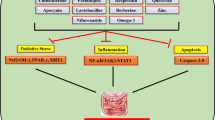
Abstract
The therapeutical benefits of methotrexate (MTX) antifolate agents are non-negligible. However, their ability to cause severe intestinal and nephrotoxicity initiates burden on the patient’s life quality. Andrographis paniculata, “kings of bitter” with anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, detoxicant and anti-viral properties, is a preferred Asian medicinal plant for treating various disease ailments. Our study aims to determine the potential of aqueous leaf extract of A. paniculata (ALEAP) against MTX-induced intestinal and nephrotoxicity. Rats (n = 6) in 5 groups were allocated. Group 1 (normal control), group 2 (MTX − 20 mg/kg; i.p. single administration, 9th day), group 3 (MTX + ALEAP (500 mg/kg; p.o. for 10 days)), group 4 (MTX + Silymarin (100 mg/kg; p.o. for 10 days)) and group 5 (ALEAP alone for 10 days). The rats were assessed for significant alterations in renal markers, intestine and renal antioxidant levels, histopathology, cytokine levels (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10), and apoptosis marker expression range (caspase 3, 8, BCL-2). ALEAP attenuates elevated renal markers; intestine and renal MDA, TNF-α, IL-6, caspase 3 & 8, and histopathological modifications. ALEAP restored intestine and renal antioxidant enzymes, IL-10, and BCL-2. The aqueous leaf extract of A. paniculata produced a significant outcome by maintaining intestine and kidney function and preventing cellular damage.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akash MSH, Rehman K, Liaqat A, Numan M, Mahmood Q, Kamal S (2018) Biochemical investigation of gender-specific association between insulin resistance and inflammatory biomarkers in types 2 diabetic patients. Biomed Pharmacother 106:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2018.06.044
Alasyam N, Narapogu V, John P, Ubedulla S, Pokala N (2017) Evaluation of hepatoprotective activity of aqueous extract of Andrographis paniculata in Wistar rats. Int J Pharmacol Clin Sci 5(4):113–117. https://doi.org/10.5530/IJPCS.5.4.4
Ali SK, Makeen HA, Khuwaja G, Alhazmi HA, Sharma M, Koty A, Mazahirul I, Parveen H, Mohammed A, Mukhtar S, Alam MF (2023) Assessment of the phytochemical profile, antioxidant capacity, and hepatoprotective effect of Andrographis paniculata against CCl4-induced liver dysfunction in Wistar Albino rats. Medicina. 59(7):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/MEDICINA59071260
Alshanwani AR, Mohamed AM, Faddah LM, Shaheen S, Arafah MM, Hagar H, Alhusaini AM, Alharbi FMB, AlHarthii A, Badr AM (2021) Cyanocobalamin and/or calcitriol mitigate renal damage-mediated by tamoxifen in rats: implication of caspase-3/NF-κB signaling pathways. Life Sci 277:119512
Amitai I, Rozovski U, El-Saleh R, Shimony S, Shepshelovich D, Rozen-Zvi B, Raanani P, Gafter-Gvili A, Gurion R (2020) Risk factors for high-dose methotrexate associated acute kidney injury in patients with hematological malignancies. Hematol Oncol 38(4):584–588. https://doi.org/10.1002/HON.2759
Bedoui Y, Guillot X, Sélambarom J, Guiraud P, Giry C, Jaffar-Bandjee MC, Ralandison S, Gasque P (2019) Methotrexate an old drug with new tricks. Int J Mol Sci 20(20):5023. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS20205023
Ben Azaiz M, Ben Jemaa A, Sellami W, Romdhani C, Ouslati R, Gharsallah H, Ghazouani E, Ferjani M (2022) Deciphering the balance of IL-6/IL-10 cytokines in severe to critical COVID-19 patients. Immunobiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IMBIO.2022.152236
Chan ESL, Cronstein BN (2010) Methotrexate—How does it really work? Nature reviews. Rheumatology 6(3):175–178. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.5
Chao WW, Lin BF (2010) Isolation and identification of bioactive compounds in Andrographis paniculata (Chuanxinlian). Chin Med 5(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8546-5-17
Dadhania VP, Tripathi DN, Vikram A, Ramarao P, Jena GB (2010) Intervention of α-lipoic acid ameliorates methotrexate-induced oxidative stress and genotoxicity: a study in rat intestine. Chem Biol Interact 183(1):85–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CBI.2009.10.020
Ebrahimi R, Sepand MR, Seyednejad SA, Omidi A, Akbariani M, Gholami M, Sabzevari O (2019) Ellagic acid reduces methotrexate-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction via up-regulating Nrf2 expression and inhibiting the IĸBα/NFĸB in rats. DARU J Pharm Sci 27(2):721. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40199-019-00309-9
