variation of enrichment and contamination of heavy metals in the surface water of Qua Iboe River Estuary and adjoining creeks, South-South Nigeria. J Oceanogr Mar Sci 5(6):45–54
Drever JI (1997) The geochemistry of natural waters; surface and groundwater environments, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, pp 138–196
Edet A, Ukpong A, Nganje T (2014) Baseline concentration and sources of trace elements in groundwater of Cross River State, Nigeria. Int J Environ Monit Anal 2(1):1–13
Edith-Etakah BT, Shapi M, Penaye J, Mimba ME, Nguemhe Fils SC, Nadasan DS, Davies TC, Jordaan MA (2017) Background concentrations of potentially harmful elements in soils of the Kette-Batouri region, Eastern Cameroon. Res J Environ Toxicol 11:40–54. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjet.2017.40.54
Eneji IS, Onuche AP, Sha’Ato R (2012) Spatial and temporal variation in water quality of River Benue, Nigeria. J Environ Prot 3:915–921
Ficklin WH, Plumlee GS, Smith KS, McHugh JB (1992) Geochemical classification of mine drainages and natural drainages in mineralised areas. In: Kharaka YK, Maest AS (Eds.) Proceedings of 7th International Symposium, Water Rock Interaction, p 381–384
Foumena WC, Bamenjo JN (2013) Artisanal Mining—a challenge to the Kimberly process: a case study of the Kadey Division, east region of Cameroon, RELUFA extractive industries programme team. http://www.relufa.org/documents/BOOKENGLISH_NET.pdf. Accessed 24 February 2017
Franz C, Abbt-Braun G, Lorz C, Roig HL, Makeschin F (2014) Assessment and evaluation of metal contents in sediment and water samples within an urban watershed: an analysis of anthropogenic impacts on sediment and water quality in Central Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 72:4873–4890
Freyssinet PH, Lecompte P, Edimo A (1989) Dispersion of gold base metals in the Mborguene lateritic profile, East Cameroon. J Geochem Explor 32:99–116
Garizi AZ, Sheikh V, Sadoddin A (2011) Assessment of seasonal variations of chemical characteristics in surface water using multivariate statistical methods. Int J Environ Sci Tech 8(3):581–589
Grasby SE, Hutcheon I, Krouse HR (1997) Application of the stable isotope composition of SO4 2− to tracing anomalous TDS in Nose Creek, southern Alberta. Canada. Appl Geochem 12(5):567–575
Hem JD (1985) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water. United States Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 2254
Hook Z (2005) An assessment of the quality of drinking water in rural districts in Zimbabwe. The case of Gokwe South, Nkayi Lupene and Nwenezi districts. Phys Chem Earth 30:859–866
Kamtchueng BT, Fantong WY, Wirmvem MJ et al (2016) Hydrogeochemistry and quality of surface water and groundwater in the vicinity of Lake Monoun, West Cameroon: approach from multivariate statistical analysis and stable isotopic characterization. Environ Monit Assess 188(9):524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5514-x
Kelepertzis E, Argyraki A, Daftsis E (2012) Geochemical signature of surface and stream sediments of a mineralized drainage basin at NE Chalkidiki Greece: a pre-mining survey. J Geochem Explor 114:70–81
Khazheeva ZI, Tulokhonov AK (2007) Dashibalova LT (2007) Seasonal and spatial dynamics of TDS and major ions in the Selenga River. Water Resour 34(4):444–449
Kpan DK, Opoku AB, Gloria A (2014) Heavy metal pollution in soil and water in some selected towns in Dunkwa-on-Offin District in the Central Region of Ghana as a result of small scale gold mining. J Agric Chem Environ 3:40–47
Kumar M, Ramanathan Al, Roa MS, Kumar B (2006) Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India. Environ Geol 50:1025–1039
Markewitz D, Davidson EA, Figueiredo RO, Victoria RL, Krusche AV (2001) Control of cation concentrations in stream waters by surface soil processes in an Amazonian watershed. Nature 410:802–805
Meybeck M (1987) Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. Am J Sci 287:401–428
Milesi JP, Toteu SF, Deschamps Y et al (2006) An overview of the geology and major ore deposits of Central Africa: explanatory note for the 1:4,000,000 map ‘‘Geology and major ore deposits of Central Africa”. J Afr Earth Sci 44:571–595
Mimba ME, Ohba T, Nguemhe Fils SC, Wirmvem MJ, Bate Tibang EE, Nforba MT, Aka FT (2017) Regional hydrogeochemical mapping for environmental studies in the mineralized Lom Basin, East Cameroon: a pre-industrial mining survey. Hydrology 5(2):15–31. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.hyd.20170502.11
Neba A (1999) Modern geography of the Republic of Cameroon, 3rd edn. Neba, Bamenda
