Abstract
Background
The most effective and common treatment for end-stage renal disease is kidney transplantation.
The personalized approach to kidney transplantation, which utilizes precision medicine principles, determines distinctive genomics characteristics of candidates/recipients that must be taken into account. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA4) may be a suitable candidate gene for studying allograft rejection. The aim of this study was to understand whether we can consider two common variants of the CTLA4 gene as a risk factor of transplant rejection in a group of Iranian population.
Methods
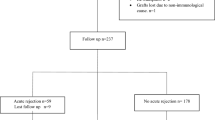
Totally, 169 kidney transplant recipients, including acute rejections (N=39) and non-rejection (N=130) groups who underwent transplantation were included in this study. The genotyping of rs5742909 (−318C/T) and rs231775 (+49A/G) variants of the CTLA4 gene were performed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) technique.
Results
The AG genotype frequency of rs231775 variant was the same in both patients with and without a history of rejection while, none of those groups had homozygote genotype. In rs5742909, both CT and TT frequencies of patients with rejected transplant were lower than patients with a normal outcome.
Conclusions
The results of the presented study suggest that rs231775 and rs5742909 of CTLA4 genetic variants are not linked to acute rejection who underwent kidney transplantation. So, these variants cannot be considered as risk factors of acute allograft rejection in a group of Iranian renal transplantation recipients. However, the transplantation precision medicine may be an important area for the improvement of patients outcome as the precision medicine has already entered clinical practice in kidney transplantation.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
This project’s data will be open to the public.
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
allograft rejection
- CTLA4:
-
cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated protein 4
- SNP:
-
single nucleotide polymorphism
- PCR-RFLP:
-
polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism
- SD:
-
standard deviation
- BUN:
-
blood urea nitrogen
References
Krichen H, Sfar I, Kacem HH, Bardi R, Jendoubi-Ayed S, Makhlouf M, et al., editors. repeat in the 3′ untranslated region of the CTLA-4 gene and susceptibility to acute allograft rejection in Tunisian renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010;42:4314–7.
Alegre M-L, Frauwirth KA, Thompson CB. T-cell regulation by CD28 and CTLA-4. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1(3):220.
Marson A, Housley WJ, Hafler DA. Genetic basis of autoimmunity. J Clin Investig. 2015;125(6):2234–41.
Orrù V, Steri M, Sole G, Sidore C, Virdis F, Dei M, et al. Genetic variants regulating immune cell levels in health and disease. Cell. 2013;155(1):242–56.
Van Gelder T, Van Schaik RH, Hesselink DA. Pharmacogenetics and immunosuppressive drugs in solid organ transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10(12):725–31.
Willis JC, Lord GM. Immune biomarkers: the promises and pitfalls of personalized medicine. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(5):323–9.
Gautreaux MD, Freedman BI. Genotypic variation and outcomes in kidney transplantation: donor and recipient effects. Kidney Int. 2013;84(3):431–3.
Ueda H, Howson JM, Esposito L, Heward J, Chamberlain G, Rainbow DB, et al. Association of the T-cell regulatory gene CTLA4 with susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Nature. 2003;423(6939):506.
Kristiansen O, Larsen Z, Pociot F. CTLA-4 in autoimmune diseases–a general susceptibility gene to autoimmunity? Genes Immun. 2000;1(3):170.
Kalantari T, Mostafavi H, Pezeshki A, Farjadian S, Doroudchi M, Yeganeh F, et al. Exon-1 polymorphism of ctla-4 gene in Iranian patients with Graves' disease. Autoimmunity. 2003;36(5):313–6.
Wiśniewski A, Kusztal M, Magott-Procelewska M, Klinger M, Jasek M, Łuszczek W, et al., editors. Possible association of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 gene promoter single nucleotide polymorphism with acute rejection of allogeneic kidney transplant. Transplant Proc. 2006;38:56–8.
Howard TD, Postma DS, Hawkins GA, Koppelman GH, Zheng SL, Wysong AK, et al. Fine mapping of an IgE-controlling gene on chromosome 2q: analysis of CTLA4 and CD28. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;110(5):743–51.