Famurewa AC, Aja PM, Maduagwuna EK, Ekeleme-Egedigwe CA, Ufebe OG, Azubuike-Osu SO (2017) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of virgin coconut oil supplementation abrogate acute chemotherapy oxidative nephrotoxicity induced by anticancer drug methotrexate in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 96:905–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2017.12.008
García-González CM, Baker J (2022) Treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis: methotrexate and beyond. Curr Opin Pharmacol 64:102227. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COPH.2022.102227
Guo H, Yin H, Zuo Z, Yang Z, Yang Y, Wei L, Cui H, Deng H, Chen X, Chen J, Zhu Y, Ouyang P, Geng Y, Du Z, Tang H, Wang F, Fang J (2021) Oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis and autophagy involved in Ni-induced nephrotoxicity in the mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 228:112954. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2021.112954
Hafez SMNA, Elbassuoni E, Abdelzaher WY, Welson NN, Batiha GES, Alzahrani KJ, Abdelbaky FAF (2021) Efficacy of vitamin E in protection against methotrexate induced placental injury in albino rats. Biomed Pharmacother 139:111637. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2021.111637
Hassanein EHM, Kamel EO, Ali FEM, Ahmed MAR (2021) Berberine and/or zinc protect against methotrexate-induced intestinal damage: role of GSK-3β/NRF2 and JAK1/STAT-3 signaling pathways. Life Sci 281:119754. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LFS.2021.119754
Heidari R, Ahmadi A, Mohammadi H, Ommati MM, Azarpira N, Niknahad H (2018) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress are involved in the mechanism of methotrexate-induced renal injury and electrolytes imbalance. Biomed Pharmacother 107:834–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.050
Hossain MS, Urbi Z, Sule A, Rahman KMH (2014) Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Wall. ex Nees: a review of ethnobotany, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/274905
Hosten AO (1990) BUN and creatinine. Clinical methods: the history, physical, and laboratory examinations
Howard SC, McCormick J, Pui C-H, Buddington RK, Harvey RD (2016) Preventing and managing toxicities of high-dose methotrexate. Oncologist 21(12):1471. https://doi.org/10.1634/THEONCOLOGIST.2015-0164
Huang X, Fang Q, Rao T, Zhou L, Zeng X, Tan Z, Chen L, Ouyang D (2020) Leucovorin ameliorated methotrexate induced intestinal toxicity via modulation of the gut microbiota. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 391:114900. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TAAP.2020.114900
Hussain SP, Amstad P, He P, Robles A, Lupold S, Kaneko I, Ichimiya M, Sengupta S, Mechanic L, Okamura S, Hofseth LJ, Moake M, Nagashima M, Forrester KS, Harris CC (2004) p53-Induced Up-regulation of MnSOD and GPx but not catalase increases oxidative stress and apoptosis. Cancer Res 64(7):2350–2356. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-2287-2
Jafaripour L, Naserzadeh R, Alizamani E, Mashhadi SMJ, Moghadam ER, Nouryazdan N, Ahmadvand H (2021) Effects of rosmarinic acid on methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in Wistar rats. Indian J Nephrol 31(3):218. https://doi.org/10.4103/IJN.IJN_14_20
Jayakumar T, Hsieh CY, Lee JJ, Sheu JR (2013) Experimental and clinical pharmacology of Andrographis paniculata and its major bioactive phytoconstituent andrographolide. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/846740
Katturajan R, Evan Prince S (2021) A role of connexin 43 on the drug-induced liver, kidney, and gastrointestinal tract toxicity with associated signaling pathways. Life Sci 280:119629. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.LFS.2021.119629
Katturajan R, Rasool SV, Evan Prince M (2021) Molecular toxicity of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis treatment: a novel perspective and therapeutic implications. Toxicology 461:152909. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TOX.2021.152909
Katturajan R, Sabina EP (2021) Joint inflammation: insights of osteoarthritis, gouty and rheumatoid arthritis and its prevalence, mechanism, medications and remedies. Indian J Pharm Sci 83(5):886–898. https://doi.org/10.36468/PHARMACEUTICAL-SCIENCES.840
