Abstract
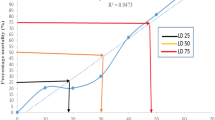
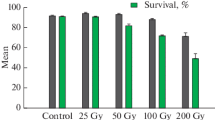
Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) is one of the most popular fruits in Cameroon and the world at large. However, the extreme sensitivity of watermelon to parasites and climatic vagaries makes its cultivation demanding of chemical inputs that can have negative impacts on human health and the environment. In Cameroon, there is a slow improvement of fruit yield in watermelon breeding due to the lack of natural heritable genetic variation, which is a prerequisite for genetic improvement of crops. Such variation can be created through either random or targeted processes on genotypes with appropriate doses of radiation. Genetic improvement by induced mutagenesis appears today alongside hybridization as an alternative method of creating new plant varieties. However, the success of this approach is determined by the application of an appropriate and ideal dose of mutagen. The objective of this study was to evaluate the radiosensitivity of the two most cultivated watermelon varieties in Cameroon to gamma radiation from 60Co in order to determine an optimal dose or lethal dose 50 (LD50) for the induction of the genetic variability necessary for genetic improvement. Seeds of the Kaolack and Crimson sweet watermelon varieties were irradiated with five doses of gamma radiation (100, 200, 300, 400 and 600 Gy) in the laboratory of the International Atomic Energy Agency in Seibersdorf, Austria. These seeds were cultivated in a greenhouse following an utterly randomized device with three repetitions, and parameters such as the germination rate, the survival rate and the shoot length of plants were evaluated. High rates of 90% and 75% germination were obtained, respectively, for the control treatments of Kaolack and Crimson sweet, while the lowest rates were 35% at 600 Gy for Kaolack and 30% at 400 Gy for Crimson sweet. The highest survival rate of plants (96.66%) was obtained with the control seeds of the Kaolack. This variety had the lowest survival rate (45.6%) at 600 Gy dose. Statistical analysis of data obtained helped to estimate the ideal LD50 doses based on growth reduction of seedlings’ heights after gamma-ray treatment. Using a linear regression model based on parameters like plant size, the LD50 doses for Kaolack and Crimson sweet were calculated at 225.40 Gy and 221.56 Gy, respectively, and predicted between 200 and 250 Gy. These results show that the two varieties evaluated were radiosensitive as clearly expressed in the parameters evaluated, where the values decreased with the increase in the irradiation dose. The LD50 doses from this study could be safely applied as reference doses for large-scale gamma irradiation of watermelon genotypes to create desirable agronomic traits in the mutation breeding efforts.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayodele OJ, Shittu OS (2013) Cost-benefit analysis of melon (egusi) seed and seed-oil yield responses to phosphorus fertilizer application. Int Res J Agric Sci Soil Sci 3:152–155
Bado S, Forster BP, Nielen S, Ghanim A, Lagoda PJL, Till BJ, Laimer M (2015) Plant mutation breeding: current progress and future assessment. Plant Breed Rev 39:23–88
Bahari M, Rafii MY, Saleh GB, Latif MA (2012) Combining ability analysis in complete diallel cross of Watermelon [Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. and Nakai]. Sci World J 2012:1–6
Bajaj YPS, Saettler AW, Adams MW (1970) Gamma irradiation studies on seeds, seedlings and callus tissue cultures of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Rad Bot 10:119–124
Biswas R, Ghosal S, Chattopadhyay A, Datta S (2017) A comprehensive review on watermelon seed oil—An underutilized product. J Pharm 71:2250–3013
Boualem A, Lemhemdi A, Sari MA, Pignoly S, Troadec C, Choucha FA, Solmaz I, Sari N, Dogimont C, Bendahmane A (2016) The andromonoecious sex determination gene predates the separation of Cucumis and Citrullus genera. PLoS ONE 11:1–13
