Abstract
Objective
The abnormal expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) and Aquaporin 4 (AQP4) closely associates with the traumatic brain injury (TBI) development.
Methods
Here, we investigated the relationship between miR-211-5p and MMP9/AQP4 axis in TBI patients and astrocyte cells. Demographics, clinical features, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples were collected from traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients (n = 96) and controls (n = 30) for pathological and gene expression analyses. Luciferase activity assay and gene expression analyses were performed to dissect the regulatory mechanism of miR-211-5p on MMP9/AQP4 in human astrocyte cells.
Results
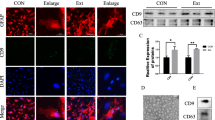
miR-211-5p mRNA was significantly decreased in the CSF of TBI patients, which positively correlated with the expression of both MMP9 and AQP4. miR-211-5p could target MMP9 directly in SVG P12 cells. Overexpression of miR-211-5p decreased the expression of MMP9, on the contrary, knockdown miR-211-5p through inhibitors increased the expression of both MMP9 and AQP4.
Conclusion
miR-211-5p inhibits the MMP9/AQP4 axis in human astrocyte cells, which represents a promising approach for the TBI treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khellaf A, Khan DZ, Helmy A (2019) Recent advances in traumatic brain injury. J Neurol 266:2878–2889
Hyder AA, Wunderlich CA, Puvanachandra P, Gururaj G, Kobusingye OC (2007) The impact of traumatic brain injuries: a global perspective. NeuroRehabilitation 22:341–353
Langlois JA, Rutland-Brown W, Wald MM (2006) The epidemiology and impact of traumatic brain injury: a brief overview. J Head Trauma Rehabil 21:375–378
Reith FCM, Lingsma HF, Gabbe BJ, Lecky FE, Roberts I, Maas AIR (2017) Differential effects of the Glasgow coma scale score and its components: an analysis of 54,069 patients with traumatic brain injury. Injury 48:1932–1943
Zafonte RD, Hammond FM, Mann NR, Wood DL, Black KL, Millis SR (1996) Relationship between Glasgow coma scale and functional outcome. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 75:364–369
Luaute J, Plantier D, Wiart L, Tell L (2016) Group S: care management of the agitation or aggressiveness crisis in patients with TBI. Systematic review of the literature and practice recommendations. Ann Phys Rehabil Med 59:58–67
Unterberg AW, Stover J, Kress B, Kiening KL (2004) Edema and brain trauma. Neuroscience 129:1021–1029
Rasmussen MK, Mestre H, Nedergaard M (2018) The glymphatic pathway in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol 17:1016–1024
Jarius S, Franciotta D, Paul F, Ruprecht K, Bergamaschi R, Rommer PS, Reuss R, Probst C, Kristoferitsch W, Wandinger KP, Wildemann B (2010) Cerebrospinal fluid antibodies to aquaporin-4 in neuromyelitis optica and related disorders: frequency, origin, and diagnostic relevance. J Neuroinflammation 7:52
Yao X, Derugin N, Manley GT, Verkman AS (2015) Reduced brain edema and infarct volume in aquaporin-4 deficient mice after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett 584:368–372
Zador Z, Stiver S, Wang V, Manley GT (2009) Role of aquaporin-4 in cerebral edema and stroke. Handb Exp Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79885-9_7
Liang F, Luo C, Xu G, Su F, He X, Long S, Ren H, Liu Y, Feng Y, Pei Z (2015) Deletion of aquaporin-4 is neuroprotective during the acute stage of micro traumatic brain injury in mice. Neurosci Lett 598:29–35
Lusardi TA, Sandau US, Sakhanenko NA, Baker SCB, Wiedrick JT, Lapidus JA, Raskind MA, Li G, Peskind ER, Galas DJ, Quinn JF, Saugstad JA (2021) Cerebrospinal fluid microRNA changes in cognitively normal veterans with a history of deployment-associated mild traumatic brain injury. Front Neurosci 15:720778
Higashida T, Kreipke CW, Rafols JA, Peng C, Schafer S, Schafer P, Ding JY, Dornbos D 3rd, Li X, Guthikonda M, Rossi NF, Ding Y (2011) The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, aquaporin-4, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in blood-brain barrier disruption and brain edema after traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 114:92–101
Milner R, Hung S, Wang X, Spatz M, del Zoppo GJ (2008) The rapid decrease in astrocyte-associated dystroglycan expression by focal cerebral ischemia is protease-dependent. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:812–823
Amorini AM, Dunbar JG, Marmarou A (2003) Modulation of aquaporin-4 water transport in a model of TBI. Acta Neurochir Suppl 86:261–263
Baranova O, Miranda LF, Pichiule P, Dragatsis I, Johnson RS, Chavez JC (2007) Neuron-specific inactivation of the hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha increases brain injury in a mouse model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 27:6320–6332
