Abstract
Background and aims
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic condition associated with various microvascular complications, including neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy. Recent studies have suggested a potential association between serum omentin levels and the risk of developing microvascular complications in patients with T2DM. However, the existing evidence remains inconclusive. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to examine the association between serum omentin levels and microvascular complications in T2DM patients.
Methods
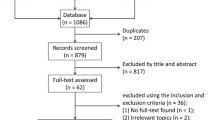
A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases to retrieve relevant articles published up to May 2023. Observational studies investigating omentin levels association with microvascular complications in T2DM patients were included. Data was extracted and hence analyzed.
Results
A total of seven cross-sectional articles met the inclusion criteria, with a total population of 1587 participants. The meta-analysis revealed a significant association between serum omentin levels and microvascular complications in patients with T2DM. Serum omentin levels were lower in patients with microvascular complications than in those without complications (Mean difference, 95% confidence interval: -1.31 [-2.50, -0.13], I2 = 99.62%).
Conclusion
This systematic review and meta-analysis provides evidence supporting an association between serum omentin levels and microvascular complications in patients with T2DM. The findings suggest that Omentin may be lower in T2DM patients with microvascular complications. Further research is warranted to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and explore the clinical implications of these findings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sukla P, Shrivastava SR, Shrivastava PS, Rao NL. Assessment of the cardiac autonomic neuropathy among the known diabetics and age-matched controls using noninvasive cardiovascular reflex tests in a south-indian population: a case-control study. Avicenna J Med. 2016;6(3):81–5.
Franceschi R, Mozzillo E, Di Candia F, Rosanio FM, Leonardi L, Liguori A, et al. A systematic review of the prevalence, risk factors and screening tools for autonomic and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in children, adolescents and young adults with type 1 Diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2022;59(3):293–308.
da Rocha RB, Silva CS, Cardoso VS. Self-care in adults with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a systematic review. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2020;16(6):598–607.
Mansoori A, Sahranavard T, Hosseini ZS, Soflaei SS, Emrani N, Nazar E, et al. Prediction of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus using hematological factors based on machine learning approaches: a cohort study analysis. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):663.
Nanayakkara N, Curtis AJ, Heritier S, Gadowski AM, Pavkov ME, Kenealy T, et al. Impact of age at type 2 Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis on mortality and vascular Complications: systematic review and meta-analyses. Diabetologia. 2021;64(2):275–87.
Freeman R. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Handb Clin Neurol. 2014;126:63–79.
Braffett BH, Gubitosi-Klug RA, Albers JW, Feldman EL, Martin CL, White NH, et al. Risk factors for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) study. Diabetes. 2020;69(5):1000–10.
Tandon R, Bajpai HS, Agrawal JK. Non-coronary cardiac complications in diabetes mellitus. J Assoc Physicians India. 1985;33(11):747.
Faselis C, Katsimardou A, Imprialos K, Deligkaris P, Kallistratos M, Dimitriadis K. Microvascular Complications of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(2):117–24.
Hejazi K, Mohammad Rahimi GR, Rosenkranz SK. Effects of Exercise training on inflammatory and cardiometabolic risk biomarkers in patients with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of Randomized controlled trials. Biol Res Nurs. 2023;25(2):250–66.
She N, Liu N, Ren X, Liu H. Association between Omentin and obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Clin Respir J. 2023;17(3):139–47.
Watanabe T, Watanabe-Kominato K, Takahashi Y, Kojima M, Watanabe R. Adipose tissue-derived Omentin-1 function and regulation. Compr Physiol. 2017;7(3):765–81.
Brunetti L, Leone S, Orlando G, Ferrante C, Recinella L, Chiavaroli A, et al. Hypotensive effects of omentin-1 related to increased adiponectin and decreased interleukin-6 in intra-thoracic pericardial adipose tissue. Pharmacol Rep. 2014;66(6):991–5.
de Souza Batista CM, Yang RZ, Lee MJ, Glynn NM, Yu DZ, Pray J, et al. Omentin plasma levels and gene expression are decreased in obesity. Diabetes. 2007;56(6):1655–61.
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Catalán V, Ortega F, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Ricart W, Frühbeck G, et al. Circulating omentin concentration increases after weight loss. Nutr Metabolism. 2010;7: 27.
Shibata R, Ouchi N, Takahashi R, Terakura Y, Ohashi K, Ikeda N, et al. Omentin as a novel biomarker of metabolic risk factors. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2012;4(1): 37.
Jung CH, Jung SH, Kim BY, Kim CH, Kang SK, Mok JO. Association of serum omentin levels with cardiac autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a hospital-based study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015;14:140.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557–60.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp Clin Trials. 2015;45:139–45.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
Pan X, Wang Z, Wu X, Wen SW, Liu A. Salivary cortisol in post-traumatic stress disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychiatry. 2018;18:1–10.