Davis AR, Webber CL, Perkins-Veazie P, Russo V, Lopez Galarza S, Sakata Y (2008) A review of production systems on watermelon quality. Cucurbitaceae 2008. In: Proceedings IXth EUCARPIA meeting on genetics and breeding of Cucurbitaceae, Avignon, France, 21–24 May
Edwards AI, Vinyard BT, Wiley ER, Brown ED, Collins IK, Perkins-Veazie P, Baker RA, Clevidence BA (2003) Consumption of watermelon juice increases plasma concentrations of lycopene and ß-carotene in humans. J Nutr 133:1043–1050
Enzonga-Yoca JA, Nitou JG, Allou Kippré V, Niamayoua RK, Mvoula-Tsieri M, Silou T (2011) Caractérisation chimique et évaluation de la température de conservation du lait des graines de cucurbitacées: Cucumeropsis mannii et Citrullus lanatus. J Anim Plant Sci 10:1232–1238
Ertan SK, Ahmet B, Dilek K (2017) Determination of semi-lethal (LD50) doses for mutation breeding of Turkish winter squash (Cucurbita maxima Duch.) and pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch.). Fresenius Environ Bull 26:3209–3216
Esquinas-Alcazar JT, Gulick PJ (1983) Genetic resources of Cucurbitaceae. A global report. International Board for Plant Genetic Resources, Rome, p 101
Essel E, Asante IK, Odamtten G (2016) Mutagenic effect of gamma irradiation on seed germination and yield components of cowpea. J Ghana Sci Assoc 17:53–59
FAO (2009) FAO’s Director-General on how to feed the World in 2050. Popul Dev Rev 35:837–839
FAO (2013) Food and agriculture organisation of the United Nations: Economic and Social Department: the statistics division. http://faostat.fao.org/site/339/default.aspx. Accessed 12 Nov 2013
Girija M, Dhanavel D (2009) Mutagenic effectiveness and efficiency of gamma rays, ethyl methane sulphonate and their combined treatments in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). Glob J Mol Sci 4:68–75
Giwa S, Abdullah LC, Adam NM (2010) Investigating Egusi (Citrullus colocynthis L.) seed oil as potential biodiesel feedstock. Energies 3:607–618
Gnankambary K, Teyouré BJ, Nerbéwendé S, Mahamadou S, Djibril Y, Tinga JO (2019) Assessment of radio-sensitivity for three cowpea genotypes to gamma irradiation. Int J Genet Mol Biol 11:29–33
Guerin De Montgareuil P (1984) Radioagronomie in Echos. Groupe CEA, France, pp 56–57
Guo S, Zhang J, Sun H (2012) The draft genome of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) and resequencing of 20 diverse accessions. Nat Genet 45:51–58
Guoyao W, Collins JK, Perkins-Veazie P and Siddiq M (1992) Dietary supplementation with melon pomace juice enhances arginine availability and ameliorates the metabolic syndrome in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Nutr 45:34–54
Gusmini G, Wehner TC (2005) Foundations of yield improvement in watermelon. Crop Sci 45:141–146
Horn LN, Shimelis H (2013) Investigation on radio-sensitivity of gamma irradiation on selected cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) genotypes. Sci Res and Ess 8:1991–1997
Huh YC, Solmaz I, Sarı N (2008) Morpholojical characterization of Korean and Turkish watermelon germplasm. In: Pitrat M (ed) Cucurbitaceae 2008, Proceedings of the IXth EUCARPIA meeting on genetics and breeding of Cucurbitaceae, INRA, Avignon, France, 21–24 May 2008
Johnson JT, Iwang EU, Hemen JT, Odey MO, Efion EE, Eteng OE (2012) Evaluation of anti-nutrient contents of watermelon Citrullus lanatus. Annal Biol Res 3:5145–5150
Karidiatou G, Teyouré BJ, Nerbéwendé S, Mahamadou S, Djibril Y, Tinga JO (2019) Assessment of radio-sensitivity for three cowpea genotypes to gamma irradiation. Int J Genet Mol Biol 11:29–33
Kodym A, Afza R, Forster BP, Ukai Y, Nakagawa H (2012) Methodology for physical and chemical mutagenic treatments. In: Plant mutation breeding and biotechnology, pp 169–180
Kumar R, Shunmugavalli N (2018) Assessment of gamma rays induced variability in M2 generation of Sesamum (Sesamum indicum L.). Int J Chem 6:292–296
Kuvare USK (2005) Greenhouse production of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Stellenbosch, South Africa, Department of Horticulture, University of Stellenbosch, MS Thesis, p 300
