Abstract
Introduction
There exists clinical interest in the following question: Is there an association between HOMA-IR and the risk of developing metabolic diseases?
Aims
Assessing the association between high values of HOMA-IR with the incidence of T2DM, MACE, essential hypertension, dyslipidemia, NASH, and cancer in healthy participants and participants with a component of metabolic syndrome.
Methods
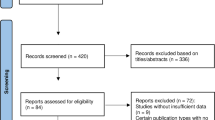
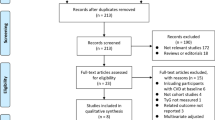
Databases were searched by an experienced librarian to find eligible studies. Observational cohort studies enrolling healthy adults and adults with metabolic syndrome components that evaluated HOMA as a marker of IR were considered for inclusion. Eligibility assessment, data extraction and risk of bias assessment were performed independently and in duplicate. Baseline characteristics of patients, cutoff values of HOMA-IR to predict metabolic events were extracted independently and in duplicate.
Results
38 studies (215,878 participants) proved eligible. A higher HOMA-IR value had a significant effect on the risk of developing T2DM (HR 1.87; CI 1.40–2.49), presenting non-fatal MACE (HR 1.46; CI 1.08–1.97) and hypertension (HR 1.35; CI 1.15–1.59). No association was found regarding cancer mortality and fatal MACE with higher HOMA-IR values, there was not enough information to carry out a meta-analysis to establish an association between higher values of HOMA with cancer incidence, dyslipidemia, and NASH.
Conclusions
High values of HOMA were associated with an increased risk of diabetes, hypertension, and non-fatal MACE; yet, not for cardiovascular or cancer mortality. More research is needed to determine the value of the HOMA index in metabolic and cardiovascular outcomes.
PROSPERO Registration Number
CRD42020187645.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin X, Xu Y, Pan X, Xu J, Ding Y, Sun X, et al. Global, regional, and national burden and trend of diabetes in 195 countries and territories: an analysis from 1990 to 2025. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14790.
Reaven GM. Pathophysiology of insulin resistance in human disease. Physiol Rev. 1995;75(3):473–86.
Wilcox G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin Biochem Rev. 2005;26(2):19–39.
Matsuda M, DeFronzo RA. Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(9):1462–70.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985;28(7):412–9.
Otten J, Ahrén B, Olsson T. Surrogate measures of insulin sensitivity vs the hyperinsulinaemic–euglycaemic clamp: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2014;57(9):1781–8.
Gutierrez-Buey G, Núñez-Córdoba JM, Llavero-Valero M, Gargallo J, Salvador J, Escalada J. Is HOMA-IR a potential screening test for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults with type 2 diabetes? Eur J Intern Med. 2017;41:74–8.
Baek JH, Kim H, Kim KY, Jung J. Insulin resistance and the risk of diabetes and dysglycemia in Korean General Adult Population. Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(4):296–307.
Bonora E, Formentini G, Calcaterra F, Lombardi S, Marini F, Zenari L, et al. HOMA-estimated insulin resistance is an independent predictor of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetic subjects: prospective data from the Verona Diabetes Complications Study. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(7):1135–41.
Kurl S, Zaccardi F, Onaemo VN, Jae SY, Kauhanen J, Ronkainen K, et al. Association between HOMA-IR, fasting insulin and fasting glucose with coronary heart disease mortality in nondiabetic men: a 20-year observational study. Acta Diabetol. 2015;52(1):183–6.
Boyko EJ, Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, Chitson P, Tuomilehto J, Alberti KGMM. A prospective study of glycemia, body size, insulin resistance and the risk of hypertension in Mauritius. J Hypertens. 2008;26(9):1742–9.
Robins SJ, Lyass A, Zachariah JP, Massaro JM, Vasan RS. Insulin resistance and the relationship of a dyslipidemia to coronary heart disease: the framingham heart study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31(5):1208–14.
Gast KB, Tjeerdema N, Stijnen T, Smit JWA, Dekkers OM. Insulin resistance and risk of incident cardiovascular events in adults without diabetes: meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(12): e52036.
Tohidi M, Baghbani-Oskouei A, Ahanchi NS, Azizi F, Hadaegh F. Fasting plasma glucose is a stronger predictor of diabetes than triglyceride-glucose index, triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Acta Diabetol. 2018;55(10):1067–74.
