Abstract
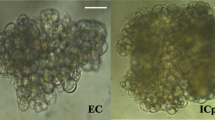
In this study, non-embryogenic callus (NEC), embryogenic callus (EC), and somatic embryos (SE) sourced from various culture materials were employed to investigate somatic embryogenesis in Cinnamomum camphora. Utilizing RNA-Seq technology, we conducted transcriptome sequencing and analysis of C. camphora culture materials to elucidate the genes and metabolic pathways associated with somatic embryogenesis. Correlation analysis among the samples indicated substantial differences between the groups, confirming the representativeness of the three materials utilized. The analysis revealed three distinct databases of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) (SE vs EC, SE vs NEC, EC vs NEC) containing 10,449, 9,561, and 8,867 DEGs, respectively. Clustering analysis of DEGs unveiled significant separation among SE, EC, and NEC from different C. camphora materials. Notably, 21 genes were significantly up-regulated in SE and EC compared to NEC, predominantly comprising adversity stress-responsive genes, hormone-responsive genes, and zinc finger proteins. Of particular interest was the expression of the VACUOLAR IRON TRANSPORTER 1 (VIT1) gene, which was 78.33 and 3.05 times higher in SE than in NEC and EC, respectively. This suggests a potential crucial regulatory role for Fe2+ in C. camphora somatic embryogenesis. Further analysis of DEGs, in conjunction with Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment, unveiled a close association of C. camphora somatic embryogenesis with biological processes, transcriptional regulation, responses to salt stress and abscisic acid, cell nucleus activity, and DNA-binding transcription factors. Moreover, KEGG pathway analysis emphasized the significant enrichment of DEGs in plant hormone signal transduction, featuring 187 differential genes, highlighting the pivotal role of hormone signaling in C. camphora somatic embryogenesis. Most genes related to phytohormone synthesis, signal transduction, transcription factors, and stress responses were up-regulated, thereby promoting somatic embryogenesis in C. camphora. The findings of this study provide valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying somatic embryogenesis in C. camphora and related species.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson DH (2015) Fast and sensitive protein alignment using diamond. Nat Methods 12:59–60
Canto AM, Ceciliato PHO, Ribeiro B, Morea FAO, Garcia AAF, Silva-Filho MC, Moura DS (2014) Biological activity of nine recombinant AtRALF peptides: implications for their perception and function in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Bioch 75:45–54
Chen YK, Xu XP, Liu ZX, Zhang ZH, Han XX, Lin YL, Lai ZX (2020) Global scale transcriptome analysis reveals differentially expressed genes involve inearly somatic embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan lour. BMC Genom 21:4
Dai XY, Liu XL, Zhang T, Jiang L, Cheng Z (2019) Embryogenic callus induction and somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos of Cinnamomum camphor. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis 41:1120–1129
Devadasu ER, Madireddi SK, Nama S, Subramanyam R (2016) Iron deficiency cause changes in photochemistry, thylakoid organization, and accumulation of photosystem II proteins in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Photosynth Res 130:469–478
Du L, Ye YM, Bao MZ (2006) Study on somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of immature zygotic embryo of Cinnamomum camphora. Sc Silv Sin 42:37–39
Du L, Li YP, Yao Y, Zhang LW (2015) An efficient protocol for plantlet regeneration via direct organogenesis by using nodal segments from embryo-cultured seedlings of Cinnamomum camphora L. PLoS ONE 10:e0127215
Etienne H, Montoro P, Michaux-Ferriere N, Carron MP (1993) Effects of desiccation, medium osmolarity and abscisic acid on the maturation of Hevea brasiliensis somatic embryos. J Exp Bot 44:1613–1619
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2000) The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 5:199–206