Lum T, Connolly M, Marx A, Beidler J, Hooshmand S, Kern M, Liu C, Hong MY (2019) Effect of fresh watermelon consumption on the acute satiety response and cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese adults. Nutrients 11:595
Mahure HR, Choudhary ML, Prasad KV, Singh SK (2010) Mutation in chrysanthemum through gamma irradiation. Indian J Hort 67:356–358
Mallick MFR, Masui M (1986) Origin, distribution and taxonomy of melons. Sci Hort 28:251–261
Maluszynski M, Szarejko I, Maluszynski J (2003) Mutation techniques. In: Thomas B, Murphy DJ, Murray BG (eds) Encyclopedia of applied plant sciences. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, pp 186–201
Manju P, Gopimony R (2009) A new okra variety through induced mutation in interspecific hybrids of Abelmoschus Species. In: Shu QY (ed) Induced plant mutations in the genomics era. Joint FAO/IAEA Programme, Vienna, Austria, pp 91–94
Maoto M, Beswa D, Jideani AIO (2019) Watermelon as a potential fruit snack. Int J Food Prop 22:355–370
Marcu D, Damian G, Cosma C, Cristea V (2013) Gamma radiation effects on seed germination, growth and pigment content, and ESR study of induced free radicals in maize (Zea mays). J Bio Phy 39:625–634
Mba C (2013) Induced mutations unleash the potentials of plant genetic resources for food and agriculture. Agronomy 3:200–231
Mba C, Afza R, Bado S, Jaim SM (2010) Induced mutagenesis in plants using physical and chemical agents. In: Plant cell culture essential methods, pp 111–130
Mba C, Afza R, Shu QY (2012) Mutagenic radiations: X-rays, ionizing particles and ultraviolet. In: Shu Q, Forster BP, Nakaga-wa H (eds) Plant mutation breeding and biotechnology. CABI, Oxfordshire, UK, pp 83–90
Morère JL, Pujol R (2003) Dictionnaire raisonné de biologie. Frison-Roche, Paris
Meunier E (2005) Des plantes mutantes dans nos assiettes. Inf’OGM, 67, Septembre 2005, http://www.infogm.org/spip.php?Article2406. Accessed 10 May 2010
Morishita T, Yamaguchi H, Degi K, Shikazono N, Tanaka A, Abe T (2003) Dose response and mutation induction by ion beam irradiation in buckwheat. Nucl Instr Meth Phys Res B 206:565–569
Munisse P, Jensen BD, Andersen SB (2013) Genetic differentiation of watermelon landraces in Mozambique using microsatellite markers. Afr J Biotechnol 12:5513–5521
Naz A, Butt MS, Sultan MT, Qayyum MMN, Naiz RS (2014) Watermelon lycopene and allied health claims. Excli J 13:650–666
Olasupo FO, Ilori CO, Forster BP, Bado S (2016) Mutagenic effects of gamma radiation on eight accessions of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp.). American J Plant Sci 7:339–351
Olasupo FO, Ilori CO, Forster BP, Bado S (2018) Selection for novel mutations induced by gamma irradiation in cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]. Int J Plant Breed Genet 12:1–12
Olson JA (1999) Carotenoids. In: Shils ME, Olson JA, Shike M, Ross AC (eds) Modern nutrition in health and disease, 9th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 525–541
Owoseni O, Okwaro H, Afza R, Bado S, Dixon A, Mba C (2007) Radiosensitivity and in vitro mutagenesis in African accessions of cassava, Manihot esculenta Crantz. Plant Mutat Rep 1:32–36
Ray DK, Mueller ND, West PC, Foley JA (2013) Yield trends are insufficient to double global crop production by 2050. PLoS ONE 8:e66428
Ronald P (2011) Plant genetics, sustainable agriculture and global food security. Genetics 188:11–20
Roychowdhury R, Tah J (2013) Mutagenesis A potential approach for crop improvement. In: Hakeem KR, Ahmad P, Ozturk M (eds) Crop improvement: new approaches and modern techniques. Springer, Boston, pp 149–187
Sari N, Abak K (1996) Farkli Isin dozlarininveIs¸ I nlamaya alternative uygulamalarinkarpuzda haploid embryo uyartımınaetkileri. Tu rkiye II. UlusalBahçe Bitkileri Kongresi Bildirileri, Cilt II, Adana, Turkey. pp 212–215
Schippers RR (2000) African indigenous vegetables. An overview of the cultivated species. Natural resources institute/ACP-EU technical centre for agricultural and rural cooperation, Chatham, UK, pp 214
