Abstract
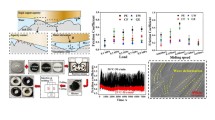
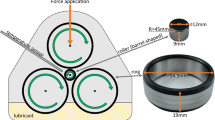
In present experimentation study, iron (Fe) matrix-based self-lubricating composite samples were prepared using powder metallurgy process. Tribological as well as mechanical properties of iron molybdenum-based composites with varied content of barium fluoride as solid lubricant were studied under different experimental conditions. The influence of applied normal load (NL) and sliding distance (SD) on friction and wear behaviour was studied. Dry sliding tribological tests were performed on reciprocating ball-on-disc tribometer. From the results, it was reported that hardness and compressive strength were higher for base composition compared to the composites samples. Introduction of barium fluoride increases the tribological properties of the composite. Coefficient of friction (COF) and wear volume (WV) were least for 8 wt% solid lubricant sample. Self-lubricating behaviour of the BaF2 reinforcement in the matrix material was attributed to enhancement in friction and wear properties of the composite.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.G. Kostornov, O.I. Fushchich, V.F. Gorban, T.M. Chevychelova, O.D. Kostenko, Effect of dry friction parameters on the tribosynthesis of secondary structures on composite antifriction iron-based material. Powder Metall. Metal Ceram. 51, 412–419 (2012)
J. Han, J. Jia, J. Lu, J. Wang, High temperature tribological characteristics of Fe–Mo-based self-lubricating composites. Tribol. Lett. (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-009-9423-9
R. Annamalai, A. Upadhyaya, D. Agrawal, An investigation on microwave sintering of Fe, Fe–Cu and Fe–Cu–C alloys. Bull. Mater. Sci. 36, 447–456 (2013)
S. Dhanasekaran, R. Gnanamoorthy, Microstructure, strength and tribological behavior of Fe–C–Cu–Ni sintered steels prepared with MoS2 addition. J. Mater. Sci. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0385-0
W.B. James, N. Chandrachud, K.S. Narasimhan, Hardenability response of Fe–Mo–Ni–C powder metallurgy alloys
W.F. Mohamad, A.A. Khan, F. Ahmad, A. Yassin, Phase analysis and microstructure study of sintered Ni-Cr composites containing MoS2, Ag and CaF2 additives as solid lubricants. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 14(2), 6548–6556 (2020)
L. Jinyinzi, L. Changsheng, T. Hua, H. Zhili, G. Zhicheng, Tribological properties of self-lubricating Fe–Ni based composites mixed with MoS2 and CaF2. Chin. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 7 (2013)
Y. Ye, J. Chen, H. Zhou, An investigation of friction and wear performances of bonded molybdenum disulfide solid film lubricants in fretting conditions. Wear (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2008.12.012
D.L. Deadmore, H.E. Sliney, Hardness of CaF2 and BaF2 solid lubricants at 25 to 670 °C. NASA Technical Memorandum (1987)
J.D.B. De Mello, C. Binder, G. Hammes, R. Binder, A.N. Klein, Tribological behaviour of sintered iron based self-lubricating composites. Friction 5, 285–307 (2017)
B. Parveez, M.F. Wani, Tribological behaviour of nano-zirconia reinforced iron-based self-lubricating composites for bearing applications. Tribol. Int. 159, 106969 (2021)
J. Han, J. Jia, J. Lu, J. Wang, High temperature tribological characteristics of Fe–Mo-based self-lubricating composites. Tribol. Lett. 34, 193–200 (2009)
G. Hammes, K.J. Mucelin, P. da Costa Gonçalves, C. Binder, R. Binder, R. Janssen, J.D.B. de Mello, Effect of hexagonal boron nitride and graphite on mechanical and scuffing resistance of self lubricating iron based composite. Wear 376, 1084–1090 (2017)
K.P. Furlan, P. da Costa-Gonçalves, D.R. Consoni, M.V.G. Dias, G.A. de Lima, J.D.B. de Mello, A.N. Klein, Metallurgical aspects of self-lubricating composites containing graphite and MoS2. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 26, 1135–1145 (2017)
J.L. Li, D.S. Xiong, Tribological properties of nickel-based self-lubricating composite at elevated temperature and counterface material selection. Wear 265, 533–539 (2008)
G. Hammes, R. Schroeder, C. Binder, A.N. Klein, J.D.B. de Mello, Effect of double pressing/double sintering on the sliding wear of self-lubricating sintered composites. Tribol. Int. 70, 119–127 (2014)
M.I.U. Haq, A. Raina, A. Anand, S.M. Sharma, R. Kumar, Elucidating the effect of MoS2 on the mechanical and tribological behavior of AA7075/Si3N4 composite. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 29, 7445–7455 (2020)
A. Gupta, S. Mohan, A. Anand, M.I.U. Haq, A. Raina, R. Kumar, M. Kamal, Tribological behaviour of Fe–C–Ni self-lubricating composites with WS2 solid lubricant. Mater. Res. Express 6, 126507 (2019)
P.D. Srivyas, M.S. Charoo, Friction and wear characterization of spark plasma sintered hybrid aluminum composite under different sliding conditions. J. Tribol. 142, 121701 (2020)
P.D. Srivyas, M.S. Charoo, Effect of load on the tribological behavior of self-lubricating hybrid aluminum composite under dry sliding conditions. Mater. Res. Express 6, 125702 (2019)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to acknowledge National Institute of Technology Srinagar for their wholehearted support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivyas, P.D., Charoo, M.S. Tribological Characterization of Iron-Based Self-Lubricating Composite under Dry Sliding Conditions. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-021-00265-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-021-00265-2