Kitamura M, Kitamura S, Fujioka M, Kamijo R, Sato S, Sawayama Y, Uramatsu T, Obata Y, Mochizuki Y, Nishikido M, Sakai H, Miyazaki Y, Mukae H, Nishino T (2018) Methotrexate-induced acute kidney injury in patients with hematological malignancies: three case reports with literature review. Ren Replace Ther 4(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/S41100-018-0180-9/TABLES/3
Mahmoud AM, Hussein OE, Abd El-Twab SM, Hozayen WG (2019) Ferulic acid protects against methotrexate nephrotoxicity via activation of Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling and PPARγ, and suppression of NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Food Funct 10(8):4593–4607. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9FO00114J
Malakouti M, Hoxie D, No DJ, Jacob SE (2022) Methotrexate. J Dermatol Nurses Assoc 10(2):92–94. https://doi.org/10.1097/JDN.0000000000000381
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of the superoxide anion radical in the autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47(3):469–474. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1432-1033.1974.TB03714.X
Mehta S, Sharma AK, Singh RK (2021) Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms of pure and crude extract of Andrographis paniculata: an update. Phytomed Plus 1(4):100085. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYPLU.2021.100085
Miyazono Y, Gao F, Horie T (2009) Oxidative stress contributes to methotrexate-induced small intestinal toxicity in rats. Scand J Gastroenterol 39(11):1119–1127. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365520410003605
Moron MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B (1979) Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Gen Subj 582(1):67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(79)90289-7
Mussard E, Cesaro A, Lespessailles E, Legrain B, Berteina-Raboin S, Toumi H (2019) Andrographolide, a natural antioxidant: an update. Antioxidants 8(12):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/ANTIOX8120571
National Research Council (US) Committee for the update of the guide for the care and use of laboratory animals (2011) guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. https://doi.org/10.17226/12910
Nikiphorou E, Negoescu A, Fitzpatrick JD, Goudie CT, Badcock A, Ösẗor AJK, Malaviya AP (2014) Indispensable or intolerable? Methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis: a retrospective review of discontinuation rates from a large UK cohort. Clin Rheumatol 33(5):609–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10067-014-2546-X/TABLES/4
Nithiyanandam S, Evan Prince S (2020) Toxins mechanism in instigating hepatotoxicity. Toxin Rev 40(4):616–631. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2020.1818105
Nithiyanandam S, Evan Prince S (2023) Caesalpinia bonducella mitigates oxidative damage by paracetamol intoxication in the kidney and intestine via modulating pro/anti-inflammatory and apoptotic signaling: an in vivo mechanistic insight. 3 Biotech 13(6):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13205-023-03601-3/METRICS
Nwaechefu OO, Olaolu TD, Akinwunmi IR, Ojezele OO, Olorunsogo OO (2022) Cajanus cajan ameliorated CCl4-induced oxidative stress in Wistar rats via the combined mechanisms of anti-inflammation and mitochondrial-membrane transition pore inhibition. J Ethnopharmacol 289:114920. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEP.2021.114920
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95(2):351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Okhuarobo A, Ehizogie Falodun J, Erharuyi O, Imieje V, Falodun A, Langer P (2014) Harnessing the medicinal properties of Andrographispaniculata for diseases and beyond: a review of its phytochemistry and pharmacology. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 4(3):213. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2222-1808(14)60509-0
Osman AT, Sharkawi SMZ, Hassan MIA, Abo-youssef AM, Hemeida RAM (2021) Empagliflozin and neohesperidin protect against methotrexate-induced renal toxicity via suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation in male rats. Food Chem Toxicol 155:112406. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FCT.2021.112406
Pan Z, Yin H, Wang S, Xiong G, Yin Z (2020) Bcl-xL expression following articular cartilage injury and its effects on the biological function of chondrocytes. Eng Life Sci 20(12):571. https://doi.org/10.1002/ELSC.202000039