Shah TM, Mirza JI, Haq MA, Atta BM (2008) Radiosensitivity of various chickpea genotypes in M1 generation in laboratory studies. Pak J Bot 40:649–665
Shu Q, Forster BP, Nakagawa H (2012) Plant mutation breeding and biotechnology. CABI
Sikder, S, Biswas, P, Hazra, P, Akhtar, S, Chattopadhyay, A, Badigannavar, AM and D’Souza SF (2013) Induction mutation in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) by gamma irradiation and EMS. Indian J Genet 73: 392–399
Singh S, Singh R, Singh N, Prasad J, Shahi J (2007) Mutagenic efficiency of gamma-rays, ethyl methane sulphonate and its combination on microsperma lentil (Lens culinaris Medik). Int J Agric Sci 3:113–118
Solanki I, Sharma B (1994) Mutagenic effectiveness and efficiency of gamma rays, ethylene imine and N-nitroso-N-ethyl urea in macrosperma lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.). The Indian J Genet Plant Breed 54:72–76
Tabasum A, Cheema AA, Hameed A, Rashid M, Ashraf M (2011) Radiosensitivity of rice genotypes to gamma radiations based on seedling traits and physiological indices. Pak J Bot 43:1211–1222
Taiwo AA, Agbotoba MO, Oyedepo JA, Shobo OA, Oluwadare I and Olawunmi MO (2008) Effects of drying methods on properties of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) seed oil. Af J Food Agric Nutr and Dev 8:1456–1460
Taskin H, Yucel NK, Baktemur G, Comlekcioglu S, Buyukalaca S (2013) Incidence de divers genotypes et doses de rayons gamma sur l’haploidisation par la technique du pollen irradié chez la pastèque (Citrullus lanatus L.). Can J Plant Sci 93:1165–1168
Tester M, Langridge P (2010) Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 327:818–822
Tshilenge-Lukanda L, Funny-Biola C, Tshiyoyi-Mpunga A, Mudibu J, Ngoie-Lubwika M, Mukendi-Tshibingu R, Kalonji-Mbuyi A (2012) Radio-sensitivity of some groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) genotypes to gamma irradiation: indices for use as improvement. Brit J Biotechnol 3:169–178
Tshilenge-Lukanda LA, Kalonji-Mbuyi A, Nkongolo KKC, Kizungu RV (2013) Effect of gamma irradiation on morpho-agronomic characteristics of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Am J Plant Sci 4:2186–2192
Ulukapi K, Ozdemir B, Onus N (2015) Determination of proper gamma radiation dose in mutation breeding in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). In: Advances in Environmental and Agricultural Science, pp 149–153
Van Harten AM (1998) Mutation breeding: theory and practical applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 330
Verma AK, Sharma S, Kakani RK, Meena RD, Choudhary S (2017) Gamma radiation effects seed germination, plant growth and yield attributing characters of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.). Int J Current Microbiol Appl Sci 6:2448–2458
Webster JE, Romshe FA (1951) Watermelon syrup: its composition and composition of the juice from which it was made. Am Soc Hort Sci 57:302–304
Wilde HD, Chen Y, Jiang P, Bhattacharya A (2012) Targeted mutation breeding of horticultural plants. Emir J Food Agric 24:31–41
Ukai Y (1983) Mutation breeding. Gamma Field Symposia N° 20 Suppl. Yokendo, Tokyo
Zaini NAM, Anwar F, Hamid AA, Saari N (2011) Kundur [Benincasa hispida (Thunb.) Cogn.]: a potential source for valuable nutrients and functional foods. Food Res Int 44:2368–2376
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FPE, BJM and GNN conceived and designed the experiments. MNA, OAS and NHB performed the experiments and drafted the manuscript. BJM and MR analyzed the data. MAA helped perform the analysis with constructive discussion. MT reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the submitted manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paul Ernest, F., Hortense Noëlle, M., Godswill, NN. et al. Radiosensitivity of two varieties of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) to different doses of gamma irradiation. Braz. J. Bot 43, 897–905 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-020-00659-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-020-00659-8