Fowler MR, Ong LM, Russinova E, Atanassov AI, Scott NW, Slater A, Elliott MC (1998) Early changes in gene expression during direct somatic embryogenesis in alfalfa revealed by RAP-PCR. J Exp Bot 49:249–253
Goldental-Cohen S, Isracli A, Ori N, Yasuor H (2017) Auxin response dynamics during wild-type and entire flower development in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol 58:1661–1672
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M, Levin JZ, Thompson DA, Amit I, Adiconis X, Fan L, Raychowdhury R, Zeng QD, Chen ZH, Mauceli E, Hacohen N, Gnirke A, Rhind N, Palma FD, Birren BW, Nusbaum C, Lindblad-Toh K, Friedman N, Regev A (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652
Guo HH, Guo HX, Zhang L, Tang ZM, Yu XM, Wu JF, Zeng FC (2019) Metabolome and transcriptome association analysis reveals dynamic regulation of purine metabolism and flavonoid synthesis in transdifferentiation during somatic embryogenesis in cotton. Int J Mol Sci 20:2070
Hecht V, Vielle-Calzada JP, Hartog MV, Schmidt ED, Boutilier K, Grossniklaus U, de Vries SC (2001) The arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR KINASE 1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol 127:803–816
Horstman A, Willemsen V, Boutilier K, Heidstra R (2014) AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE proteins: hubs in a plethora of networks. Trends Plant Sci 19:146–157
Jiménez VM (2005) Involvement of plant hormones and plant growth regulators on in vitro somatic embryogenesis. Plant Growth Regul 47:91–110
Jing RY, Wang PL, Huang Z, Li ZH (2019) Histocytological study of somatic embryogenesis in the tree Cinnamomum camphora L. (Lauraceae). Not Bot Horti Agrobo 47:1348–1358
Kim J, Kim HY (2006) Molecular characterization of a bHLH transcription factor involved in Arabidopsis abscisic acid-mediated response. BBA-Gene Regul Mech 1759:191–194
Kitamiya E, Suzuki S, Sano T, Nagata T (2000) Isolation of two genes that were induced upon the initiation of somatic embryogenesis on carrot hypocotyls by high concentrations of 2,4-D. Plant Cell Rep 19:551–557
Lapinskas PJ, Lin SJ, Culotta VC (1996) The role of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCC1 gene in the homeostasis of manganese ions. Mol Microbiol 21:519–528
Li QF, Zhang SG, Wang JH (2014) Transcriptome analysis of callus from Picea balfouriana. BMC Genomics 15:553
lkeda-Iwai M, Satoh S, Kamada H, (2002) Establishment of a reproducible tissue culture system for the induction of Arabidopsis somatic embryos. J Exp Bot 53:1575–1580
Lou H, Huang YT, Cai WWZ, ZY, Cai HY, Liu ZQ, Sun L, Xu QJ, (2022) Overexpression of the AtWUSCHEL gene promotes somatic embryogenesis and lateral branch formation in birch (Betula platyphylla Suk.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 150:371–383
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. Embnet J 17:10–12
Marcelo dOS, Romano E, Yotoko KSC, Tinoco MLP, Dias BBA, Aragão FJL (2005) Characterisation of the cacao somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase (SERK) gene expressed during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Sci 168: 723–729
Morcilo F, Gallard A, Pillot M, Jouannic S, Aberlenc-Bertossi F, Collin M, Verdeil JL, Tregear JW (2007) EgAP2-1, an AINTEGUMENTA-like (AIL) gene expressed in meristematic and proliferating tissues of embryos in oil palm. Planta 226:1353–1362
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, Mccue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-seq. Nat Methods 5:621–628
Palovaara J, Hallberg H, Stasolla C, Hakman I (2010) Comparative expression pattern analysis of WUSCHEL-related homeobox 2 (WOX2) and WOX8/9 in developing seeds and somaticembryos of the gymnosperm Picea abies. New Phytol 188:122–135
Patro R, Duggal G, Love MI, Irizarry RA, Kingsford C (2017) Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat Methods 14:417–419
Prasinos C, Krampis K, Samakovli D, Hatzopoulos P (2005) Tight regulation of expression of two Arabidopsis cytosolic Hsp90 genes during embryo development. J Exp Bot 56:633–644
