Abstract
Purpose
Dysphagia is a common complication after a stroke. Home-based rehabilitation would be an alternative or complementary solution to dysphagia management. This study aimed to validate the effect of an individualized digital coaching program on swallowing function in stroke patients.
Methods
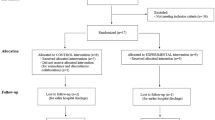
A total of 109 patients were enrolled and randomly assigned to either the intervention group (received a 6-week individualized digital coaching program) or the control group (standard care). The primary outcome was a functional oral intake scale (FOIS). The secondary outcomes were the swallowing quality-of-life questionnaire (SWAL-QOL) and pneumonia.
Results
Among 101 patients, the number of patients who recovered from dysphagia in the intervention group was significantly more than that of the control group at three weeks. Concurrently, the comparison between the control and intervention groups was non-significant at six weeks. The change in the swallowing quality-of-life questionnaire of the intervention group was significantly more significant than that of the control group. No significant difference in the incidence of pneumonia was observed.
Conclusion
The individualized digital coaching program can improve swallowing function and swallowing quality-of-life (SWAL-QOL) in stroke patients, indicating its potential for home-based rehabilitation.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Arnold M, Liesirova K, Broeg-Morvay A, Meisterernst J, Schlager M, Mono ML, El-Koussy M, Kagi G, Jung S, Sarikaya H (2016) Dysphagia in acute stroke: incidence, burden and impact on clinical outcome. PLoS One 11:e0148424
Askim T, Langhammer B, Ihle-Hansen H, Gunnes M, Lydersen S, Indredavik B, LAST Collaboration Group (2018) Efficacy and safety of individualized coaching after stroke: the LAST study (life after stroke): a pragmatic randomized controlled trial. Stroke 49:426–432
Benzo RP, Kramer KM, Hoult JP, Anderson PM, Begue IM, Seifert SJ (2018) Development and feasibility of a home pulmonary rehabilitation program with health coaching. Respir Care 63:131–140
Cameron JI, Naglie G, Silver FL, Gignac MA (2013) Stroke family caregivers’ support needs change across the care continuum: a qualitative study using the timing it right framework. Disabil Rehabil 35:315–324
Constantinescu G, Loewen I, King B, Brodt C, Hodgetts W, Rieger J (2017) Designing a mobile health app for patients with dysphagia following head and neck cancer: a qualitative study. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol 4:e3
Crary MA, Mann GD, Groher ME (2005) Initial psychometric assessment of a functional oral intake scale for dysphagia in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:1516–1520
Frontera WR (2015) Clinical trials in physical medicine and rehabilitation. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 94:829
Horan TC, Andrus M, Dudeck MA (2008) CDC/NHSN surveillance definition of health care-associated infection and criteria for specific types of infections in the acute care setting. Am J Infect Control 36:309–332
Howells SR, Cornwell PL, Ward EC, Kuipers P (2019) Understanding dysphagia care in the community setting. Dysphagia 34:681–691
Ko N, Lee HH, Sohn MK, Kim DY, Shin YI, Oh GJ, Lee YS, Joo MC, Lee SY, Song MK, Han J, Ahn J, Lee YH, Chang WH, Choi SM, Lee SK, Lee J, Kim YH (2021) Status Of dysphagia after ischemic stroke: a korean nationwide study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 102(2343–2352):e2343
Krekeler BN, Broadfoot CK, Johnson S, Connor NP, Rogus-Pulia N (2018) Patient adherence to dysphagia recommendations: a systematic review. Dysphagia 33:173–184
Lambert TE, Harvey LA, Avdalis C, Chen LW, Jeyalingam S, Pratt CA, Tatum HJ, Bowden JL, Lucas BR (2017) An app with remote support achieves better adherence to home exercise programs than paper handouts in people with musculoskeletal conditions: a randomised trial. J Physiother 63:161–167
Legg L, Langhorne P, Outpatient Service Trialists (2004) Rehabilitation therapy services for stroke patients living at home: systematic review of randomised trials. Lancet 363:352–356
Lin B, Zhang Z, Mei Y, Liu L, Ping Z (2021) The influential factors of adherence to physical activity and exercise among community-dwelling stroke survivors: a path analysis. J Clin Nurs. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.16091
Lin S, Xiao LD, Chamberlain D (2020) A nurse-led health coaching intervention for stroke survivors and their family caregivers in hospital to home transition care in Chongqing, China: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 21:240
Lin S, Xiao LD, Chamberlain D, Ullah S, Wang Y, Shen Y, Chen Z, Wu M (2022) Nurse-led health coaching programme to improve hospital-to-home transitional care for stroke survivors: a randomised controlled trial. Patient Educ Couns 105:917–925
