Abstract
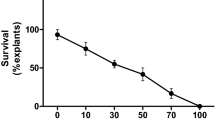
The genetic transformation is a genotype specific phenomena in potato, which complicates the trait specific genetic manipulations and mandates optimisation of protocol for each cultivar. In the present study, heat shock treatment was used to develop genotype independent Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation protocol of potato. Initially six cultivars of potato namely, ‘Kufri Chipsona 1’ (CS-1), ‘Kufri Chipsona 2’ (CS-2), ‘Kufri Pukhraj’ (KP), ‘Kufri Khyati’ (KK), ‘Kufri Jyoti’ (KJ) and ‘Kufri Chandramukhi’ (KCM), were tested for genetic transformation efficiencies using previously optimised Agrobacterium mediated T-DNA delivery protocol and the outcome was highly genotype dependent. Based on the response, cultivars were grouped as ‘high’ (CS-1, CS-2, KK) and ‘low’ (KP, KCM, KJ) genetic transformation efficiency cultivars. Further, the attempts were made to understand the biochemical basis of variation in genetic transformation efficiencies of these cultivars. It was noteworthy that in ‘low genetic transformation efficiency’ cultivars, the level of antioxidant enzymes and phenols was significantly higher than ‘high genetic transformation efficiency’ cultivars. In order to optimise a genotype independent protocol, explants from all the cultivars (both groups) were subjected to heat shock treatment (30–50 °C; 15–45 min) immediately before infection. The heat shock treatment at 40 °C for 15 min resulted in a significant increase in transient GUS expression, callogenesis and regeneration of transgenic shoots. Using this approach, transgenic shoots were recovered from all the cultivars. Following the heat shock treatment, levels of antioxidant enzymes and phenols were significantly affected, thus it seems that cultivars with stronger defense system are likely to be more difficult for A. tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Avaialability of data and material
Authors confirm that data and material used in this study support our publication claims.
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
6-Benzyladenine
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- GA3:
-
Gibberellic acid
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- HS:
-
Heat shock
- CS1:
-
Kufri Chipsona 1
- CS2:
-
Kufri Chipsona 2
- KP:
-
Kufri Pukhraj
- KK:
-
Kufri Khyati
- KJ:
-
Kufri Jyoti
- KCM:
-
Kufri Chandramukhi
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Aggarwal D, Kumar A, Reddy MS (2011) Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated genetic transformation of selected elite clone(s) of Eucalyptus tereticornis. Acta Physiol Plant 33:1603–1611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0695-3
Armstrong MR, Vossen J, Tze-Yin Lim J, Hutten RCB, Xu J, Strachan SM, Harrower B, Champouret N, Gilroy EM, Hein I (2018) Tracking disease resistance deployment in potato breeding by enrichment sequencing. Plant Biotechnol J 17:540–549. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12997
Boyko A, Matsuoka A, Kovalchuk I (2009) High frequency Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated plant transformation induced by ammonium nitrate. Plant Cell Rep 28:737–757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0676-4
Bradley DJ, Kjellbom P, Lamb CJ (1992) Elicitor-and wound-induced oxidative cross-linking of a proline-rich plant cell wall protein: a novel, rapid defense response. Cell 70:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(92)90530-P
Chakraborty S, Chakraborty N, Datta A (2000) Increased nutritive value of transgenic potato by expressing a non-allergenic seed albumin gene from Amaranthus hypochondriacus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3724–3729. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.7.3724
Chakravarty B, Pruski GW, Flinn B, Gustafson V, Regan S (2007) Genetic transformation in potato: approaches and strategies. Am Potato J 84:301–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02986242
Chateau S, Sangwan RS, Sangwan-Norreel BS (2000) Competance of Arabidopsis thaliana genotypes and mutants for Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated gene transfer: role of phytohormones. J Exp Bot 51:1961–1968. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/51.353.1961
Chen P-Y, Wang C-K, Soong S-C, To K-Y (2003) Complete sequence of the binary vector pBI121 and its applications in cloning T-DNA insertion from transgenic plants. Mol Breed 11:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023475710642
Chinchilla D, Bauer Z, Regenass M, Boller T, Felix G (2006) The Arabidopsis receptor kinase FLS2 binds flg22 and determines the specificity of flagellin perception. Plant Cell 18:465–476. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.036574
Conner AJ, Williams MK, Abernethy DJ, Fletcher PJ, Genet RA (1994) Field performance of transgenic potatoes. New Zeal J Crop Hort 22:361–371. https://doi.org/10.1080/01140671.1994.9513847
Dale PJ, Hampson KK (1995) An assessment of morphogenic and transformation efficiency in a range of varieties of potato (Solanum tuberosum). Euphytica 85:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023936