Leonardo CC, Pennypacker KR (2009) Neuroinflammation and MMPs: potential therapeutic targets in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. J Neuroinflammation 6:13
Wang K, Jin W, Jin P, Fei X, Wang X, Chen X (2017) miR-211-5p suppresses metastatic behavior by targeting SNAI1 in renal cancer. Mol Cancer Res 15:448–456
Liang M, Jia J, Chen L, Wei B, Guan Q, Ding Z, Yu J, Pang R, He G (2019) LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes proliferation and invasion through regulating miR-211-5p/SPARC axis in papillary thyroid cancer. Endocrine 65:318–326
Wang Q, Zheng D, Li Y, Zhang Y, Sui R, Chen Y, Liang H, Shi J, Pan R, Xu X, Sun D (2021) Circular RNA circ_0001588 sponges miR-211-5p to facilitate the progression of glioblastoma via up-regulating YY1 expression. J Gene Med 23:e3371
Pan Y, Wang R, Zhang F, Chen Y, Lv Q, Long G, Yang K (2015) MicroRNA-130a inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and migration in human breast cancer by targeting the RAB5A. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:384–393
Abdolvahabi Z, Nourbakhsh M, Hosseinkhani S, Hesari Z, Alipour M, Jafarzadeh M, Ghorbanhosseini SS, Seiri P, Yousefi Z, Yarahmadi S, Golpour P (2019) MicroRNA-590-3P suppresses cell survival and triggers breast cancer cell apoptosis via targeting sirtuin-1 and deacetylation of p53. J Cell Biochem 120:9356–9368
Lusardi TA, Phillips JI, Wiedrick JT, Harrington CA, Lind B, Lapidus JA, Quinn JF, Saugstad JA (2017) MicroRNAs in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 55:1223–1233
Liu W, Rong Y, Wang J, Zhou Z, Ge X, Ji C, Jiang D, Gong F, Li L, Chen J, Zhao S, Kong F, Gu C, Fan J, Cai W (2020) Exosome-shuttled miR-216a-5p from hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. J Neuroinflammation 17:47
Fukuda AM, Badaut J (2012) Aquaporin 4: a player in cerebral edema and neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 9:279
Nag S, Manias JL, Stewart DJ (2009) Pathology and new players in the pathogenesis of brain edema. Acta Neuropathol 118:197–217
Ding Q, Yu Q, Tao L, Guo Y, Zhao J, Yu J (2022) DL-3-n-butylphthalide enhances synaptic plasticity in mouse model of brain impairments. STEMedicine 3:e113
Feiler S, Plesnila N, Thal SC, Zausinger S, Scholler K (2011) Contribution of matrix metalloproteinase-9 to cerebral edema and functional outcome following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Cerebrovasc Dis 32:289–295
Hishikawa T, Ono S, Ogawa T, Tokunaga K, Sugiu K (2008) Date I: Effects of deferoxamine-activated hypoxia-inducible factor-1 on the brainstem after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Neurosurgery 62:232–240 (discussion 240-231)
Tait MJ, Saadoun S, Bell BA, Verkman AS, Papadopoulos MC (2010) Increased brain edema in aqp4-null mice in an experimental model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroscience 167:60–67
Li S, Li Y, Huang S, Fan B, Wei J, Ouyang L, Chen Z, Jiang B (2020) Silencing matrix metalloproteinase 9 exerts a protective effect on astrocytes after oxygen-glucose deprivation and is correlated with suppression of aquaporin-4. Neurosci Lett 731:135047
Datta A, Sarmah D, Kaur H, Chaudhary A, Mounica KL, Kalia K, Borah A, Yavagal DR, Bhattacharya P (2022) Post-stroke impairment of the blood-brain barrier and perifocal vasogenic edema is alleviated by endovascular mesenchymal stem cell administration: modulation of the PKCdelta/MMP9/AQP4-mediated pathway. Mol Neurobiol 59:2758–2775
Li M, Ma RN, Li LH, Qu YZ, Gao GD (2013) Astragaloside IV reduces cerebral edema post-ischemia/reperfusion correlating the suppression of MMP-9 and AQP4. Eur J Pharmacol 715:189–195
Sun E, Liu X, Lu C, Liu K (2021) Long noncoding RNA TTNAS1 regulates the & nbsp; proliferation, invasion and migration of triplenegative breast cancer by targeting miR2115p. Mol Med Rep 23:1
Tang J, Yang J, Hu H, Cen Y, Chen J (2021) miR-211-5p inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion, and induces apoptosis of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating TGFbetaR2 expression. Ann Transl Med 9:864
Funding
The study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (HH2020206543).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All procedures perfomed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects, and approved by the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University’s Medical Ethics Board (#2022-R258).
Informed consent
The written informed consent was obtained from all the participants of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Yu, X., Li, B. et al. miR-211-5p targeting MMP9 regulates the expressions of AQP4 in traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurol Belg 123, 1321–1329 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02205-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02205-1