Abstract
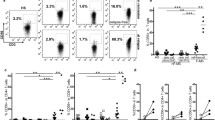
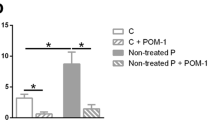
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disorder induced by the infiltration of autoreactive immune cells into the central nervous system. Akt/PKB signaling pathway is crucially involved in T cell development and survival. We aimed to determine whether Akt1 expression levels of regulatory T (Treg) cells are altered in MS and are associated with disease activity. Relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis (RR-MS, n = 17) patients and healthy individuals (n = 20) were enrolled. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated and anti-CD3, -CD4, -CD8, -CD25, -CD127 monoclonal antibodies were used to identify the T cell subsets. After stimulation with phorbol myristate acetate/ionomycin, the Akt1 and phosphorylated-Akt1 (p-Akt1) levels of T cell subsets were detected with intracellular staining using flow cytometry. Total Akt1 and p-Akt1 expression levels were found to be suppressed in CD4+ T cell and Treg populations of RR-MS patients. Progression indices were positively correlated with Akt1 expression levels of Tregs indicating that the Akt pathway might partake in the progression of multiple sclerosis. Flow cytometry may effectively be used for the evaluation of the Akt pathway activity. Our findings suggest that the magnitude of suppression of the Akt pathway might serve as a biomarker for the prognosis of multiple sclerosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials as well as software application support the published claims and comply with field standards.
Abbreviations
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- p-Akt1:
-
Phosphorylated Akt1
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell
- RR-MS:
-
Relapsing–Remitting MS
- Th:
-
T Helper Cells
- Treg:
-
Regulatory T Cells
References
Disanto G, Morahan JM, Barnett MH, Giovannoni G, Ramagopalan SV (2012) The evidence for a role of B cells in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 78(11):823–832
Bennett JL, Stuve O (2009) Update on inflammation, neurodegeneration, and immunoregulation in multiple sclerosis therapeutic implications. Clin Neuropharmacol 32(3):121–132
Abbas AK, Lichtman A, Pillai S (2012) Cellular and molecular immunology, 7th edn. Elsevier Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 137–199
Giacalone G, Clarelli F, Osiceanu AM, Guaschino C, Brambilla P, Sorosina M, Liberatore G et al (2015) Analysis of genes, pathways and networks involved in disease severity and age at onset in primary-progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler J 21(11):1431–1442
Yu CC, Hung SK, Lin HY, Chiou WY, Lee MS, Liao HF, Huang HB, Ho HC, Su YC (2017) Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway as an effectively radiosensitizing strategy for treating human oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 8(40):68641–68653
Viglietta V, Baecher-Allan C, Weiner HL, Hafler DA (2004) Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med 199(7):971–979
Dendrou CA, Fugger L, Friese MA (2015) Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol 15(9):545–558
Frisullo G, Nociti V, Iorio R et al (2009) Regulatory T cells fail to suppress CD4T+-bet+ T cells in relapsing multiple sclerosis patients. Immunology 127(3):418–428
Fletcher JM, Lonergan R, Costelloe L et al (2009) CD39+Foxp3+ regulatory T Cells suppress pathogenic Th17 cells and are impaired in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 183(11):7602–7610
Borsellino G, Kleinewietfeld M, Di Mitri D et al (2007) Expression of ectonucleotidase CD39 by Foxp3+ Treg cells: hydrolysis of extracellular ATP and immune suppression. Blood 110(4):1225–1232
Rossi S, Motta C, Studer V, Monteleone F, De Chiara V, Buttari F, Barbieri F, Bernardi G, Battistini L, Cutter G, Stüve O, Salvetti M, Centonze D (2013) A genetic variant of the anti-apoptotic protein Akt predicts natalizumab-induced lymphocytosis and post-natalizumab multiple sclerosis reactivation. Mult Scler 19(1):59–68
Crellin NK, Garcia RV, Levings, (2007) MK Altered activation of AKT is required for the suppressive function of human CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Blood 109(5):2014–2022
Thompson AJ, Baranzini SE, Geurts J, Hemmer B, Ciccarelli O (2018) Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol 17(2):162–173
Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Wang S, Maiese K (2012) A Critical Kinase Cascade in Neurological Disorders: PI 3-K, Akt, and mTOR. Future Neurol 7(6):733–748
Ouyang S, Zeng Q, Tang N, Guo H, Tang R, Yin W, Wang A, Tang H, Zhou J, Xie H, Langdon WY, Yang H, Zhang J (2019) Akt-1 and Akt-2 Differentially regulate the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by controlling proliferation of thymus-derived regulatory T cells. J Immunol 202(5):1441–1452
Achiron A, Feldman A, Mandel M, Gurevich M (2007) Impaired expression of peripheral blood apoptotic-related gene transcripts in acute multiple sclerosis relapse. Ann NY Acad Sci 1107:155–167
Tegla CA, Cudrici CD, Azimzadeh P, Singh AK, Trippe R 3rd, Khan A, Chen H, Andrian-Albescu M, Royal W 3rd, Bever C, Rus V, Rus H (2013) Dual role of Response gene to complement-32 in multiple sclerosis. Exp Mol Pathol 94(1):17–28
Barragán M, de Frias M, Iglesias-Serret D, Campàs C, Castaño E, Santidrián AF, Coll-Mulet L, Cosialls AM, Domingo A, Pons G, Gil J (2006) Regulation of Akt/PKB by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent and -independent pathways in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells: role of protein kinase C{beta}. J Leukoc Biol 80(6):1473–1479
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the patients for participating and thank Abdullah Yilmaz, technician of Istanbul University-Aziz Sancar Institute of Experimental Medicine-Department of Immunology-Istanbul/ Turkey, for his help in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Fund of Istanbul University. Project No. TYL-2018–28628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards and with subsequent amendments of the Helsinki Declaration or comparable ethical standards. The study was approved by the institutional Ethics Committee of the Istanbul University (2018/459).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants
Consent to participate
All participants signed the consent form.
Consent for publication
All authors give their consent for publication of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oktelik, F.B., Yilmaz, V., Turkoglu, R. et al. Expression of Akt1 and p-Akt1 in peripheral T cell subsets of multiple sclerosis patients. Acta Neurol Belg 121, 1777–1782 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-020-01518-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-020-01518-9