Han SJ, Boyko EJ, Kim SK, Fujimoto WY, Kahn SE, Leonetti DL. Association of thigh muscle mass with insulin resistance and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese Americans. Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(6):488–95.
Wargny M, Smati S, Pichelin M, Bigot-Corbel E, Authier C, Dierry V, et al. Fatty liver index is a strong predictor of changes in glycemic status in people with prediabetes: the IT-DIAB study. PLoS ONE. 2019;14(8):e0221524.
Arellano-Campos O, Gómez-Velasco DV, Bello-Chavolla OY, Cruz-Bautista I, Melgarejo-Hernandez MA, Muñoz-Hernandez L, et al. Development and validation of a predictive model for incident type 2 diabetes in middle-aged Mexican adults: the metabolic syndrome cohort. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019;19(1):41.
Cederholm J, Zethelius B. SPISE and other fasting indexes of insulin resistance: risks of coronary heart disease or type 2 diabetes. Comparative cross-sectional and longitudinal aspects. Ups J Med Sci. 2019;124(4):265–72.
Lee S, Lacy ME, Jankowich M, Correa A, Wu WC. Association between obesity phenotypes of insulin resistance and risk of type 2 diabetes in African Americans: the Jackson Heart Study. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2019;19:1002210.
Maliszewska K, Adamska-Patruno E, Goscik J, Lipinska D, Citko A, Krahel A, et al. The role of muscle decline in type 2 diabetes development: a 5-year prospective observational cohort study. Nutrients. 2019;11(4):834.
Lee SH, Kwon HS, Park YM, Ha HS, Jeong SH, Yang HK, et al. Predicting the development of diabetes using the product of triglycerides and glucose: the Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort (CMC) study. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(2):e90430.
Morimoto A, Tatsumi Y, Deura K, Mizuno S, Ohno Y, Miyamatsu N, et al. Impact of impaired insulin secretion and insulin resistance on the incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Japanese population: the Saku study. Diabetologia. 2013;56(8):1671–9.
Ruijgrok C, Dekker JM, Beulens JW, Brouwer IA, Coupé VMH, Heymans MW, et al. Size and shape of the associations of glucose, HbA1c, insulin and HOMA-IR with incident type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Study. Diabetologia. 2018;61(1):93–100.
Ghasemi A, Tohidi M, Derakhshan A, Hasheminia M, Azizi F, Hadaegh F. Cut-off points of homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, beta-cell function, and fasting serum insulin to identify future type 2 diabetes: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Acta Diabetol. 2015;52(5):905–15.
Derakhshan A, Tohidi M, Arshi B, Khalili D, Azizi F, Hadaegh F. Relationship of hyperinsulinaemia, insulin resistance and B-cell dysfunction with incident diabetes and pre-diabetes: the Theran Lipid and Glucose Study. Diabet Med. 2015;32(1):24–32.
Zethelius B, Cederholm J. Comparison between indexes of insulin resistance for risk prediction of cardiovascular diseases or development of diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;110(2):183–92.
Bonora E, Kiechl S, Willeit J, Oberhollenzer F, Egger G, Meigs JB, et al. Population-based incidence rates and risk factors for type 2 diabetes in white individuals: the Bruneck study. Diabetes. 2004;53(7):1782–9.
Flores-Guerrero JL, Connelly MA, Shalaurova I, Gruppen EG, Kieneker LM, Dullaart RPF, et al. Lipoprotein insulin resistance index, a high-throughput measure of insulin resistance, is associated with incident type II diabetes mellitus in the Prevention of Renal and Vascular End-Stage Disease study. J Clin Lipidol. 2019;13(1):129–37.
Venkataraman K, Khoo CM, Leow MK, Khoo EY, Issac AV, Zagorodnov, et al. New measure of insulin sensitivity predicts cardiovascular disease better than HOMA estimated insulin resistance. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74410.
Kim CH, Kim HK, Kim EH, Bae SJ, Park JY. Relative contributions of insulin resistance and B-cell dysfunction to the development of Type 2 diabetes in Koreans. Diabet Med. 2013;30(9):1075–9.