Parthasarathy M, Prince SE (2023) Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees alleviates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in Wistar Albino rats. Life. 13(5):1173. https://doi.org/10.3390/LIFE13051173
Patel A, Burns E, Burkemper NM (2018) Methotrexate use in allergic contact dermatitis: a retrospective study. Contact Dermat 78(3):194–198. https://doi.org/10.1111/COD.12925
Perazella MA, Herlitz LC (2021) The crystalline nephropathies. Kidney Int Rep 6(12):2942. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EKIR.2021.09.003
Perazella MA, Rosner MH (2022) Drug-induced acute kidney injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 17(8):1220–1233. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.11290821
Rahmi EP, Kumolosasi E, Jalil J, Buang F, Jamal JA (2022) Extracts of Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Nees leaves exert anti-gout effects by lowering uric acid levels and reducing monosodium urate crystal-induced inflammation. Front Pharmacol 12:3952. https://doi.org/10.3389/FPHAR.2021.787125/BIBTEX
Rotruck JT, Pope AL, Ganther HE, Swanson AB, Hafeman DG, Hoekstra WG (1973) Selenium: biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase. Science 179(4073):588–590. https://doi.org/10.1126/SCIENCE.179.4073.588
Safaei F, Mehrzadi S, Khadem Haghighian H, Hosseinzadeh A, Nesari A, Dolatshahi M, Esmaeilizadeh M, Goudarzi M (2018) Protective effects of gallic acid against methotrexate-induced toxicity in rats. Acta Chir Belg 118(3):152–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/00015458.2017.1394672
Sayed AM, Abdel-Fattah MM, Arab HH, Mohamed WR, Hassanein EHM (2022) Targeting inflammation and redox aberrations by perindopril attenuates methotrexate-induced intestinal injury in rats: role of TLR4/NF-κB and c-Fos/c-Jun pro-inflammatory pathways and PPAR-γ/SIRT1 cytoprotective signals. Chem Biol Interact 351:109732. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CBI.2021.109732
Shiga S, Machida T, Yanada T, Machida M, Hirafuji M, Iizuka K (2020) The role of nitric oxide in small intestine differs between a single and a consecutive administration of methotrexate to rats. J Pharmacol Sci 143(1):30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPHS.2020.02.006
Sikka S (2012) Relative impact of oxidative stress on male reproductive function. Curr Med Chem 8(7):851–862. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867013373039
Simon JP, Evan Prince S (2021) Ameliorative activity of aqueous leaf extract from Madhuca longifolia against diclofenac-administered toxicity on rat stomach and intestine. J Histotechnol 44(3):114–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/01478885.2020.1861917
Simon JP, Parthasarathy M, Nithyanandham S, Katturaja RK, Namachivayam A, Prince SE (2019) Protective effect of the ethanolic and methanolic leaf extracts of Madhucalongifolia against diclofenac-induced toxicity in female Wistar albino rats. Pharmacol Rep 2019 71(6):6. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHAREP.2019.05.013
Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, Moreland LW, O’Dell J, Winthrop KL, Beukelman T, Bridges SL, Chatham WW, Paulus HE, Suarez-Almazor M, Bombardier C, Dougados M, Khanna D, King CM, Leong AL, Matteson EL, Schousboe JT, Moynihan E, Kolba KS, Jain A, Volkmann ER, Agrawal H, Bae S, Mudano AS, Patkar NM, Saag KG (2012) 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64(5):625–639. https://doi.org/10.1002/ACR.21641
Sinha AK (1972) Colorimetric assay of catalase. Anal Biochem 47(2):389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(72)90132-7
Song Y, Liu L, Liu B, Liu R, Chen Y, Li C, Liu G, Song Z, Lu C, Lu A, Liu Y (2021) Interaction of nobiletin with methotrexate ameliorates 7-OH methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity through endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent PERK/CHOP signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res 165:105371. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHRS.2020.105371
Thompson JA, Love JS, Hendrickson RG (2021) Methotrexate toxicity from unintentional dosing errors: calls to a poison center and death descriptions. J Am Board Family Med 34(6):1246–1248. https://doi.org/10.3122/JABFM.2021.06.210120
Torun AN, Kulaksizoglu S, Kulaksizoglu M, Pamuk BO, Isbilen E, Tutuncu NB (2009) Serum total antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation marker malondialdehyde levels in overt and subclinical hypothyroidism. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 70(3):469–474. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2008.03348.x