De Block M (1988) Genotype-independent leaf disk transformation of potato (Solanum tuberosum) using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Theor Appl Genet 76:767–774. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00303524
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Enriquez-Obregon GA, Prieto-Samsonov DL, Riva GA, Perez M, Selman-Housein G, Vazquez-Padron RI (1999) Agrobacterium-mediated Japonica rice transformation: A procedure assisted by an antinecrotic treatment. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 59:1659–1681. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006307527449
Ezura H, Yuhashi K-I, Yasuta T, Minamisawa K (2000) Effect of ethylene on Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated gene transfer to melon. Plant Breed 119:75–79. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0523.2000.00438.x
Farhanah A, Suharsono S, Wattimena GA, Widyastuti U (2017) Genetic engineering of potato plant (Solanum tuberosum L.) cv. JalaIpam with MmPMA gene encoding plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Pak J Biotechnol 14:37–42
Fatahillah SS, Astuti UW (2016) Genetic transformation of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cv. Nooksack with FBPase/ClRan1 genes mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Pak J Biotechnol 13:187–192
Felcher KJ, Douches DS, Kirk WW, Hammerschmidt R, Li W (2003) Expression of a fungal glucose oxidase gene in three potato cultivars with different susceptibility to late blight (Phytophthora infestans Mont. deBary). J Am Soc Hortic Sci 128:238–245. https://doi.org/10.21273/JASHS.128.2.0238
Felix G, Duran JD, Volko S, Boller T (1999) Plants have a sensitive perception system for the most conserved domain of bacterial flagellin. Plant J 18:265–276. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00265.x
Godwin I, Todd G, Ford-Lloyd B, Newbury HJ (1991) The effect of acetosyringone and pH on Agrobacterium-mediated transformation vary according to plant species. Plant Cell Rep 9:671–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235354
Gurel S, Gurel E, Kaur R, Wong J, Meng L, Tan HQ, Lemaux PG (2009) Efficient reproducible Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of sorghum using heat treatment of immature embryos. Plant Cell Rep 28:429–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0655-1
Han EH, Goo YM, Lee MK, Lee SW (2015) An efficient transformation method for a potato (Solanum tuberosum L. var. Atlantic) J Plant Biotechnol 42:77–82. http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5010/JPB.2015.42.2.77
Hiei Y, Ishida Y, Kasaoka K, Komari T (2006) Improved frequency of transformation in rice and maize by treatment of immature embryos with centrifugation and heat prior to infection with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 87:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-006-9157-4
Jia Y, Yao X, Zhao M, Zhao Q, Du Y, Yu C, Xie F (2015) Comparison of soyabean transformation efficiency and plant factors affecting transformation during Agrobacterium infection process. Int J Mol Sci 16:18522–18543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818522
Jongedijk E, De schutter AAJM, Stolte T, Van den Elzen PJM, Cornelissen BJC, (1992) Increased resistance to potato virus-x and preservation of cultivar properties in transgenic potato under field conditions. Bio/technology 10:422–429. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0492-422
Kaur A, Reddy MS and Kumar A (2017) Efficient, one step and cultivar independent shoot organogenesis of potato. Physiol Mol Biol-Plant 23:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-017-0418-y
Kaur A, Guleria S, Reddy MS, Kumar A (2020) A robust genetic transformation protocol to obtain non-chimeric transgenic shoots of Solanum tuberosum L. cultivar ‘Kufri Chipsona 1’. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-0074-7-4
Kaur A (2019) Biotechnological approaches for development of blight resistance in selected Indian potato cultivar(s). A Ph.D. thesis, Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology, Patiala, India
Khanna R, Huq E, Kikis EA, Al-Sady B, Lanzatella C, Quail PH (2004) A novel molecular recognition motif necessary for targeting photoactivated phytochrome signaling to specific basic helix–loop–helix transcription factors. Plant Cell 16:3033–3044. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.104.025643
Khatun A, Hasan MM, Bachchu MAA, Moniruzzaman M, Nasiruddin KM (2012) Agrobacterium-mediated Genetic transformation of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) var. Cardinal and Heera the Agriculturists 10:81–86. https://doi.org/10.3329/agric.v10i1.11068
Kumar A, Palni LMS, Sood A, Sharma A, Palni UT, Gupta AK (2002) Heat shock induced somatic embryogenesis in callus culture of Gladiolus in the presence of high sucrose. J Hortic Sci Biotech 77:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2002.11511460
Lee CW, Efetova M, Engelmann JC, Kramell R, Wasternack C, Ludwig-Müller J, Hedrich R, Deeken R (2009) Agrobacterium tumefaciens promotes tumor induction by modulating pathogen defense in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 21:2948–2962. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.064576