Domański1AB L, Bobrek-Lesiakowska1B K, Kłoda1E K, Pawlik2AD A, Safranow3C K, Kurzawski2D M, et al. The impact of rs231775 (+ 49AG) CTLA4 gene polymorphism on transplanted kidney function. Ann Transplant. 2012;17(3):29–35.
Gao J-w, Guo Y-f, Fan Y, J-x Q, Bao E-d, Liu Y, et al. Polymorphisms in cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated antigen-4 influence the rate of acute rejection after renal transplantation in 167 Chinese recipients. Transpl Immunol. 2012;26(4):207–11.
Bouqbis L, Izaabel H, Akhayat O, Perez-Lezaun A, Calafell F, Bertranpetit J, et al. Association of the CTLA4 promoter region (− 1661G allele) with type 1 diabetes in the south Moroccan population. Genes Immun. 2003;4(2):132.
Miller S, Dykes D, Polesky H. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16(3):1215.
Haimila K, Turpeinen H, Alakulppi NS, Kyllönen LE, Salmela KT, Partanen J. Association of genetic variation in inducible costimulator gene with outcome of kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2009;87(3):393–6.
Pd R, Pravica V, Hop W, Boor P, Metselaar HJ, Hutchinson IV, et al. Recipient ctla-4+ 49 G/G genotype is associated with reduced incidence of acute rejection after liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2003;3(12):1587–94.
Gorgi Y, Sfar I, Abdallah TB, Abderrahim E, Ayed SJ, Aouadi H, et al., editors. Ctla-4 exon 1 (+ 49) and promoter (− 318) gene polymorphisms in kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2006;38:2303–5.
Kusztal M, Kościelska-Kasprzak K, Drulis-Fajdasz D, Magott-Procelewska M, Patrzałek D, Janczak D, et al. The influence of CTLA-4 gene polymorphism on long-term kidney allograft function in Caucasian recipients. Transplant Immunol. 2010;23(3):121–4.
Kim H-J, Jeong K-H, Lee S-H, Moon J-Y, Lee T-w, Kang SW, et al. Polymorphisms of the CTLA4 gene and kidney transplant rejection in Korean patients. Transplant Immunol. 2010;24(1):40–4.
Gendzekhadze K, Rivas-Vetencourt P, Montano RF. Risk of adverse post-transplant events after kidney allograft transplantation as predicted by CTLA-4+ 49 and TNF-α− 308 single nucleotide polymorphisms: a preliminary study. Transplant Immunol. 2006;16(3–4):194–9.
Dmitrienko S, Hoar DI, Balshaw R, Keown PA. Immune response gene polymorphisms in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2005;80(12):1773–82.
Marder BA, Schröppel B, Lin M, Schiano T, Parekh R, Tomer Y, et al. The impact of costimulatory molecule gene polymorphisms on clinical outcomes in liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2003;3(4):424–31.
Kouki T, Sawai Y, Gardine CA, Fisfalen M-E, Alegre M-L, DeGroot LJ. CTLA-4 gene polymorphism at position 49 in exon 1 reduces the inhibitory function of CTLA-4 and contributes to the pathogenesis of graves’ disease. J Immunol. 2000;165(11):6606–11.
Krichen H, Sfar I, Jendoubi-Ayed S, Makhlouf M, Rhomdhane TB, Bardi R, et al. Editors. Genetic polymorphisms of immunoregulatory proteins in acute renal allograft rejection. Transplant Proc. 2006;38(7):2303–5.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge all subjects that generously has agreed to participate in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MH managed the project and provided guidance to the research; AT and NS drafted the manuscript and performed lab genotyping; MA performed the statistical analysis; MS sample collection; MN provided clinical guidance to the research. All authors contributed to and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing of interest
There are no conflicts of interest declared by the authors.
Consent for publication
All patients signed written consent forms and the study was approved by the ethical committee.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taleb, A., Afshari, M., Samzadeh, M. et al. Influence of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 genetic variants on acute rejection in kidney transplant patients: precision medicine perspective. J Diabetes Metab Disord 21, 69–75 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00936-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-021-00936-7