Mustafa HI, Zbaar SA, Salman MS. Study the role serum Omentin-1 in occurrence and development of Diabetic Retinopathy. Prof(Dr. RK Sharma. 2020;20(4):41915.
Senthilkumar GP, Anithalekshmi MS, Yasir M, Parameswaran S, Packirisamy RM, Bobby Z. Role of omentin 1 and IL-6 in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients with diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018;12(1):23–6.
Herder C, Bongaerts BWC, Ouwens DM, Rathmann W, Heier M, Carstensen-Kirberg M, et al. Low serum omentin levels in the elderly population with type 2 Diabetes and polyneuropathy. Diabet Med. 2015;32(11):1479–83.
Wan W, Li Q, Zhang F, Zheng G, Lv Y, Wan G, et al. Serum and vitreous concentrations of Omentin-1 in Diabetic Retinopathy. Dis Markers. 2015;2015:754312.
Devi RV, Subramaniam V, Adole PS, Senthilkumar GP, Mehalingam V. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and its association with serum omentin and leptin. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020;9(6):2926–30.
Eimal Latif AH, Anwar S, Gautham KS, Kadurei F, Ojo RO, Hafizyar F et al. Association of plasma omentin-1 levels with Diabetes and its Complications. Cureus. 2021;13(9):e18203.
Zorlu M, Kiskac M, Güler EM, Gültepe I, Yavuz E, Çelik K, et al. Serum obestatin and omentin levels in patients with diabetic Nephropathy. Niger J Clin Pract. 2017;20(2):182–7.
Abdelraouf Korany M, Sonbol A, Mohamed Elgouhary S. Omentin-1 and diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Alexandria J Med. 2018;54(4):323–6.
Omae T, Nagaoka T, Yoshida A. Effect of circulating omentin-1 on the retinal circulation in patients with type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(12):5086–92.
Scanlon PH, Sallam A, Van Wijngaarden P. A practical manual of diabetic retinopathy management. John Wiley & Sons; 2017.
Robberecht H, Hermans N. Biomarkers of metabolic syndrome: biochemical background and clinical significance. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2016;14(2):47–93.
Al-Karawi IN, Al-Fahdawi SSM. Assessment of Omentin-1 as a predictor and Renoprotective for type 2 Diabetic Nephropathy. Iraqi J Community Med. 2017;30(1).
Sun Y-M, Su Y, Li J, Wang L-F. Recent advances in understanding the biochemical and molecular mechanism of diabetic Nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;433(4):359–61.
Abid O, Sun Q, Sugimoto K, Mercan D, Vincent J-L. Predictive value of microalbuminuria in medical ICU patients: results of a pilot study. Chest. 2001;120(6):1984–8.
Kataoka Y, Shibata R, Ohashi K, Kambara T, Enomoto T, Uemura Y, et al. Omentin prevents myocardial ischemic injury through AMP-activated protein kinase-and akt-dependent mechanisms. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(24):2722–33.
Akiyama Y, Oshima K, Kuhara T, Shin K, Abe F, Iwatsuki K, et al. A lactoferrin-receptor, intelectin 1, affects uptake, sub-cellular localization and release of immunochemically detectable lactoferrin by intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. J Biochem. 2013;154(5):437–48.
Moreno-Navarrete J, Ortega F, Bassols J, Ricart W, Fernández-Real J. Decreased circulating lactoferrin in insulin resistance and altered glucose tolerance as a possible marker of neutrophil dysfunction in type 2 Diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metabolism. 2009;94(10):4036–44.
Yamawaki H, Kuramoto J, Kameshima S, Usui T, Okada M, Hara Y. Omentin, a novel adipocytokine inhibits TNF-induced vascular inflammation in human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;408(2):339–43.
Kellogg AP, Wiggin TD, Larkin DD, Hayes JM, Stevens MJ, Pop-Busui R. Protective effects of cyclooxygenase-2 gene inactivation against peripheral nerve dysfunction and intraepidermal nerve fiber loss in experimental Diabetes. Diabetes. 2007;56(12):2997–3005.
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Catalán V, Ortega F, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Ricart W, Frühbeck G, et al. Circulating omentin concentration increases after weight loss. Nutr Metabolism. 2010;7:1–6.
Gürsoy G, Kırnap N, Eşbah O, Acar Y, Demirbaş B, Akçayöz S, et al. The relationship between plasma omentin-1 levels and insulin resistance in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetıc women. Clin Rev Opin. 2010;2(4):49–54.
Forbes JM, Cooper ME. Mechanisms of diabetic Complications. Physiol Rev. 2013;93(1):137–88.
Kazama K, Usui T, Okada M, Hara Y, Yamawaki H. Omentin plays an anti-inflammatory role through inhibition of TNF-α-induced superoxide production in vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;686(1–3):116–23.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the researchers whose work was included in this study.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 643 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kazemzadeh, K., Bayani, M., Khademi, R. et al. Association of serum omentin levels with microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Diabetes Metab Disord (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-023-01359-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-023-01359-2