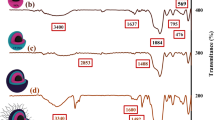
Abstract
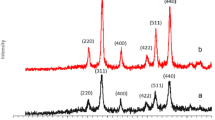
In this study, new statistical magnetic organo-silane star polymers were designed, synthesized based on different surface functionalization processes of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and conducting the polymerization reaction between phenylenediamine derivatives and dichlorophenylsilane on their functionalized surfaces. Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX), field-emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) and transmittance electron microscope (TEM) images, X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern, thermogravimetric (TG) analysis, vibrating-sample magnetometer (VSM), and dynamic light-scattering (DLS) and zeta potential measurements were employed to characterize the structural features. Based on the MTT assay and considering the highest concentration (1000 μg mL−1) of statistical magnetic organo-silane star polymer based on p-phenylenediamine as model derivative, the cell viability percentage of was reported 89.7%. In addition, the hyperthermia performance of this magnetic star polymer was evaluated by its exposure to an alternating magnetic field (AMF). Given the obtained results from different concentrations, the highest specific absorption rate (66.18 W g−1) was determined for 0.5 mg mL−1 of prepared sample. Therefore, it can be concluded that this new magnetic nanocomposite can be considered as an efficient agent for the next generation of therapeutic researches.
Graphic abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ren, J.M., et al.: Star polymers. Chem. Rev. 116, 6743–6836 (2016)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., Radinekiyan, F., Maleki, A., Bani, M.S., Azizi, M.: A new generation of star polymer: magnetic aromatic polyamides with unique microscopic flower morphology and in vitro hyperthermia of cancer therapy. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 319–336 (2020)
Aloorkar, N., Kulkarni, A., Patil, R., Ingale, D.: Star polymers: an overview. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 5, 1675–1684 (2012)
Wu, W., He, Q., Jiang, C.: Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 3, 397 (2008)
Ali, A., et al.: Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 9, 49 (2016)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., et al.: Synthesis of core-shell magnetic supramolecular nanocatalysts based on amino-functionalized calix [4] arenes for the synthesis of 4H-chromenes by ultrasonic waves. ChemistryOpen 9, 735–742 (2020)
Asgharnasl, S., Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., Radinekiyan, F., Maleki, A.: Preparation of a novel magnetic bionanocomposite based on factionalized chitosan by creatine and its application in the synthesis of polyhydroquinoline, 1, 4-dyhdropyridine and 1, 8-dioxo-decahydroacridine derivatives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 144, 29–46 (2020)
Hajizadeh, Z., Maleki, A., Rahimi, J., Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.J.S.: Halloysite nanotubes modified by Fe3O4 nanoparticles and applied as a natural and efficient nanocatalyst for the symmetricalhantzsch reaction. SILICON 12, 1247–1256 (2020)
Esmaeili, M.S., Varzi, Z., Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., Maleki, A., Ghafuri, H.: Design and development of natural and biocompatible raffinose-Cu2O magnetic nanoparticles as a heterogeneous nanocatalyst for the selective oxidation of alcohols. Mol. Catal. 492, 111037 (2020)
Huang, C.-C., et al.: New insight on optical and magnetic Fe3O4 nanoclusters promising for near infrared theranostic applications. Nanoscale 7, 12689–12697 (2015)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., Radinekiyan, F., Asgharnasl, S., Maleki, A., Bahreinizad, H.: A natural and eco-friendly magnetic nanobiocomposite based on activated chitosan for heavy metals adsorption and the in-vitro hyperthermia of cancer therapy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 12244–12259 (2020)
Mokhtarzadeh, A., et al.: Nanomaterial-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic virus. Trends. Anal. Chem. 97, 445–457 (2017)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., et al.: Dengue virus: a review on advances in detection and trends–from conventional methods to novel biosensors. Microchim. Acta 186, 329 (2019)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., et al.: Recent progress in optical and electrochemical biosensors for sensing of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin. Trends. Anal. Chem. 103, 184–197 (2018)
Mohammadinejad, A., et al.: Development of biosensors for detection of alpha-fetoprotein: as a major biomarker for Hepatocellular carcinoma. Trends. Anal. Chem. 130, 115961 (2020)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., Pashazadeh, P., Hejazi, M., de la Guardia, M., Mokhtarzadeh, A.: Recent advances in nanomaterial-mediated bio and immune sensors for detection of aflatoxin in food products. Trends. Anal. Chem. 87, 112–128 (2017)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., et al.: Recent advances on nanomaterial based electrochemical and optical aptasensors for detection of cancer biomarkers. Trends. Anal. Chem. 100, 103–115 (2018)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., et al.: Carbon based nanomaterials for tissue engineering of bone: building new bone on small black scaffolds: a review. J. Adv. Res. 18, 185–201 (2019)