Levine A, Tenhaken R, Dixon R, Lamb C (1994) H2O2 from the oxidative burst orchestrates the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Cell 79:583–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(94)90544-4
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McEwen CM Jr (1971) Monoamine oxidase [rabbit serum]. Methods Enzymol 17B:686–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(71)17119-4
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Olhoft PM, Somers DA (2001) L-cysteine increases Agrobacterium-mediated T-DNA delivery into soyabean cotyledonary-node cells. Plant Cell Rep 20:706–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990100379
Patel MA, Dewey RE, Qu R (2013) Enhancing Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation efficiency of perennial ryegrass and rice using heat and maltose treatment during bacterial infection. Plant Cel Tiss Organ Cult 114:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-013-0301-7
Saporta R, Pedro TS, Gisbert C (2016) Attempts at grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) breeding through genetic transformation: The main limiting factors. Vitis 55:173–186. https://doi.org/10.5073/vitis.2016.55.173-186
Sawahel WA (2002) The production of transgenic potato plants expressing human alpha interferon using lipofectin-mediated transformation. Cell Mol Biol Lett 7:19–29
Schaffer WM, Bronnikova TV (2012) Peroxidase-ROS interactions. Nonlinear Dyn 68:413–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0314-x
Snyder GW, Belknap WR (1993) A modified method for routine Agrobacterium mediated transformation of in vitro grown potato microtubers. Plant Cell Rep 12:324–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237428
Stiekema WJ, Heidekamp F, Louwerse JD, Verhoeven HA, Dijkhuis P (1988) Introduction of foreign genes into potato cultivars Bintje and Desiree using an Agrobacterium tumefaciens binary vector. Plant Cell Rep 7:47–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272976
Swain T, Hillis WE (1959) The phenolic constituents of Prunus domestica. I.-The quantitative analysis of phenolic constituents. J Sci Food Agric 10:63–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2740100110
Trujillo C, Rodriguez-Arango E, Jaramillo S, Hoyos R, Orduz S, Arango R (2001) One-step transformation of two Andean potato cultivars (Solanum tuberosum L. subsp. andigena). Plant Cell Rep 20:637–641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990100381
Tsai YL, Wang MH, Gao C, Klusener S, Baron C, Narberhaus F, Lai E-M (2009) Small heat‐shock protein HspL is induced by VirB protein(s) and promotes VirB/D4‐mediated DNA transfer in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Microbiology 155:3270–3280. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.030676-0
Visser RGF, Jacobsen E, Hesseling-Meinders A, Schans MJ, Witholt B, Feenstra WJ (1989) Transformation of homozygous diploid potato with an Agrobacterium tumefaciens binary vector system by adventitious shoot regeneration on leaf and stem segments. Plant Mol Biol 12:329–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043210
Weisburg WA, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S rDNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991
Yahong L, Tsuji Y, Nishikubo N, Kajita S, Morohoshi N (2001) Analysis of Transgenic Poplar in which the expression of Peroxidase gene is suppressed. Progr Biotechnol 18:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-0423(01)80073-3
Yu L, Chen X, Wang Z, Wang S, Wang Y, Zhu Q, Li S, Xiang C (2013) Arabidopsis enhanced drought tolerance1/HOMEODOMAIN GLABROUS11 confers drought tolerance in transgenic rice without yield penalty. Plant Physiol 162:1378–1391. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.217596
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to TIFAC-CORE, Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology for providing facilities for conducting experiments. Authors also thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Extramural Research Division, New Delhi for funding this study through the Project 38(1465)/18/EMR-II.
Funding
This study has received funding from Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Extramural Research Division, New Delhi through the project 38(1465)/18/EMR-II.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AK conducted the experiments, compiled data, analyzed the results and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. AK and AK conceived and designed the experiments. MSR helped in statistical analysis and molecular studies. AK finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
Authors give their consent to publish the results and data reported in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, A., Reddy, M.S. & Kumar, A. Heat shock enhanced Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated T-DNA delivery to potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 31, 853–863 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-021-00762-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-021-00762-1