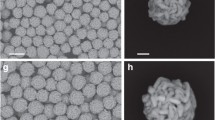
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) nanoporous gold (NPG) shows promising applications in various fields. However, its most common fabrication strategy (i.e., dealloying) faces the problems of high energy consumption, resource waste, the use of corrosive solvent, and residue of the sacrificial component. Here, we report a general bottom-up nanowelding strategy to fabricate high-purity NPG from Au nanoparticles (NPs), accomplished via interfacial self-assembly of the Au NPs into monolayer Au NP film, its subsequent layer-by-layer transfer onto a solid substrate, and direct current (DC) nanowelding. We show that the DC nanowelding process can gradually evolve the layered Au NP film into NPG at low temperatures within 10 s, while not damaging their spherical structure. This is because during the nanowelding, electrons are preferred to be localized at the high-resistance NP/NP junctions, whose electrostatic repulsion in turn strengthens their surface atom diffusion to initiate a mild solid-state diffusion nanowelding. Furthermore, when using differently sized Au NPs as the starting building blocks, this strategy allows readily tuning the thickness, ligament size, and pore size, thereby offering great flexibility to create functional porous nanomaterials, e.g., electrocatalyst for methanol electrooxidation. Surely, low-temperature nanowelding can play a role for the production of diverse nanoporous materials from other NPs beyond Au NPs.

摘要
三维纳米多孔金具有高的比表面积、高的导电性和等离激元特 性等众多优异的物理化学性质, 可以应用于多个领域. 然而, 其最常见 的制备方法, 即脱合金, 面临着高能耗、资源浪费、需使用腐蚀性液体 和牺牲组分的残留等问题. 本文中, 我们报道了一种较普适性的自下而 上的纳米焊接方法, 用于从金纳米粒子制造高纯度三维纳米多孔金. 该 方法先将化学合成的金纳米粒子在液-液界面自组装成致密的单层金 纳米粒子薄膜, 随后将其逐层转移到固体基底上形成多层的金纳米粒 子膜, 最后对该多层金纳米粒子膜在空气中通直流电进行纳米焊接. 研 究结果表明, 直流电纳米焊接工艺可在10 s内在低温下将层状金纳米颗 粒薄膜逐渐转变为纳米多孔金, 同时不会破坏母体金纳米粒子的球形 结构. 这是因为在纳米焊接过程中, 电子更倾向于聚集在高电阻的粒 子/粒子结点处, 造成该处的表面原子受到较强的静电排斥作用, 从而 强化了该处的表面原子扩散并引发温和的固态扩散纳米焊接. 此外, 当 使用不同尺寸的金纳米粒子作为起始构筑单元时, 该方法可有效调整 纳米多孔金的厚度、韧带尺寸和孔径, 从而为构筑功能性多孔纳米材 料(如用于甲醇电氧化的电催化剂)提供极大的灵活性. 可以预料, 该低 温纳米焊接方法也可用于除金纳米粒子以外的其他纳米粒子为起始构 筑单元构筑其他类型的纳米多孔材料.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruffino F, Grimaldi MG. Nanoporous gold-based sensing. Coatings, 2020, 10: 899
Seker E, Reed ML, Begley MR. Nanoporous gold: Fabrication, characterization, and applications. Materials, 2009, 2: 2188–2215
Huang J, He Z, He X, et al. Island-like nanoporous gold: Smaller island generates stronger surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9: 28902–28910
Wittstock A, Zielasek V, Biener J, et al. Nanoporous gold catalysts for selective gas-phase oxidative coupling of methanol at low temperature. Science, 2010, 327: 319–322
Liu Z, Ma H, Sun H, et al. Nanoporous gold-based microbial biosensor for direct determination of sulfide. Biosens Bioelectron, 2017, 98: 29–35
Lang X, Hirata A, Fujita T, et al. Nanoporous metal/oxide hybrid electrodes for electrochemical supercapacitors. Nat Nanotech, 2011, 6: 232–236
Deng Y, Huang W, Chen X, et al. Facile fabrication of nanoporous gold film electrodes. Electrochem Commun, 2008, 10: 810–813
Nishio K, Masuda H. Anodization of gold in oxalate solution to form a nanoporous black film. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2011, 50: 1603–1607
Meldrum FC, Seshadri R. Porous gold structures through templating by echinoid skeletal plates. Chem Commun, 2000, 1: 29–30
Huang J, He Z, Liu Y, et al. Large surface-enhanced Raman scattering from nanoporous gold film over nanosphere. Appl Surf Sci, 2019, 478: 793–801
Gao W, Xia XH, Xu JJ, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous gold structure as an efficient matrix for solid-state electrochemiluminescence of Ru(bpy)32+/TPA system with high sensitivity. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111: 12213–12219
Hernández-Saravia LP, Sukeri A, Bertotti M. Fabrication of nanoporous gold-islands via hydrogen bubble template: An efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution reactions. Int J Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44: 15001–15008
Kim SH. Nanoporous gold: Preparation and applications to catalysis and sensors. Curr Appl Phys, 2018, 18: 810–818
Lu Z, Li C, Han J, et al. Three-dimensional bicontinuous nanoporous materials by vapor phase dealloying. Nat Commun, 2018, 9: 276
Wada T, Yubuta K, Inoue A, et al. Dealloying by metallic melt. Mater Lett, 2011, 65: 1076–1078
Guo S, Wang E. Noble metal nanomaterials: Controllable synthesis and application in fuel cells and analytical sensors. Nano Today, 2011, 6: 240–264
Chen A, Holt-Hindle P. Platinum-based nanostructured materials: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Chem Rev, 2010, 110: 3767–3804
Qin GW, Liu J, Balaji T, et al. A facile and template-free method to prepare mesoporous gold sponge and its pore size control. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112:10352–10358
Zhang Z, Li H, Zhang F, et al. Investigation of halide-induced aggregation of Au nanoparticles into spongelike gold. Langmuir, 2014, 30: 2648–2659
Christiansen MUB, Seselj N, Engelbrekt C, et al. Chemically controlled interfacial nanoparticle assembly into nanoporous gold films for electrochemical applications. J Mater Chem A, 2018, 6: 556–564
Kim M, Jeong GH, Lee KY, et al. Fabrication of nanoporous superstructures through hierarchical self-assembly of nanoparticles. J Mater Chem, 2008, 18: 2208–2212