Rao, W., Deng, Z.-S.: A review of hyperthermia combined with radiotherapy/chemotherapy on malignant tumors. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 38, 101–106 (2010)
Guibert, C., Dupuis, V., Peyre, V., Fresnais, J.: Hyperthermia of magnetic nanoparticles: experimental study of the role of aggregation. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 28148–28154 (2015)
Ahmad, A., et al.: Hyperbranched polymer-functionalized magnetic nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia and niclosamide bimodal therapy of colorectal cancer cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 6, 1102–1111 (2019)
Li, T.-J., et al.: In vivo anti-cancer efficacy of magnetite nanocrystal-based system using locoregional hyperthermia combined with 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy. Biomaterials 34, 7873–7883 (2013)
Zamora-Mora, V., et al.: Magnetic core–shell chitosan nanoparticles: rheological characterization and hyperthermia application. Carbohydr. Polym. 102, 691–698 (2014)
Fadhilah, H., Saepudin, E., Khalil, M. In: AIP conference proceedings 2020, vol. 1, p. 040003. AIP Publishing LLC
Shen, L., Li, B., Qiao, Y.: Fe3O4 nanoparticles in targeted drug/gene delivery systems. Materials 11, 324 (2018)
Boyer, C., Whittaker, M.R., Bulmus, V., Liu, J., Davis, T.P.: The design and utility of polymer-stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles for nanomedicine applications. NPG Asia Mater. 2, 23–30 (2010)
Arias, J.L., Reddy, L.H., Couvreur, P.: Fe3O4/chitosan nanocomposite for magnetic drug targeting to cancer. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 7622–7632 (2012)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., et al.: A novel biocompatible core-shell magnetic nanocomposite based on cross-linked chitosan hydrogels for in vitro hyperthermia of cancer therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 140, 407–414 (2019)
Furlan, D.M., et al.: Sisal cellulose and magnetite nanoparticles: formation and properties of magnetic hybrid films. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 2170–2179 (2019)
Diaz-Bleis, D., Vales-Pinzón, C., Freile-Pelegrín, Y., Alvarado-Gil, J.: Thermal characterization of magnetically aligned carbonyl iron/agar composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 99, 84–90 (2014)
Seenuvasan, M., et al.: Fabrication, characterization and application of pectin degrading Fe3O4–SiO2 nanobiocatalyst. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 33, 2273–2279 (2013)
Le, T.T.H., et al.: Optimizing the alginate coating layer of doxorubicin-loaded iron oxide nanoparticles for cancer hyperthermia and chemotherapy. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 13826–13842 (2018)
Li, T.-J., et al.: Handheld energy-efficient magneto-optical real-time quantitative PCR device for target DNA enrichment and quantification. NPG Asia Mater. 8, e277 (2016)
Adebayo, L.L., et al.: Facile preparation and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Fe3O4@ PVDF nanocomposite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 2513–2521 (2020)
Li, J., et al.: Three-dimensional graphene supported Fe3O4 coated by polypyrrole toward enhanced stability and microwave absorbing properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 762–772 (2020)
Bani, M.S., et al.: Casein-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for in vitro hyperthermia for cancer therapy. Spin 9, 1940003 (2019)
Marutani, E., et al.: Surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate on magnetite nanoparticles. Polymer 45, 2231–2235 (2004)
Hu, H., et al.: Preparation of amino-functionalized magnetite nanoclusters by ring-opening polymerization and application for targeted magnetic resonance imaging. J. Mater. Sci. 48, 7686–7695 (2013)
Rana, S., Jadhav, N.V., Barick, K., Pandey, B., Hassan, P.: Polyaniline shell cross-linked Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for heat activated killing of cancer cells. Dalton. Trans. 43, 12263–12271 (2014)
Ahmad, A., Khan, F., Mishra, R.K., Khan, R.: Precision cancer nanotherapy: evolving role of multifunctional nanoparticles for cancer active targeting. J. Med. Chem. 6, 10475–10496 (2019)
Gupta, A., et al.: Correction to “Nanocarrier composed of magnetite core coated with three polymeric shells mediates LCS-1 delivery for synthetic lethal therapy of BLM-defective colorectal cancer cells.” Biomacromol 20, 4623–4623 (2019)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., Bahrami, N., Radinekiyan, F., Maleki, A., Mahdavi, M.: Palladium-coated thiourea core-shell nanocomposite as a new, efficient, and magnetic responsive nanocatalyst for the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. Mater. Res. Express 8, 026102 (2021)
