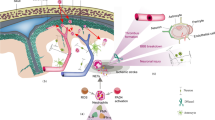
Abstract
Background and objective
A correlation between neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and ischemic stroke (IS) has been hypothesized, but the results of relevant studies remain controversial. The purpose was to determine whether NETs have an impact on ischemic stroke.
Methods
The studies on the correlation between NETs and IS were retrieved from CNKI, Wanfang Data, VIP, CBM, PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, and Cochrane databases by computer from the start of the database to December 2022. The study adhered to PRISMA guidelines. The PICOS model was used to create inclusion criteria. Two researchers screened the literature and extracted the relevant data. The quality of the included studies was evaluated using the NOS and the 11 items recommended by the AHRQ, and meta-analysis was completed using Stata 15.1 software.
Results
The researchers included 752 patients in 7 studies (4 case–control studies and 3 cross-sectional studies). The meta-analysis found NETs are positively associated with the severity of IS at the time of onset [r(95% CI) = 0.31(0.24, 0.38), P < 0.001]. NETs are positively associated with a worse prognosis of IS [r(95% CI) = 0.34(0.13, 0.53), P = 0.003].
Conclusion
The presence of NETs is positively related to the severity and prognosis of IS. Higher levels of NETs indicate a more severe disease and a poorer prognosis. Because the number and quality of included studies are limited, the above results must be supported by further high-quality studies.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier: CRD42022356619.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
References
O’Donnell MJ, Chin SL, Rangarajan S et al (2016) Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (Interstroke): a case-control study. Lancet 388(10046):761–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)30506-2
Wang L, Liu J, Yang Y, Peng B, Wang Y (2019) The Prevention and treatment of stroke still face huge challenges ——brief report on stroke prevention and treatment in China, 2018. Chinese Circulation J 34(02):105–119
Halverson TW, Wilton M, Poon KK, Petri B, Lewenza S (2015) DNA is an antimicrobial component of neutrophil extracellular traps. PLoS Pathog 11(1):e1004593. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1004593
Qin Q, Cao X (2022) The role of NETs and Cdc42 in neurological injury in ischemic stroke. Neural Injury Functional Reconst 17(03):145–47. https://doi.org/10.16780/j.cnki.sjssgncj.20210203
Borissoff JI, Joosen IA, Versteylen MO et al (2013) Elevated levels of circulating DNA and chromatin are independently associated with severe coronary atherosclerosis and a prothrombotic state. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(8):2032–40. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.113.301627
Ducroux C, Di Meglio L, Loyau S et al (2018) Thrombus neutrophil extracellular traps content impair tpa-induced thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 49(3):754–57. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.117.019896
Laridan E, Denorme F, Desender L et al (2017) Neutrophil extracellular traps in ischemic stroke thrombi. Ann Neurol 82(2):223–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24993
Novotny J, Oberdieck P, Titova A et al (2020) Thrombus NET content is associated with clinical outcome in stroke and myocardial infarction. Neurology 94(22):e2346–e60. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000009532
Yang J, Wu Z, Long Q et al (2020) Insights into immunothrombosis: the interplay among neutrophil extracellular trap, von Willebrand Factor, and ADAMTS13. Front Immunol 11:610696. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.610696
Locke M, Longstaff C (2021) Extracellular histones inhibit fibrinolysis through noncovalent and covalent interactions with fibrin. Thromb Haemost 121(4):464–76. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1718760
Zhou P, Li T, Jin J et al (2020) Interactions between neutrophil extracellular traps and activated platelets enhance procoagulant activity in acute stroke patients with ICA occlusion. EBioMedicine 53:102671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102671
Zhou Y, Tao W, Shen F, Du W, Xu Z, Liu Z (2021) The Emerging Role of neutrophil extracellular traps in arterial, venous and cancer-associated thrombosis. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:786387. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2021.786387
Kang L, Yu H, Yang X et al (2020) Neutrophil extracellular traps released by neutrophils impair revascularization and vascular remodeling after stroke. Nat Commun 11(1):2488. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16191-y
Jorch SK, Kubes P (2017) An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat Med 23(3):279–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4294
Allen C, Thornton P, Denes A et al (2012) Neutrophil cerebrovascular transmigration triggers rapid neurotoxicity through release of proteases associated with decondensed DNA. J Immunol 189(1):381–92. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1200409
Cai W, Liu S, Hu M et al (2020) Functional dynamics of neutrophils after Ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res 11(1):108–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12975-019-00694-y
Ge L, Zhou X, Ji WJ et al (2015) Neutrophil extracellular traps in ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced myocardial no-reflow: therapeutic potential of DNase-based reperfusion strategy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 308(5):H500-9. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00381.2014
