Abstract
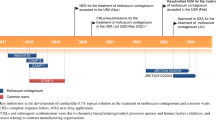
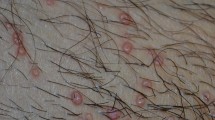
Berdazimer topical gel, 10.3% (ZELSUVMI™) is a nitric oxide (NO) releasing topical gel developed by Novan Inc. (a Ligand Pharmaceuticals company) for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum (MC). Novan has used their proprietary NO-based technology platform (NITRICIL™), which stores gaseous NO species on large polymers, in the development of berdazimer topical gel, 10.3%. In January 2024, berdazimer topical gel, 10.3% was approved for the topical treatment of MC in adult and paediatric patients 1 year of age and older in the USA. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of berdazimer topical gel, 10.3% leading to this first approval for the treatment of MC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eichenfield L, Hebert A, Mancini A, et al. Therapeutic approaches and special considerations for treating molluscum contagiosum. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20(11):1185–90.
Lacarrubba F, Micali G, Trecarichi AC, et al. New developing treatments for molluscum contagiosum. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022;12(12):2669–78.
Olsen JR, Gallacher J, Finlay AY, et al. Time to resolution and effect on quality of life of molluscum contagiosum in children in the UK: a prospective community cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15(2):190–5.
Oza VS. Molluscum contagiosum therapeutics—new options may be around the corner. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158(8):863–4.
US Food & Drug Administration. FDA approves first treatment for molluscum contagiosum [media release]. 24 Jul 2023. https://www.fda.gov/.
Sugarman JL, Hebert A, Browning JC, et al. Berdazimer gel for molluscum contagiosum: an integrated analysis of 3 randomized controlled trials. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023;00(00):1–10.
Maeda-Chubachi T, Hebert D, Messersmith E, Siegfried EC. SB206, a nitric oxide-releasing topical medication, induces the beginning of the end sign and molluscum clearance. JID Innov. 2021;1(3):1–8.
Del Rosso JQ, Kircik J. Spotlight on the use of nitric oxide in dermatology: What is it? What does it do? Can it become an important addition to the therapeutic armamentarium for skin disease? J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16(1 Suppl):s4–10.
Banerjee NS, Moore DW, Wang HK, et al. NVN1000, a novel nitric oxide-releasing compound, inhibits HPV-18 virus production by interfering with E6 and E7 oncoprotein functions. Antiviral Res. 2019;170(00):1–9.
Cartwright M, Enloe C, Stripling S, Maeda-Chubachi T. Pharmacokinetic profile, safety, and tolerability of topical berdazimer gel, 10.3% in patients with molluscum contagiosum. J Drugs Dermatol. 2022;21(10):1104–10.
Novan Inc. Our Science: NITRICILTM. 2024. https://novan.com/our-science/. Accessed 31 Jan 2024.
LNHC Inc. ZELSUVMI™ (berdazimer topical gel, 10.3%): US prescribing information. 2024. https://zelsuvmi.com/. Accessed Jan 9, 2024
Sato Pharmaceutical Co Ltd. Open-label study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of SB206 in Japanese patients with molluscum contagiosum. 2020. https://jrct.niph.go.jp/latest-detail/jRCT2031230123. Accessed 30 Jan 2024.
Ligand Pharmaceuticals Inc. Ligand acquires assets of Novan, Inc. for $12.2 million [media release]. 27 Sep 2023. https://investor.ligand.com/.
Ligand Pharmaceuticals Inc. Ligand acquires milestone and royalty rights to SB206 from Novan, Inc [media release]. 6 May 2019. https://investor.ligand.com/.
Novan Inc. Novan expands nitric oxide dermatology business partnership with Sato in Japan [media release]. 8 Oct 2018. https://www.novan.com/.
Browning JC, Enloe C, Cartwright M, et al. Efficacy and safety of topical nitric oxide-releasing berdazimer gel in patients with molluscum contagiosum: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2022;158(8):871–8.
Ward BM, Riccio DA, Cartwright M, Maeda-Chubachi T. The antiviral effect of berdazimer sodium on molluscum contagiosum virus using a novel in vitro methodology. Viruses. 2023;15(12):1–11.
Stripling S, Hebert A, Enloe C, et al. Clinical development program of novel topical nitric oxide releasing medication berdazimer gel 10.3% for the once-daily treatment of molluscum contagiosum [abstract no. and poster]. In: SCALE 2022. 2022.
Novan Inc. A phase 3 efficacy & safety of SB206 & vehicle gel for the treatment of MC (B-SIMPLE2). 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/. Accessed 1 Feb 2024.
Novan Inc. A phase 3 randomized parallel group study comparing the efficacy & safety of SB206 & vehicle gel in the treatment of MC (B-SIMPLE1). 2022. https://clinicaltrials.gov/. Accessed 1 Feb 2024.
Hebert AA, Siegfried EC, Durham T, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of an investigational nitric oxide-releasing topical gel in patients with molluscum contagiosum: a randomized clinical trial. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020;82(4):887–94.
Ligand Pharmaceuticals Inc. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approves ZELSUVMI™ as a first-in-class medication for the treatment of molluscum contagiosum [media release]. 5 Jan 2024. https://investor.ligand.com/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The preparation of this review was not supported by any external funding.
Authorship and Conflict of interest
During the peer review process the manufacturer of the agent under review was offered an opportunity to comment on the article. Changes resulting from any comments received were made by the authors on the basis of scientific completeness and accuracy. Susan J. Keam is a contracted employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature, and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to this article and are responsible for its content.
Ethics approval, Consent to participate, Consent to publish, Availability of data and material, Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
This profile has been extracted and modified from the AdisInsight database. AdisInsight tracks drug development worldwide through the entire development process, from discovery, through pre-clinical and clinical studies to market launch and beyond.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Keam, S.J. Berdazimer Topical Gel, 10.3%: First Approval. Drugs 84, 363–368 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-024-02012-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-024-02012-9