Wang T, Lu J, Shi L, Chen G, Xu M, Xu Y, et al. Cardiometabolic Disease and Cancer Cohort Study Group. Association of insulin resistance and B-cell dysfunction with incident diabetes among adults in Chine: a nationwide, population-based, prospective cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8(2):115–124.
Lee CH, Shih AZ, Woo YC, Fong CH, Leung OY, Janus E, et al. Optimal cut-offs of homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) to identify dysglycemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 15-year prospective study in Chinese. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(9):e0163424.
Sorrentino P, Terracciano L, D’Angelo S, Ferbo U, Bracigliano A, Vecchione R. Predicting fibrosis worsening in obese patients with NASH through parenchymal fibronectin, HOMA-IR, and hypertension. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105(2):336–44.
Arshi B, Tohidi M, Derakhshan A, Asgari S, Azizi F, Hadaegh F. Sex-specific relations between fasting insulin, insulin resitance and incident hypertension: 89 years follow-up in a Middel-Eastern population. J Hum Hypertens. 2015;29(4):260–7.
Bruno G, Fornengo P, Segre O, Novelli G, Panero F, Perotto M, et al. What is the clinical usefulness of the metabolic syndrome? The Casale Monferrato study. J Hypertens. 2009;27(12):2403–8.
Kouvari M, Panagiotakos DB, Yannakoulia M, Gerogousopoulou E, Critselis E, Chrysohoou C, et al. Transition from metabolically benign to metabolically unhealthy obesity and 10-year cardiovascular disease incidence: the ATTICA cohort study. Metabolism. 2019;93:18–24.
Hellgren MI, Daka B, Jansson PA, Lindblad U, Larsson CA. Insulin resistance predicts early cardiovascular morbidity in men without diabetes mellitus, with effect modification by physical activity. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2015;22(7):940–9.
Wieberdink RG, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Breteler MM, Ikram MA. Insulin resistance and the risk of stroke and stroke subtypes in the nondiabetic elderly. Am J Epidemiol. 2012;176(8):699–707.
Rundek T, Gardener H, Xu Q, Goldberg RB, Wright CB, Boden-Albala B, et al. Insulin resistance and risk of ischemic stroke among nondiabetic individuals from the northern Manhattan study. Arch Neurol. 2010;67(10):1195–200.
Hedblad B, Nilsson P, Engström G, Berglund G, Janzon L. Insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects is associated with increased incidence of myocardial infarction and death. Diabet Med. 2002;19(6):470–5.
Ghoreishian H, Tohidi M, Derakhshan A, Hajsheikkholeslami F, Azizi F, Kazempour-Ardebili S, et al. Presence of hypertension modifies the impact of insulin resistance on incident cardiovascular disease in a Middle Eastern population: the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Diabet Med. 2015;32(10):1311–8.
Nakamura K, Sakurai M, Miura K, Morikawa Y, Ishizaki M, Yoshita K, et al. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance and the risk of cardiovascular events in middle-aged non-diabetic Japanese men. Diabetologia. 2010;53(9):1894–902.
Vulcan A, Manjer J, Ohlsson B. High blood glucose levels are associated with higher risk of colon cancer in men: a cohort study. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):842.
Hsu CN, Chang CH, Lin YS, Lin JW, Caffrey JL. Association for serum C-peptide concentrations with cancer mortality risk in pre-diabetes or undiagnosed mortality. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(2):e55625.
Perseghin G, Calori G, Lattuada G, Ragogna F, Dugnani E, Garancini MP, et al. Insulin resistance/hyperinsulinemia and cancer mortality: the Cremona study at the 15th year of follow-up. Acta Diabetol. 2012;49(6):421–8.
Kwanbujan K, Panprathip P, Phosat C, Chumpathat N, Wechjakwen N, Puduang S, et al. Association of retinol binding protein 4 and transthyretin with triglyceride levels and insulin resistance in rural thais with high type 2 diabetes risk. BMC Endocr Disord. 2018;18(1):26.
Tatsumi Y, Morimoto A, Asayama K, Sonoda N, Miyamatsu N, Ohno Y, et al. Fasting blood glucose predicts incidence of hypertension independent of HbA1c levels and insulin resistance in middle-aged Japanese: the Saku study. Am J Hypertens. 2019;32(12):1178–85.