Mahmood A, Solomon JM, English C, Bhaskaran U, Menon G, Manikandan N (2020) Measurement of adherence to home-based exercises among community-dwelling stroke survivors in India. Physiother Res Int 25:e1827
Mandigout S, Chaparro D, Borel B, Kammoun B, Salle JY, Compagnat M, Daviet JC (2021) Effect of individualized coaching at home on walking capacity in subacute stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial (Ticaa’dom). Ann Phys Rehabil Med 64:101453
Martino R, Beaton D, Diamant NE (2010) Perceptions of psychological issues related to dysphagia differ in acute and chronic patients. Dysphagia 25:26–34
Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R (2005) Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke 36:2756–2763
Mayo NE (2016) Stroke rehabilitation at home: lessons learned and ways forward. Stroke 47:1685–1691
McHorney CA, Robbins J, Lomax K, Rosenbek JC, Chignell K, Kramer AE, Bricker DE (2002) The SWAL-QOL and SWAL-CARE outcomes tool for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults: III. Documentation of reliability and validity. Dysphagia 17:97–114
Medin J, Larson J, von Arbin M, Wredling R, Tham K (2010) Striving for control in eating situations after stroke. Scand J Caring Sci 24:772–780
Moloney J, Walshe M (2018) “I had no idea what a complicated business eating is...”: a qualitative study of the impact of dysphagia during stroke recovery. Disabil Rehabil 40:1524–1531
Mountain A, Patrice Lindsay M, Teasell R, Salbach NM, de Jong A, Foley N, Bhogal S, Bains N, Bowes R, Cheung D, Corriveau H, Joseph L, Lesko D, Millar A, Parappilly B, Pikula A, Scarfone D, Rochette A, Taylor T, Vallentin T, Dowlatshahi D, Gubitz G, Casaubon LK, Cameron JI (2020) Canadian stroke best practice recommendations: rehabilitation, recovery, and community participation following stroke. Part two: transitions and community participation following stroke. Int J Stroke 15:789–806
Nicholson SL, Donaghy M, Johnston M, Sniehotta FF, van Wijck F, Johnston D, Greig C, McMurdo ME, Mead G (2014) A qualitative theory guided analysis of stroke survivors’ perceived barriers and facilitators to physical activity. Disabil Rehabil 36:1857–1868
Phan TG, Kooblal T, Matley C, Singhal S, Clissold B, Ly J, Thrift AG, Srikanth V, Ma H (2019) Stroke severity versus dysphagia screen as driver for post-stroke pneumonia. Front Neurol 10:16
Sakakibara BM, Lear SA, Barr SI, Benavente O, Goldsmith CH, Silverberg ND, Yao J, Eng JJ (2018) A telehealth intervention to promote healthy lifestyles after stroke: the stroke coach protocol. Int J Stroke 13:217–222
Sakakibara BM, Lear SA, Barr SI, Goldsmith CH, Schneeberg A, Silverberg ND, Yao J, Eng JJ (2022) Telehealth coaching to improve self-management for secondary prevention after stroke: a randomized controlled trial of stroke coach. Int J Stroke 17:455–464
Starmer HM, Abrams R, Webster K, Kizner J, Beadle B, Holsinger FC, Quon H, Richmon J (2018) Feasibility of a mobile application to enhance swallowing therapy for patients undergoing radiation-based treatment for head and neck cancer. Dysphagia 33:227–233
Teasell R, Salbach NM, Foley N, Mountain A, Cameron JI, Jong A, Acerra NE, Bastasi D, Carter SL, Fung J, Halabi ML, Iruthayarajah J, Harris J, Kim E, Noland A, Pooyania S, Rochette A, Stack BD, Symcox E, Timpson D, Varghese S, Verrilli S, Gubitz G, Casaubon LK, Dowlatshahi D, Lindsay MP (2020) Canadian stroke best practice recommendations: rehabilitation, recovery, and community participation following stroke. Part one: rehabilitation and recovery following stroke; 6th edition update 2019. Int J Stroke 15:763–788
Vanroy C, Vanlandewijck Y, Cras P, Truijen S, Vissers D, Swinnen A, Bosmans M, Wouters K, Feys H (2019) Does a cycling program combined with education and followed by coaching promote physical activity in subacute stroke patients? A randomized controlled trial. Disabil Rehabil 41:413–421
Wang Z, Shi Y, Zhang L, Wu L, Fang Q, Huiling L (2022) Nomogram for predicting swallowing recovery in patients after dysphagic stroke. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 46:433–442
Wolpaw JR (2012) Harnessing neuroplasticity for clinical applications. Brain 135:e215
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank my supervisor, HL L, for her guidance through each stage of the study. My research partner, YS S, was instrumental in defining the path of my study. This work was funded by The Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program of Jiangsu Province [grant number JSSCBS20210895].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Zhuo Wang and Xiaoping Dai contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Dai, X. & Wu, C. Effect of an individualized digital coaching program on swallowing function in stroke patients. Acta Neurol Belg 123, 963–969 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-022-02153-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-022-02153-2