Abstract
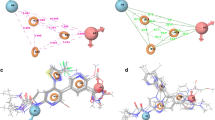
Among the many anticancer agents targeting topoisomerase IIα enzyme, palladium (II) analogues have gained in popularity as a promising enzyme inhibitor. In this article, molecular docking method and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were employed to study the mechanism through which oxali-palladium (oxali-Pd) inhibits the enzymatic activity of human topo IIα. The results of docking simulation confirm the inhibitory effects of oxali-Pd on the catalytic core of topoisomerase IIα enzyme through a non-competitive process. Also, it is suggested that oxali-Pd might intercalate within the DNA bases according to the topo IIα dynamicity as well. The results of MD simulations reveal that oxali-Pd is surrounded by Arg713, Ser714, Lys723, GLN726, Ser 763, Met766, Thr767, Asn770, Leu771, Glu854, Gly855, and Arg929 residues of protein. The average value of ΔGsolv is about − 93.1 kJ.mol−1 for protein and − 95.1 kJ.mol−1 for complex. The average values of Coulombic and Lennard–Jones interaction energies are calculated to be about − 78.1 ± 18.9 and − 81.8 ± 10.2 kJ.mol−1, respectively. These interaction energy values demonstrate the both electrostatic and van der Waals forces are important in complex formation between topo IIα protein and oxali-Pd molecule. Therefore, based on the data obtained from this study, oxali-Pd acts as a catalytic inhibitor of human topo IIα and is not a poison to the enzyme.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausaf Ali S, Hassan I, Islam A, Ahmad F (2014) A review of methods available to estimate solvent-accessible surface areas of soluble proteins in the folded and unfolded states. Curr Protein Pept Sci 15:456–476
Barra CV, Rocha FV, Morel L, Gautier A, Garrido SS, Mauro AE et al (2016) DNA binding, topoisomerase inhibition and cytotoxicity of palladium(II) complexes with 1,10-phenanthroline and thioureas. Inorg Chim Acta 446:54–60
Bau JT, Kurz EU (2011) Sodium salicylate is a novel catalytic inhibitor of human DNA topoisomerase II alpha. Biochem Pharmacol 81:345–354
Champoux JJ (2001) DNA topoisomerases: structure, function, and mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem 70:369–413
Chikamori K, Grozav AG, Kozuki T, Grabowski D, Ganapathi R, Ganapathi MK (2010) DNA topoisomerase II enzymes as molecular targets for cancer chemotherapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 10:758–771
Czarnomysy R, Radomska D, Szewczyk OK, Roszczenko P, Bielawski K (2021) Platinum and palladium complexes as promising sources for antitumor treatments. Int J Mol Sci 22:8271
Deweese JE, Osheroff N (2009) The DNA cleavage reaction of topoisomerase II: wolf in sheep’s clothing. Nucleic Acids Res 37:738–748
Gholamian A, Divsalar A, Saiedifar M, Ghalandari B, Saboury AA, Koohshekan B (2017) Generation of reactive oxygen species via inhibition of liver catalase by oxalli-palladium: a spectroscopic and docking study. Process Biochem 52:165–173
Hadian Rasanani S, Eslami Moghadam M, Soleimani E, Divsalar A, Tarlani A (2017) Improving activity of anticancer oxalipalladium analog by the modification of oxalate group with isopentylglycine. J Coord Chem 70:3769–3789
Hasinoff BB, Wu X, Krokhin OV, Ens W, Standing KG, Nitiss JL et al (2005) Biochemical and proteomics approaches to characterize topoisomerase IIalpha cysteines and DNA as targets responsible for cisplatin-induced inhibition of topoisomerase IIalpha. Mol Pharmacol 67:937–947
Hasinoff BB, Wu X, Begleiter A, Guziec LJ, Guziec F Jr, Giorgianni A et al (2006) Structure-activity study of the interaction of bioreductive benzoquinone alkylating agents with DNA topoisomerase II. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 57:221–233
Hevener K, Verstak TA, Lutat KE, Riggsbee DL, Mooney JW (2018) Recent developments in topoisomerase-targeted cancer chemotherapy. Acta Pharm Sin B 8:844–861
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996a) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14(33–8):27–28
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996b) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14:33–38
Kawanishi S, Yokoyama A, Tanaka H (1972) Studies on the sulfur-containing chelating agents. XXXII. the reaction of palladium (II) Ion with monothio-β-diketones and their disulfides. Chem Pharm Bull 20:262–8
Li T-K, Liu LF (2001) Tumor cell death induced by topoisomerase-targeting drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:53–77
Mancheño OG, Arrayás RG, Carretero JC (2005) Palladium complexes of chiral planar 1-phosphino-2-sulfenylferrocenes as efficient catalysts in enantioselective diels−alder reactions. Organometallics 24:557–561
Nitiss JL (2009) DNA topoisomerase II and its growing repertoire of biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer 9:327–337
Rocha FV, Barra CV, Garrido SS, Manente FA, Carlos IZ, Ellena J et al (2016) Cationic Pd(II) complexes acting as topoisomerase II inhibitors: Synthesis, characterization, DNA interaction and cytotoxicity. J Inorg Biochem 159:165–168
Rubin EH,Hait WN, Topoisomerase biology. In: Donald W Kufe, Raphael E Pollock, Ralph R Weichselbaum, Robert C Bast, Ted S Gansler, James F Holland, et al., editors. Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine. 6th ed. Hamilton: BC Decker; 2003
Sanner MF (1999) Python: a programming language for software integration and development. J Mol Graph Model 17:57–61
Sousa da Silva AW, Vranken WF (2012) ACPYPE - Antechamber python parser interface. BMC Res Notes 5:367
Syrovets T, Büchele B, Gedig E, Slupsky JR, Simmet T (2000) Acetyl-boswellic acids are novel catalytic inhibitors of human topoisomerases I and IIalpha. Mol Pharmacol 58:71–81
Trott O, Olson AJ (2010) AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem 31:455–461
Van Der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B, Groenhof G, Mark AE, Berendsen HJC (2005) GROMACS: fast, flexible, and free. J Comput Chem 26:1701–1718
Wang J, Cieplak P, Kollman PA (2000) How well does a restrained electrostatic potential (RESP) model perform in calculating conformational energies of organic and biological molecules? J Comput Chem 21:1049–1074
Wendorff TJ, Schmidt BH, Heslop P, Austin CA, Berger JM (2012) The structure of DNA-bound human topoisomerase II alpha: conformational mechanisms for coordinating inter-subunit interactions with DNA cleavage. J Mol Biol 424:109–124
Yoshida C, Hishiyama K, Miyazaki K, Watanabe M, Kanbe M, Yamada Y et al (2010) Analysis of inhibition of topoisomerase IIα and cancer cell proliferation by ingenolEZ. Cancer Sci 101:374–378
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Kharazmi University of Tehran and the Iran National Science Foundation (No: 99004364) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tavakoli, N., Ghalandari, B., Badalkhani-Khamseh, F. et al. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study on the Effect of Oxali-Palladium as a Catalytic Inhibitor of Human Topoisomerase IIα. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 46, 1575–1582 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-022-01384-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-022-01384-5