Quintana-Escobar AO, Nic-Can GI, Galaz Avalos RM, Loyola-Vargas VM, Gongora-Castillo E (2019) Transcriptome analysis of the induction of somatic embryogenesis in Coffea canephora and the participation of ARF and Aux/IAA genes. Peer J 7:e7752
Robert HS, Grunewald W, Sauer M, Cannoot B, Soriano M, Soriano R, Weijers D, Bennett M, Boutilier K, Friml J (2015) Plant embryogenesis requires AUX/LAX-mediated auxin influx. Development 142:702–711
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2010) EdgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139–140
Sakai H, Honma T, Aoyama T, Sato S, Kato T, Tabata S, Oka A (2001) ARR1, a transcription factor for genes immediately responsive to cytokinins. Science 294:1519–1521
Santos M, Romano E, Yotoko KSC, Tinoco MLP, Dias BBA, Aragão FJL (2005) Characterisation of the cacao somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase (SERK) gene expressed during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Sci 168:723–729
Schmidt EDL, Guzzo F, Toonen MAJ, Vries SC (1997) A leucine-rich repeat containing receptor-like kinase marks somatic plant cells competent to form embryos. Development 124:2049–2062
Shi XP, Zhang CJ, Liu QH, Zhang Z, Zheng B, Bao MZ (2016) De novo comparative transcriptome analysis provides new insights into sucrose induced somatic embryogenesis in camphor tree (Cinnamomum camphora L.). BMC Genom 17:26
Singla B, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2014) Structural characterization and expression analysis of the SERK/SERL gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Int J Plant Genom 2009:8
Thibaud-Nissen F, Shealy RT, Khanna A, Vodkin LO (2003) Clustering of microarray data reveals transcript patterns associated with somatic embryogenesis in soybean. Plant Physiol 32:118–136
Wang XC, Niu QW, Teng C (2009) Overexpression of PGA37/MYB118 and MYB115 promotes vegetative-to-embryonic transition in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 19:224–235
Woodward AW, Bartel B (2005) Auxin: regulation, action, and interaction. Ann Bot 95:707–735
Wu T, Zhang HT, Wang Y, Jia WS, Xu XF, Zhang XZ, Han ZH (2012) Induction of root Fe (lll) reductase activity and proton extrusion by iron deficiency is mediated by auxin-based systemic signalling in Malus Xiaojinensis. J Exp Bot 63:859–870
Xu ZZ, Zhang CJ, Zhang XY, Liu CL, Wu ZX, Yang ZR, Zhou KH, Yang XJ, Li FG (2013) Transcriptome profiling reveals auxin and cytokinin regulating somatic embryogenesis in different sister lines of cotton cultivar CCRI24. J Integr Plant Biol 55:631–642
Xu CY, Ma YD, Tian ZF, Luo QY, Zheng TF, Wang B, Zuo ZJ (2022) Monoterpene emissions and their protection effects on adult Cinnamomum camphora against high temperature. Trees 36:711–721
Zeng FC, Zhang XL, Zhu LF, Tu LL, Guo XP, Nie YC (2006) Isolation and characterization of genes associated to cotton somatic embryogenesis by suppression subtractive hybridization and macroarray. Plant Mol Biol 60:167–183
Zheng Q, Zheng Y, Perry SE (2013) AGAMOUS-Like15 promotes somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis and soybean in part by the control of ethylene biosynthesis and response. Plant Physiol 161:2113–2127
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by grants from the Research Project from Key R&D Program and Promotion of Henan Province (Grant No. 202102110078) and Postgraduate Education Reform and Quality Improvement Project of Henan Province (Grant No. YJS2021JD17).
Funding
Funding provided by the Henan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Research Project (Grant No. 202102110078). Postgraduate Education Reform and Quality Improvement Project of Henan Province (Grant No. YJS2021JD17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study's conception and design. YL and HG curated the data and performed the analysis. HG drafted the initial manuscript. XK and LD reviewed and revised the manuscript. LD acquired funding for this research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Guo, H., Kang, X. et al. Study on somatic embryogenesis of cinnamomum camphora based on transcriptome sequencing. Braz. J. Bot (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-024-00984-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-024-00984-2