Stöber, W., Fink, A., Bohn, E.: Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 26, 62–69 (1968)
Ji, L., et al.: Facile synthesis of multiwall carbon nanotubes/iron oxides for removal of tetrabromobisphenol A and Pb (II). J. Mater. Chem. 22, 15853–15862 (2012)
Villa, S., Riani, P., Locardi, F., Canepa, F.: Functionalization of Fe3O4 NPs by silanization: use of amine (APTES) and thiol (MPTMS) silanes and their physical characterization. Materials 9, 826 (2016)
Safaiee, M., Zolfigol, M.A., Afsharnadery, F., Baghery, S.: Synthesis of a novel dendrimer core of oxo-vanadium phthalocyanine magnetic nano particles: as an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of 3, 4-dihydropyrano [c] chromenes derivatives under green condition. RSC Adv. 5, 102340–102349 (2015)
Farahi, M., Karami, B., Keshavarz, R., Khosravian, F.: Nano-Fe3O4@ SiO2-supported boron sulfonic acid as a novel magnetically heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of pyrano coumarins. RSC Adv. 7, 46644-46650 (2017)
Vieira, E.G., et al.: Synthesis and characterization of 3-[(thiourea)-propyl]-functionalized silica gel and its application in adsorption and catalysis. N. J. Chem. 37, 1933–1943 (2013)
Lu, X.-W., Wu, W., Chen, J.-F., Zhang, P.-Y., Zhao, Y.-B.: Preparation of polyaniline nanofibers by high gravity chemical oxidative polymerization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 50, 5589–5595 (2011)
Halim, M., Hudaya, C., Kim, A.-Y., Lee, J.K.: Phenyl-rich silicone oil as a precursor for SiOC anode materials for long-cycle and high-rate lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 2651–2656 (2016)
Launer, P.: Infrared analysis of organosilicon compounds: spectra-structure correlations. Inc. Burnt Hills, New York (1987)
Zhou, H., Zhou, Q., Zhou, Q., Ni, L., Chen, Q.: Highly heat resistant and thermo-oxidatively stable borosilane alkynyl hybrid polymers. RSC Adv. 5, 12161–12167 (2015)
Mouradzadegun, A., Ganjali, M.R., Mostafavi, M.A.: Design and synthesis of a magnetic hierarchical porous organic polymer: a new platform in heterogeneous phase-transfer catalysis. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 32, e4214 (2018)
Wei, S., et al.: Multifunctional composite core–shell nanoparticles. Nanoscale 3, 4474–4502 (2011)
Darwish, M.S., Nguyen, N.H., Ševců, A., Stibor, I.: Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles and their effect on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Nanomater. 2015, 416012-416022 (2015)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., Radinekiyan, F., Madanchi, H., Aliabadi, H.A.M., Maleki, A.: Graphene oxide/alginate/silk fibroin composite as a novel bionanostructure with improved blood compatibility, less toxicity and enhanced mechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 248, 116802 (2020)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., et al.: Chitosan hydrogel/silk fibroin/Mg (OH)2 nanobiocomposite as a novel scaffold with antimicrobial activity and improved mechanical properties. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–13 (2021)
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., et al.: Alginate hydrogel-polyvinyl alcohol/silk fibroin/magnesium hydroxide nanorods: a novel scaffold with biological and antibacterial activity and improved mechanical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 162, 1959–1971 (2020)
Kaushik, K., Kaushal, N., Kalla, N.R.: Conversion of apoptosis to necrosis and the corresponding alteration in the oxidative milieu of male germ cells of rat under acute heat stress: an experimental study. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 16, 577 (2018)
Hatamie, S., et al.: Graphene/cobalt nanocarrier for hyperthermia therapy and MRI diagnosis. Colloids Surf. B 146, 271–279 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the partial support from the Research Council of the Iran University of Science and Technology (IUST) and Young Scientists Festival (YSF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors whose names are listed in this article have no competing interests or other conflict of interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
40097_2021_401_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file1. Additional supporting information including the schematic synthesis processes of magnetic organo-silane star polymers, FE-SEM image of model statistical magnetic aromatic organo-silane star polymer and as well, the spectral FT-IR, EDX, FE-SEM and TG analyses of other magnetic derivatives can be observed in the online version of this article at the publisher’s web site. (PDF 1200 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R., Maleki, A. Design and synthesis of a new magnetic aromatic organo-silane star polymer with unique nanoplate morphology and hyperthermia application. J Nanostruct Chem 11, 751–767 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-021-00401-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-021-00401-0