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Ge F, Zhao L, Liu J, Zhou M, Guo Y, Zhang Q (2012) Correlation between social support and mental health of the aged based on pearson correlation Coeffi cient: a meta-analysis. Chin J Evid Based Med 12(11):1320–1329
Chen X, Wang L, Jiang M et al (2022) Leukocytes in cerebral thrombus respond to large-vessel occlusion in a time-dependent manner and the association of NETs With collateral flow. Frontiers Immunology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.834562
Denorme F, Portier I, Rustad JL et al (2022) Neutrophil extracellular traps regulate ischemic stroke brain injury. J clinical investigation. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI154225
Essig F, Kollikowski AM, Pham M et al (2020) Immunohistological analysis of neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps in human thrombemboli causing acute ischemic stroke. Int J Molecular Sci 21(19):1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197387
Vallés J, Lago A, Santos MT et al (2017) Neutrophil extracellular traps are increased in patients with acute ischemic stroke: Prognostic significance. Thrombosis Haemostasis 117(10):1919–29. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH17-02-0130
Wang H. Neutrophil extracellular traps in thrombus of patient with acute ischaemic stroke [Master]. Army Medical University, 2015.
Zhang S, Cao Y, Du J et al (2021) Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to tissue plasminogen activator resistance in acute ischemic stroke. FASEB J. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202100471RR
Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C et al (2004) Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 303(5663):1532–5. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1092385
Li C, Xing Y, Zhang Y, Hua Y, Hu J, Bai Y (2022) Neutrophil extracellular traps exacerbate ischemic brain damage. Molecular Neurobiology 59(1):643–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02635-z
Petrovic-Djergovic D, Goonewardena SN, Pinsky DJ (2016) Inflammatory Disequilibrium in Stroke. Circ Res 119(1):142–58. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.116.308022
Jickling GC, Liu D, Ander BP, Stamova B, Zhan X, Sharp FR (2015) Targeting neutrophils in ischemic stroke: translational insights from experimental studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35(6):888–901. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2015.45
Fuchs TA, Brill A, Duerschmied D et al (2010) Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(36):15880–5. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1005743107
Fuchs TA, Brill A, Wagner DD (2012) Neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) impact on deep vein thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32(8):1777–83. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.111.242859
Sambrano GR, Huang W, Faruqi T, Mahrus S, Craik C, Coughlin SR (2000) Cathepsin G activates protease-activated receptor-4 in human platelets. J Biol Chem 275(10):6819–23. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.10.6819
Massberg S, Grahl L, von Bruehl ML et al (2010) Reciprocal coupling of coagulation and innate immunity via neutrophil serine proteases. Nat Med 16(8):887–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2184
McDonald B, Urrutia R, Yipp BG, Jenne CN, Kubes P (2012) Intravascular neutrophil extracellular traps capture bacteria from the bloodstream during sepsis. Cell Host Microbe 12(3):324–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2012.06.011
Rha JH, Saver JL (2007) The impact of recanalization on ischemic stroke outcome: a meta-analysis. Stroke 38(3):967–73. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.Str.0000258112.14918.24
Zahuranec DB, Majersik JJ, Percentage of acute stroke patients eligible for endovascular treatment. Neurology 2012; 79 (13 Suppl 1): S22–5: https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31826957cf
Laridan E, Denorme F, Desender L et al (2017) Neutrophil extracellular traps in ischemic stroke thrombi. Annals Neurol 82(2):223–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24993
Genchi A, Semerano A, Gullotta GS et al (2021) Cerebral thrombi of cardioembolic etiology have an increased content of neutrophil extracellular traps. J Neurol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2021.117355
Funding
Project of Sichuan Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China (No. 2020LC0141); Project leader: Shuang-Chun Ai. (2) Project of Sichuan Province Science and Technology Support Program, China (No. 2023YF0337); Project leader: Shuang-Chun Ai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZW conceived, designed, and wrote the article; TZ searched and screened relevant literature, extracted information, and performed quality evaluation; ZW and TZ performed data processing and applied Stata software for meta-analysis; SA is responsible for the quality control and review of articles, and is responsible for the supervision and management.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, ZR., Zhou, TQ. & Ai, SC. Neutrophil extracellular traps correlate with severity and prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neurol Belg 124, 513–522 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02409-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02409-5