Tsukada T, Nakano T, Miyata T, Sasaki S (2013) Life-threatening gastrointestinal mucosal necrosis during methotrexate treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Case Rep Gastroenterol 7(3):470. https://doi.org/10.1159/000356817
Tundis R, Patra JK, Bonesi M, Das S, Nath R, Das Talukdar A, Das G, Loizzo MR (2023) Anti-cancer agent: the labdane diterpenoid-andrographolide. Plants. 12(10):1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/PLANTS12101969
Tvrdý V, Pourová J, Jirkovský E, Křen V, Valentová K, Mladěnka P (2021) Systematic review of pharmacokinetics and potential pharmacokinetic interactions of flavonolignans from silymarin. Med Res Rev 41(4):2195–2246. https://doi.org/10.1002/MED.21791
Ulrich K, Jakob U (2019) The role of thiols in antioxidant systems. Free Radic Biol Med 140:14–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FREERADBIOMED.2019.05.035
Wadhwa K, Pahwa R, Kumar M, Kumar S, Sharma PC, Singh G, Verma R, Mittal V, Singh I, Kaushik D, Jeandet P (2022) Mechanistic insights into the pharmacological significance of silymarin. Molecules 27(16):5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/MOLECULES27165327
Wang Q-H, Pan S, Yang K, Wu Y-J, Cheng X-P, Olatunji OJ, Mao Q, Zuo J (2022) Glycolysis aggravates methotrexate toxicity by fueling RFC1-controlled intestinal absorption in rheumatic rats. Biomed Pharmacother 150:113067. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2022.113067
Wei X, Wu Y, Tang H, Wang B, Wang Y, Sun W, Asenso J, Xiao F, Wang C (2021) CP-25 ameliorates methotrexate induced nephrotoxicity via improving renal apoptosis and methotrexate excretion. J Pharmacol Sci 146(1):21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JPHS.2021.02.007
Xu D, Xie M, Yang L (2022) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of IL-10 and IL-20L genes in swamp eel (Monopterus albus) against Aeromonas veronii Infection. Aquac Rep 24:101164. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQREP.2022.101164
Yan Y, Fang LH, Du GH (2018) Andrographolide. Natl Small Mol Drugs Plants. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8022-7_60
Yang L, Ge J, Ma D, Tang J, Wang H, Li Z (2022) MoS2 quantum dots as fluorescent probe for methotrexate detection. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 279:121443. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SAA.2022.121443
Younis NS, Elsewedy HS, Shehata TM, Mohamed ME (2021) Geraniol averts methotrexate-induced acute kidney injury via Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 and MAPK/NF-κB pathways. Curr Issues Mol Biol 43(3):1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/CIMB43030123
Zhang Z, Shi G, Zhang Z, Zhang R, Zhang X, Lu Y, Yang J, Zhang D, Li X, Ning G (2012) Protective effect of andrographolide against concanavalin A-induced liver injury. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 385(1):69–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00210-011-0685-Z
Zhang H, Wang J, Lang W, Liu H, Zhang Z, Wu T, Li H, Bai L, Shi Q (2022) Albiflorin ameliorates inflammation and oxidative stress by regulating the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway in methotrexate-induced enteritis. Int Immunopharmacol 109:108824. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.INTIMP.2022.108824
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to VIT for the support and facilitation required to complete this research project.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology: MP, SEP; data interpretation, writing-original draft: MP; writing-review and editing: SEP. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The animal study protocol was approved by Institutional Ethical Committee of Vellore Institute of Technology (Reg No: VIT/IAEC/18/DEC2020/16).
Conflict of interest
Manisha Parthasarathy has no conflict of interest. Sabina Evan Prince has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Parthasarathy, M., Prince, S.E. Methotrexate-induced intestine and nephrotoxicity attenuated by Andrographis paniculata via ameliorating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. ADV TRADIT MED (ADTM) 24, 553–567 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-023-00720-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-023-00720-3