Stamatelopoulos K, Apostolakis M, Augoulea A, Paschou SA, Armeni E, Panoulis K, et al. Predictors of incident hypertension in healthy non-diabetic postmenopausal women with normal renal function. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2019;35(12):1063–6.
Xun P, Liu K, Cao W, Sidney S, Williams OD, He K. Fasting insulin level is positively associated with incidence of hypertension among American young adults: a 20-year follow-up study. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(7):1532–7.
Castro LL, Brant L, Diniz MFHS, Lotufo P, Bensenor I, Griep, RH, et al. Insulin resistance independently predicts hypertension in individuals with lower education status—from the ELSA-BRASIL Cohort study. JACC. 2021;77(18).
Boyko EJ, Shaw JE, Zimmet PZ, Chitson P, Toumilehto J, Alberti KG. A prospective study of glycemia, body size, insulin resistance and the risk of hypertension in Mauritius. J Hypertens. 2008;26(9):1742–9.
Wang F, Han L, Hu D. Fasting insulin, insulin resistance and risk of hypertension in the general population: a meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem. 2017;464:57–63.
Zhang X, Li J, Zheng S, Luo Q, Zhou C, Wang C. Fasting insulin, insulin resistance, and risk of cardiovascular or all-cause mortality in non-diabetic adults: a meta-analysis. Biosci Rep. 2017;37(5).
Saboori S, Rad EY, Birjandi M, Mohiti S, Falahi E. Serum insulin level, HOMA-IR and prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13(1):110–5.
Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(6):1487–95.
Rodríguez-Gutiérrez R, Salcido-Montenegro A, González-González JG. Early clinical expressions of insulin resistance: the real enemy to look for. Diabetes Ther. 2018;9(1):435–8.
Singh B, Saxena A. Surrogate markers of insulin resistance: a review. World J Diabetes. 2010;1(2):36–47.
Pan K, Nelson RA, Wactawski-Wende J, Lee DJ, Manson JE, Aragaki AK, et al. Insulin resistance and cancer-specific and all-cause mortality in postmenopausal women: the women’s health initiative. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2020;112(2):170–8.
Zheng S, Xu H, Zhou H, Ren X, Han T, Chen Y, et al. Associations of lipid profiles with insulin resistance and β cell function in adults with normal glucose tolerance and different categories of impaired glucose regulation. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(2): e0172221.
Isokuortti E, Zhou Y, Peltonen M, Bugianesi E, Clement K, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, et al. Use of HOMA-IR to diagnose non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based and inter-laboratory study. Diabetologia. 2017;60(10):1873–82.
Ormazabal V, Nair S, Elfeky O, Aguayo C, Salomon C, Zuñiga FA. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):122.
Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, Paik JM, Srishord M, Fukui N, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2019;71(4):793–801.
Bjornstad P, Eckel RH. Pathogenesis of lipid disorders in insulin resistance: a brief review. Curr Diab Rep. 2018;18(12):127.
Gaggini M, Morelli M, Buzzigoli E, DeFronzo RA, Bugianesi E, Gastaldelli A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its connection with insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Nutrients. 2013;5(5):1544–60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: [José G González-González and René Rodríguez-Gutiérrez] ; methodology [René Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, Alejandro D González-Colmenero and Miguel Zambrano-Lucio]; formal analysis and investigation: [Miguel Zambrano-Lucio, Patricia L Castillo-Morales and Mariano Garcia-Campa]; writing-original draft preparation: [Jorge R Violante-Cumpa, Miguel Zambrano-Lucio and Erick Burciaga-Jimenez]; writing-review and editing: [Erick Burciaga-Jimenez, Jorge R Violante-Cumpa, Patricia L Castillo-Morales and Ricardo César Solis]; funding acquisition: [NA]; resources: [NA]; supervision: [José G González-González and René Rodríguez-Gutiérrez]
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or no involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
González-González, J.G., Violante-Cumpa, J.R., Zambrano-Lucio, M. et al. HOMA-IR as a predictor of Health Outcomes in Patients with Metabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 29, 547–564 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-022-00542-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-022-00542-5