Ngako V, Affaton P, Nnange JM, Njanko TH (2003) Pan-African tectonic evolution in central and southern Cameroon: transpression and transtension during sinistral shear movements. J Afr Earth Sci 36:207–221
Nganje TN, Adamu CI, Ygbaja AN, Ebieme E, Sikakwe G (2011) Environmental contamination of trace elements in the vicinity of Okpara coal mine, Enugu, Southeastern Nigeria. Arab J Geosci 44:199–205
Nganje TN, Hursthouse AS, Edet A, Stirling D, Adamu CI (2015) Hydrochemistry of surface water and groundwater in the shale bedrock, Cross River Basin and Niger Delta Region, Nigeria. Appl Water Sci. doi:10.1007/s13201–015–0308–9
Omang BO, Bih CV, Fon NN, Suh CE (2014) Regional geochemical stream sediment survey for gold exploration in the upper Lom basin, eastern Cameroon. Int J Geosci 5:1012–1026
Omang BO, Suh CE, Lehmann B, Vishiti A, Chombong NN, Fon A, Egbe JA, Shemang EM (2015) Microchemical signature of alluvial gold from two contrasting terrains in Cameroon. J Afr Earth Sci 112:1–14
Plumlee GS, Logsdon MJ (1999) An earth-system science toolkit for environmentally friendly mineral resource development. In: Plumlee GS, Logsdon MJ (eds) The environmental geochemistry of mineral deposits, part a. Processes, techniques, and health issues. Soc Econ Geologists, Littleton, pp 1–27
Rakotondrabe F, Ndam Ngoupayou JR, Mfonka Z, Rasolomanana EH, Nyangono Abolo AJ, Ako Ako A (2017) Water quality assessment in the Betare-Oya gold mining area (East Cameroon): multivariate statistical analysis approach. Sci Total Environ 610–611(2018):831–844
Salminen R, Tarvainen T, Demetriades A et al (1998) FOREGS Geochemical mapping field manual. Geol Surv Finl Guide 47:16–21
Salomons W (1995) Environmental impact of metals derived from mining activities: processes, predictions, prevention. J Geochem Explor 52:5–23
Siegel FR (2002) Environmental geochemistry of potentially toxic metals. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg
Simbarashe M, Reginald K (2014) Environmental monitoring of the effects of conventional and artisanal gold mining on water quality in Ngwabalozi River, southern Zimbabwe. Int J Eng Appl Sci 4(10):8269
Singh AK, Mondal GC, Singh PK, Singh TB, Tewary BK (2005) Hydrochemistry of reservoirs of Damodar River basin, India: weathering processes and water quality assessment. Environ Geol 8:1014–1028
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17:517–568
Soba D, Michard A, Toteu SF, Norman DI, Penaye J, Ngako V, Nzenti JP, Dautel D (1991) Donnéés géochronologiques nouvelles (Rb–Sr, U–Pb et Sm–Nd) sur la zone mobile pan-africaine de l’Est Cameroun: âge Proterozoïque superieur de la série du Lom. Comptes Rendus Acad Sci 312:1453–1458
Toteu SF, Van Schmus RW, Penaye J, Michard A (2001) New U–Pb and Sm–Nd data from north central Cameroon and its bearing on the pre-pan-African history of Central Africa. Precambr Res 108:45–73
Toteu SF, Penaye J, Poudjom DY (2004) Geodynamic evolution of the Pan-African belt in Central Africa with special reference to Cameroon. Can J Earth Sci 41:73–85
Toteu SF, Penaye J, Deloule E, Van Schmus WR, Tchameni R (2006) Diachronous evolution of volcano-sedimentary basins north of the Congo craton: insights from U-Pb ion microprobe dating of zircons from the Poli, Lom and Yaounde Series (Cameroon). J Afr Earth Sci 44:428–442
Uwah IE, Dan SF, Etiuma RA, Umoh UU (2013) Evaluation of status of heavy metals pollution of sediments in Qua-Iboe River Estuary and associated creeks, south-eastern Nigeria. Environ Pollut 2(4):110–122
Van Straaten P (2000) Mercury contamination associated with small-scale gold mining in Tanzania and Zimbabwe. Sci Total Environ 259:105–113
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 4th edn. WHO, Geneva, p 564p
Acknowledgements
This paper constitutes part of the Ph.D. thesis of the corresponding author, under the auspices of the Japanese Government (MONBUKAGAKUSHO) Scholarship at the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). The authors thank the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) for funding the project and the Institute of Geological and Mining Research (IRGM) Cameroon for providing transportation facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mimba, M.E., Ohba, T., Nguemhe Fils, S.C. et al. Seasonal Hydrological Inputs of Major Ions and Trace Metal Composition in Streams Draining the Mineralized Lom Basin, East Cameroon: Basis for Environmental Studies. Earth Syst Environ 1, 22 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-017-0026-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-017-0026-6