Lee MJ, Lim SH, Ha JM, et al. Green synthesis of high-purity mesoporous gold sponges using self-assembly of gold nanoparticles induced by thiolated poly(ethylene glycol). Langmuir, 2016, 32: 5937–5945
Zhang YX, Zeng HC. Gold sponges prepared via hydrothermally activated self-assembly of Au nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111: 6970–6975
Chen F, Yang S, Wu Z, et al. Light welding nanoparticles: From metal colloids to free-standing conductive metallic nanoparticle film. Sci China Mater, 2017, 60: 39–48
Han M, Chen F, Li M, et al. Light welding Au nanoparticles assembled at water-air interface for monolayered nanoporous gold films with tunable electrocatalytic activity. Electrochim Acta, 2020, 334: 135626
Zhang M, Li M, Han M, et al. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles, their interfacial self-assembly, and plasma welding: A solution-processable strategy to interdigital electrodes. Chem Phys Lett, 2020, 754: 137603
Liu J, Ge Y, Zhang D, et al. Plasma cleaning and self-limited welding of silver nanowire films for flexible transparent conductors. ACS Appl Nano Mater, 2021, 4: 1664–1671
Li M, Xie X, Xu Y, et al. External field-strengthened Ostwald nanowelding. Nano Res, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-12021-14001-z
Reincke F, Hickey SG, Kegel WK, et al. Spontaneous assembly of a monolayer of charged gold nanocrystals at the water/oil interface. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2004, 43: 458–462
Frens G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat Phys Sci, 1973, 241: 20–22
Zhang X, Chen H, Zhang H. Layer-by-layer assembly: From conventional to unconventional methods. Chem Commun, 2007,: 1395–1405
Lagrange M, Langley DP, Giusti G, et al. Optimization of silver nanowire-based transparent electrodes: Effects of density, size and thermal annealing. Nanoscale, 2015, 7: 17410–17423
Buffat P, Borel JP. Size effect on the melting temperature of gold particles. Phys Rev A, 1976, 13: 2287–2298
Song TB, Chen Y, Chung CH, et al. Nanoscale Joule heating and electromigration enhanced ripening of silver nanowire contacts. ACS Nano, 2014, 8: 2804–2811
Borkowska Z, Tymosiak-Zielinska A, Shul G. Electrooxidation of methanol on polycrystalline and single crystal gold electrodes. Electrochim Acta, 2004, 49: 1209–1220
Sukeri A, Saravia LPH, Bertotti M. A facile electrochemical approach to fabricate a nanoporous gold film electrode and its electrocatalytic activity towards dissolved oxygen reduction. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2015, 17: 28510–28514
Assiongbon KA, Roy D. Electro-oxidation of methanol on gold in alkaline media: Adsorption characteristics of reaction intermediates studied using time resolved electro-chemical impedance and surface plasmon resonance techniques. Surf Sci, 2005, 594: 99–119
Xia H, Ran Y, Li H, et al. Freestanding monolayered nanoporous gold films with high electrocatalytic activity via interfacial self-assembly and overgrowth. J Mater Chem A, 2013, 1: 4678–4684
Zhang J, Liu P, Ma H, et al. Nanostructured porous gold for methanol electro-oxidation. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111: 10382–10388
Abdel Hameed RM, Fetohi AE, Amin RS, et al. Promotion effect of manganese oxide on the electrocatalytic activity of Pt/C for methanol oxidation in acid medium. Appl Surf Sci, 2015, 359: 651–663
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21872047 and 21673070) and Hunan Key Laboratory of Two-Dimensional Materials (2018TP1010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Duan X and Hu J designed the study; Li M, Liu B, Xu Y, Liu J, Sun X, and Deng D performed the experiments; Li M analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the discussion and interpretation of the work.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Moxia Li is a doctoral candidate at the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University. She joined Professor Hu’s group in 2018 and her current research interests include the synthesis, characterization, self-assembly, nanowelding, and application of nanomaterials.
Jiawen Hu is a professor of chemistry at the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University. He received his PhD degree in physical chemistry from Jilin University in 2002, followed by a period of postdoctoral research at Xiamen University. His research interests include surface-enhanced Raman scattering, synthesis, characterization, self-assembly, nanowelding, and application of nanomaterials, and capacitive desalination.
Xidong Duan received his BSc degree in chemistry, MA degree in materials science, and PhD degree in chemistry from Hunan University in 1993, 1996, and 2016, respectively. Afterward, he joined the College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan University, as a professor. His current research interests include two-dimensional materials, heterostructures and their applications.
Supplementary information
Supporting data are available in the online version of the paper.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Xu, Y., Liu, B. et al. Bottom-up fabrication of three-dimensional nanoporous gold from Au nanoparticles using nanowelding. Sci. China Mater. 65, 2755–2762 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-022-2020-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40843-022-2020-9